MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) enhances network speed and efficiency by directing data from one node to the next based on short path labels rather than long network addresses. This technology supports various protocols and enables scalable, high-performance routing ideal for large enterprise networks. Explore the full article to understand how MPLS can optimize Your network infrastructure and improve data traffic management.
Table of Comparison
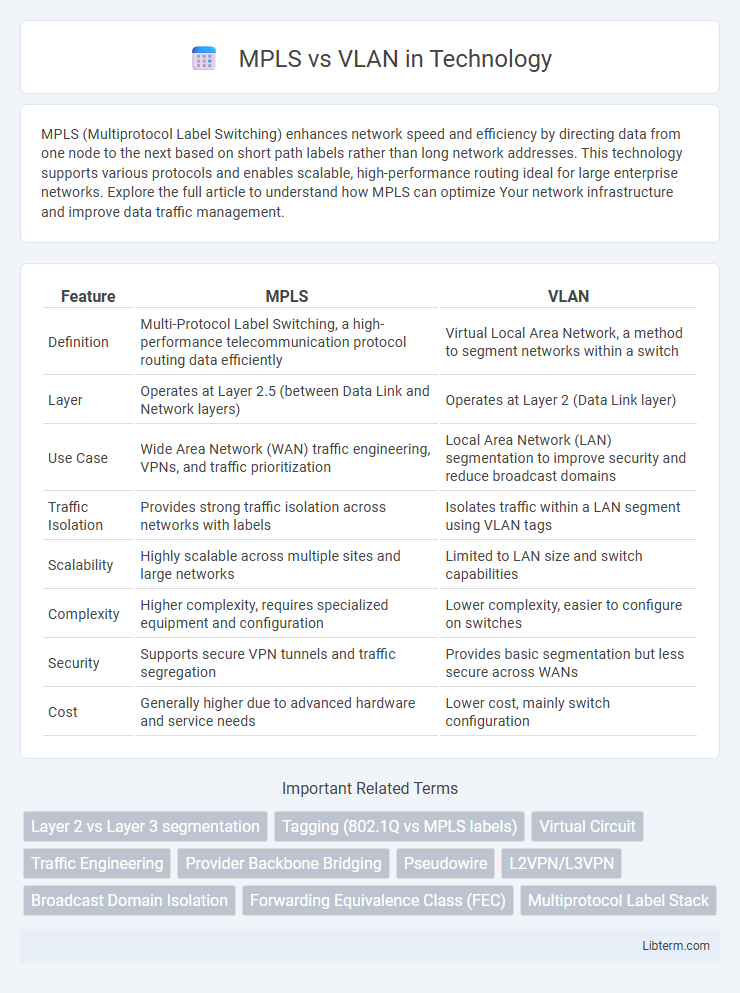
| Feature | MPLS | VLAN |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multi-Protocol Label Switching, a high-performance telecommunication protocol routing data efficiently | Virtual Local Area Network, a method to segment networks within a switch |
| Layer | Operates at Layer 2.5 (between Data Link and Network layers) | Operates at Layer 2 (Data Link layer) |
| Use Case | Wide Area Network (WAN) traffic engineering, VPNs, and traffic prioritization | Local Area Network (LAN) segmentation to improve security and reduce broadcast domains |
| Traffic Isolation | Provides strong traffic isolation across networks with labels | Isolates traffic within a LAN segment using VLAN tags |
| Scalability | Highly scalable across multiple sites and large networks | Limited to LAN size and switch capabilities |
| Complexity | Higher complexity, requires specialized equipment and configuration | Lower complexity, easier to configure on switches |
| Security | Supports secure VPN tunnels and traffic segregation | Provides basic segmentation but less secure across WANs |
| Cost | Generally higher due to advanced hardware and service needs | Lower cost, mainly switch configuration |
Introduction to MPLS and VLAN
MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) is a high-performance telecommunications technology that directs data from one node to the next based on short path labels rather than long network addresses, optimizing traffic flow and reducing latency. VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) segments a physical network into multiple logical networks, improving security and reducing broadcast domains within a local area. MPLS operates at Layer 2.5, enhancing packet forwarding efficiency across wide-area networks, while VLANs function at Layer 2 to isolate network traffic within a LAN environment.
