Quotas regulate the quantity or value of goods, services, or people allowed within a specific timeframe, impacting markets and trade policies worldwide. These limits are essential tools for managing supply, protecting domestic industries, and balancing international relations. Explore the full article to understand how quotas influence global economics and your business decisions.
Table of Comparison
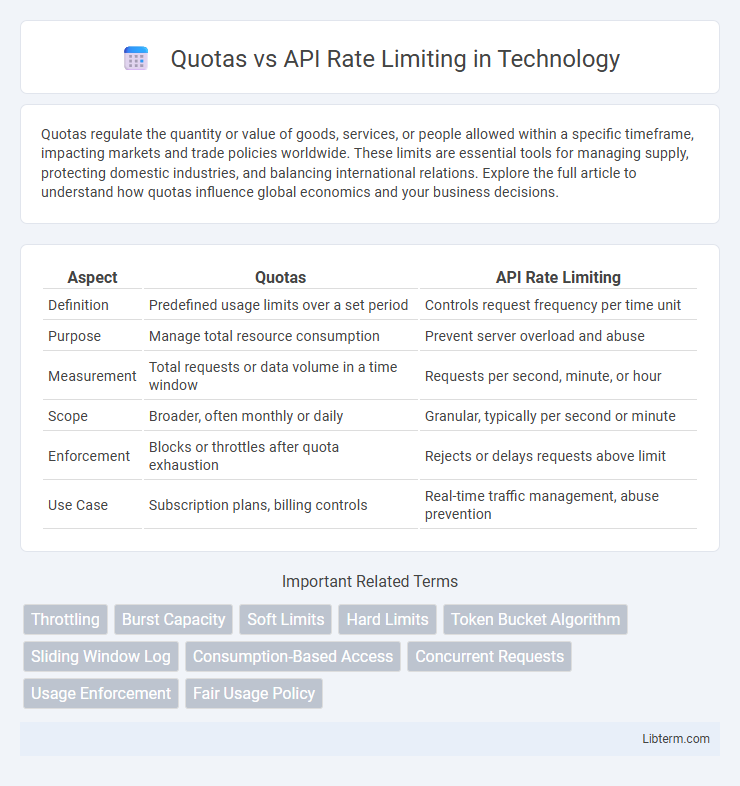
| Aspect | Quotas | API Rate Limiting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Predefined usage limits over a set period | Controls request frequency per time unit |
| Purpose | Manage total resource consumption | Prevent server overload and abuse |
| Measurement | Total requests or data volume in a time window | Requests per second, minute, or hour |
| Scope | Broader, often monthly or daily | Granular, typically per second or minute |
| Enforcement | Blocks or throttles after quota exhaustion | Rejects or delays requests above limit |
| Use Case | Subscription plans, billing controls | Real-time traffic management, abuse prevention |
Introduction to Quotas and API Rate Limiting
Quotas define the maximum number of API requests a user or application can make within a specified time period, ensuring fair resource allocation and preventing abuse. API rate limiting controls the frequency of requests over time, reducing server overload and maintaining service stability by enforcing request thresholds. Both mechanisms are essential for managing API usage, protecting system performance, and enhancing security.
Defining Quotas in API Management
Quotas in API management define the maximum number of API calls a client can make within a specified time frame, ensuring fair resource distribution and preventing abuse. These limits often include daily, hourly, or per-minute thresholds tailored to different user tiers or plans. By setting quotas, organizations can control usage patterns, maintain service availability, and align API consumption with business objectives.
Understanding API Rate Limiting
API rate limiting controls the number of requests a client can make to a server within a specified time frame, preventing abuse and ensuring fair resource distribution. Unlike quotas, which impose a total usage cap over a longer period, rate limiting enforces real-time restriction by limiting requests per second or minute. Effective API rate limiting improves system stability, reduces latency, and protects backend services from traffic spikes and denial-of-service attacks.
Key Differences Between Quotas and Rate Limiting
Quotas define the maximum number of API requests allowed over a specific time period, ensuring users do not exceed allocated resource limits, while rate limiting controls the frequency of requests to prevent system overload by restricting the number of calls per second or minute. Quotas typically enforce long-term usage policies based on subscription plans or user tiers, whereas rate limiting offers real-time throttling to maintain service stability and performance. Understanding these distinctions helps optimize API management by balancing user access and protecting backend infrastructure from excessive or abusive traffic.
Use Cases: When to Use Quotas vs. Rate Limiting
Quotas are best suited for long-term resource management, such as controlling the total number of API calls allowed per user or application over a billing period to prevent overconsumption and manage costs. API rate limiting is ideal for handling short-term traffic spikes, ensuring fair usage, and protecting backend systems from sudden overload by restricting the number of requests in a specific time window. Use quotas when enforcing monthly or daily usage caps and apply rate limiting to manage concurrency and burst traffic in real-time scenarios.
Implementation Strategies for Quotas
Implementing quotas in API management involves setting fixed allocation limits on resources or requests over a defined period to control consumption and ensure fair usage among users. Common strategies include user-specific quotas, where limits are tailored per client based on subscription tiers, and resource-specific quotas that cap access to particular endpoints or data types. Effective quota enforcement often leverages middleware or API gateways with real-time monitoring, throttling, and automated alerts to prevent abuse and maintain system stability.
Techniques for Enforcing API Rate Limits
API rate limiting techniques involve token bucket, leaky bucket, fixed window, and sliding window algorithms to control request flow and ensure fair resource usage. Token bucket allows bursts by replenishing tokens at a fixed rate, while leaky bucket smooths out traffic by processing requests at a steady rate. Fixed window counts requests in discrete intervals, whereas sliding window tracks requests over a rolling time frame for precise rate control.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Quotas
Quotas control the total number of API requests allowed over a specific period, preventing overuse and ensuring fair resource allocation. Benefits include predictable API usage limits and preventing system overloads, while drawbacks involve potential disruption if users hit hard limits, leading to service denial even during low traffic periods. Quotas may reduce flexibility compared to rate limiting, which manages request frequency, allowing for smoother traffic bursts without abrupt restrictions.
Pros and Cons of API Rate Limiting
API rate limiting controls the number of requests a client can make within a specified time frame, preventing server overload and ensuring fair resource distribution. Pros include enhanced security by mitigating denial-of-service attacks, improved performance through reduced traffic spikes, and better infrastructure stability. Cons involve potential user frustration from request rejection, complexity in configuring appropriate limits for varying use cases, and possible disruption of legitimate high-volume applications.
Best Practices for Managing API Consumption
Effective management of API consumption involves implementing quotas to limit the total number of requests over a longer period, ensuring fair resource allocation and preventing abuse. Rate limiting enforces short-term request caps, protecting APIs from traffic spikes and maintaining service stability. Combining both approaches with real-time monitoring and clear documentation helps optimize performance while enhancing developer experience.
Quotas Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com