Synthetic monitoring proactively simulates user interactions to detect website or application performance issues before they impact real users. This technique continuously checks availability, response times, and functionality from various locations worldwide. Discover how synthetic monitoring can enhance Your digital experience and ensure seamless online operations by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
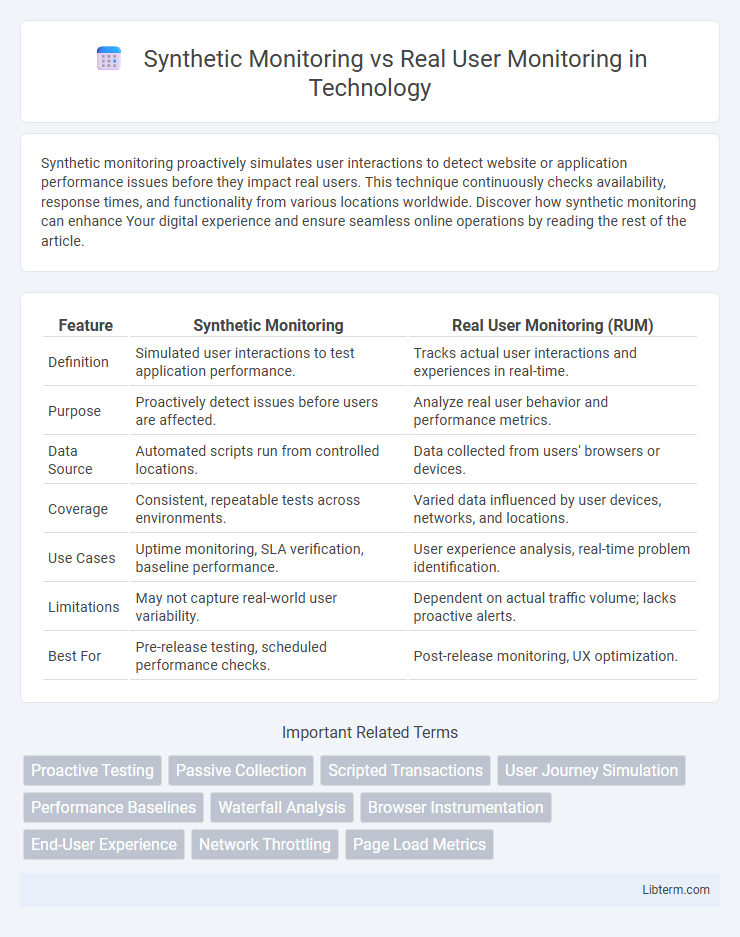
| Feature | Synthetic Monitoring | Real User Monitoring (RUM) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Simulated user interactions to test application performance. | Tracks actual user interactions and experiences in real-time. |
| Purpose | Proactively detect issues before users are affected. | Analyze real user behavior and performance metrics. |
| Data Source | Automated scripts run from controlled locations. | Data collected from users' browsers or devices. |
| Coverage | Consistent, repeatable tests across environments. | Varied data influenced by user devices, networks, and locations. |
| Use Cases | Uptime monitoring, SLA verification, baseline performance. | User experience analysis, real-time problem identification. |
| Limitations | May not capture real-world user variability. | Dependent on actual traffic volume; lacks proactive alerts. |
| Best For | Pre-release testing, scheduled performance checks. | Post-release monitoring, UX optimization. |
Introduction to Synthetic Monitoring and Real User Monitoring
Synthetic Monitoring involves using automated scripts to simulate user interactions with a website or application, providing consistent and controlled performance data from multiple locations. Real User Monitoring captures and analyzes actual user behavior and experiences in real-time, offering insights into how end users interact with digital services. Both techniques are essential for comprehensive performance optimization, with Synthetic Monitoring focusing on proactive testing and Real User Monitoring delivering genuine user experience feedback.