Understanding MPLS: Key Concepts
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) streamlines data packet forwarding by assigning fixed-length labels to packets, enabling faster and more efficient routing across complex networks compared to VLANs, which operate primarily at Layer 2 for segmenting Ethernet broadcast domains. MPLS supports traffic engineering and Quality of Service (QoS) by directing packets through predefined Label Switched Paths (LSPs), enhancing network performance and scalability beyond VLAN's capabilities. Key MPLS concepts include label stacking, label distribution protocols (LDP), and support for multiple Layer 3 protocols, which together facilitate flexible, high-speed, and reliable data transport in service provider and enterprise environments.
What is VLAN? Core Principles
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is a network segmentation technology that logically divides a physical network into multiple distinct broadcast domains to improve security and reduce congestion. Core principles of VLAN include traffic isolation, enhanced security by separating sensitive data, and simplified network management by grouping users based on function or department regardless of physical location. VLANs operate at the data link layer (Layer 2) and use tagging protocols like IEEE 802.1Q to identify and segregate traffic within the same physical infrastructure.
MPLS vs VLAN: Differences in Functionality
MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) operates at Layer 2.5, directing data based on short path labels rather than long network addresses, enabling efficient traffic engineering and QoS across large-scale networks. VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) functions at Layer 2, segmenting a single physical network into multiple logical networks to improve network management and security but lacks MPLS's advanced routing and traffic optimization capabilities.
Performance Comparison: MPLS vs VLAN
MPLS offers superior performance over VLAN by enabling faster data forwarding through label-switching rather than traditional packet inspection, reducing latency and jitter in high-traffic networks. VLANs segment networks at Layer 2, which can lead to bottlenecks and increased broadcast traffic affecting performance, while MPLS operates at Layer 3, supporting scalable, efficient routing and QoS for time-sensitive applications. Enterprises using MPLS benefit from improved bandwidth utilization and more reliable service across multiple sites compared to VLAN-based segmentation.
Security Aspects: MPLS vs VLAN
MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) enhances security by creating private, isolated paths within a shared network infrastructure, reducing exposure to external threats compared to VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks), which segment traffic within the same Layer 2 broadcast domain but can be vulnerable to VLAN hopping attacks. MPLS supports robust traffic engineering and encryption capabilities, making it suitable for secure VPN implementations across wide-area networks. In contrast, VLANs primarily provide logical separation without inherent encryption, requiring supplementary security measures like private VLANs or MAC filtering to mitigate risks.
Scalability and Flexibility Considerations
MPLS offers superior scalability by enabling efficient traffic engineering and supporting large-scale multiservice networks through label switching, which reduces routing complexity compared to VLAN's broadcast domain limitations. VLANs provide flexible segmentation within local area networks but face scalability challenges in extensive or multi-site deployments due to the limited VLAN ID space and complexity in managing numerous VLANs. Enterprises requiring dynamic and scalable WAN connectivity benefit from MPLS's ability to handle diverse protocols and prioritize traffic, whereas VLANs are better suited for isolated network segments within smaller or less complex environments.
Use Cases for MPLS and VLAN
MPLS is ideal for large-scale enterprise networks requiring efficient traffic management and high-performance routing across multiple sites, especially in service provider environments supporting VPNs and QoS-sensitive applications. VLANs are commonly used within local area networks to segment network traffic for improved security and reduced broadcast domains, making them suitable for internal network organization and cost-effective traffic isolation. While MPLS excels in wide-area network scenarios requiring scalability and traffic engineering, VLANs are preferred for layer 2 domain separation within individual network segments.
Cost Implications: MPLS vs VLAN
MPLS networks generally incur higher costs due to service provider fees, dedicated infrastructure, and advanced traffic management capabilities, making them suitable for large-scale enterprises requiring robust performance and security. VLANs offer a more cost-effective solution by utilizing existing Ethernet infrastructure to segment networks virtually, reducing hardware and operational expenses for small to medium-sized businesses. Choosing between MPLS and VLAN depends on budget constraints and network complexity, with VLAN providing lower upfront and maintenance costs compared to the premium price of MPLS deployments.
Choosing the Right Solution: MPLS or VLAN
Choosing between MPLS and VLAN depends on network scalability and performance needs. MPLS offers superior traffic management and secure, reliable connectivity ideal for large-scale enterprise WANs, while VLANs provide cost-effective segmentation within a local area network. For organizations requiring optimized path control and cross-site integration, MPLS is preferred, whereas VLAN suits smaller environments focused on internal traffic isolation.
MPLS Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com