Key Differences Between Synthetic and Real User Monitoring
Synthetic monitoring uses automated scripts to simulate user interactions and proactively detect performance issues, providing consistent data under controlled conditions. Real User Monitoring (RUM) collects data from actual user sessions, capturing diverse real-world experiences and variability across different devices, browsers, and network conditions. Key differences include synthetic monitoring's ability to predict problems before users encounter them versus RUM's insight into actual user behavior and performance impact in production environments.
How Synthetic Monitoring Works
Synthetic monitoring operates by simulating user interactions through scripted tests executed at regular intervals from multiple global locations, collecting data on application performance and availability without relying on actual user traffic. These automated tests measure critical metrics like response time, uptime, and error rates, enabling early detection of potential issues before real users are affected. The controlled environment of synthetic monitoring provides consistent and repeatable performance insights, supporting proactive maintenance and service level agreement (SLA) verification.
How Real User Monitoring Works
Real User Monitoring (RUM) captures and analyzes actual user interactions with a website or application by collecting performance data directly from users' browsers or devices in real time. This method leverages JavaScript tags or SDKs embedded in the web pages or apps to track metrics such as page load times, click paths, and error rates, providing insights into the end-user experience. By aggregating this data, RUM enables businesses to identify performance issues, understand user behavior, and optimize digital performance based on actual usage patterns.
Advantages of Synthetic Monitoring
Synthetic monitoring provides consistent, controlled testing environments that help identify performance issues before real users are impacted, enabling proactive maintenance. It allows for comprehensive coverage across multiple geographies, devices, and browsers without the need for actual user traffic, ensuring baseline performance benchmarks are met. Automated scripts run continuously, delivering precise metrics on uptime, response times, and transaction paths, which supports rapid diagnosis and resolution of potential problems.
Benefits of Real User Monitoring
Real User Monitoring (RUM) provides precise, real-time insights into actual user experiences by capturing data directly from visitors' interactions, enabling businesses to identify and resolve performance issues that synthetic tests might miss. RUM helps optimize website performance across diverse devices, browsers, and network conditions, enhancing user satisfaction and retention rates. Unlike Synthetic Monitoring, which simulates user scenarios, RUM delivers actionable analytics based on genuine user behavior, improving decision-making and ensuring accurate performance measurement under real-world conditions.
Use Cases for Synthetic Monitoring
Synthetic monitoring is ideal for proactive performance testing, enabling consistent uptime checks and immediate detection of outages before users are impacted. It excels in validating new deployments, ensuring APIs and critical workflows function according to specifications in controlled environments. Enterprises leverage synthetic monitoring to benchmark SLAs, simulate user journeys globally, and maintain service reliability regardless of actual traffic fluctuations.
Use Cases for Real User Monitoring
Real User Monitoring (RUM) provides critical insights into genuine user interactions, making it indispensable for identifying performance bottlenecks across diverse devices and network conditions. It captures real-time data on page load times, error rates, and user behavior patterns, enabling businesses to enhance user experience and drive conversion rates. Enterprises use RUM analytics to optimize application responsiveness, prioritize development efforts, and ensure a seamless end-user experience in production environments.
Hybrid Monitoring: Combining Synthetic and Real User Approaches
Hybrid monitoring integrates synthetic monitoring's proactive performance testing with real user monitoring's actual user experience data, providing comprehensive insights into application health. Synthetic monitoring simulates user interactions to detect issues before they impact users, while real user monitoring captures real-time data on user behavior and performance metrics. Combining both approaches enables organizations to optimize uptime, swiftly identify problems, and enhance overall user satisfaction through a balanced, data-driven strategy.
Choosing the Right Monitoring Solution for Your Business
Synthetic Monitoring simulates user interactions to proactively identify performance issues before they impact customers, offering controlled and consistent testing environments ideal for critical transaction paths. Real User Monitoring captures actual user behavior and experience in real-time, providing comprehensive insights into how diverse users interact with applications across different devices and networks. Selecting the right monitoring solution depends on business goals: synthetic monitoring ensures uptime and performance benchmarks, while real user monitoring delivers authentic user-centric data crucial for optimizing user experience and engagement.
Synthetic Monitoring Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com