Standards ensure consistency, quality, and safety across various industries by establishing clear guidelines and best practices. These benchmarks help businesses compete fairly while protecting consumers and promoting innovation. Explore the rest of this article to understand how standards impact your everyday products and services.
Table of Comparison
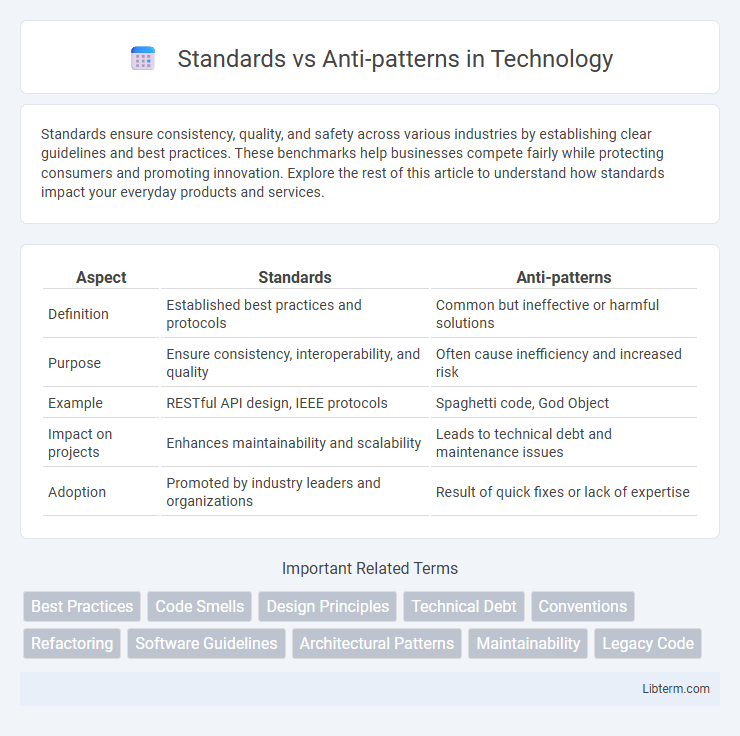
| Aspect | Standards | Anti-patterns |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Established best practices and protocols | Common but ineffective or harmful solutions |
| Purpose | Ensure consistency, interoperability, and quality | Often cause inefficiency and increased risk |
| Example | RESTful API design, IEEE protocols | Spaghetti code, God Object |
| Impact on projects | Enhances maintainability and scalability | Leads to technical debt and maintenance issues |
| Adoption | Promoted by industry leaders and organizations | Result of quick fixes or lack of expertise |
Understanding Standards and Anti-patterns
Standards provide established best practices and guidelines that ensure consistency, quality, and efficiency in software development. Anti-patterns represent common but counterproductive solutions that lead to maintenance challenges, reduced performance, or technical debt. Understanding the distinction between standards and anti-patterns is essential for improving code quality and fostering sustainable development practices.
Key Differences Between Standards and Anti-patterns
Standards are established best practices that ensure consistency, reliability, and maintainability in software development, while anti-patterns represent common but ineffective solutions that create negative consequences. Standards promote efficiency through proven guidelines such as design patterns, coding conventions, and documentation protocols, whereas anti-patterns exhibit recurring problems like spaghetti code, gold plating, or premature optimization that hinder project progress. Recognizing these key differences helps teams avoid pitfalls and adopt methodologies that align with industry benchmarks and quality expectations.
Importance of Adhering to Standards
Adhering to standards ensures consistency, reliability, and maintainability across software development projects, facilitating seamless collaboration and reducing errors. Standards promote best practices that improve code quality and scalability, preventing the pitfalls of anti-patterns, which lead to inefficiencies and technical debt. Organizations that embed standards into their workflows experience faster onboarding, improved interoperability, and enhanced long-term project viability.
Common Software Development Standards
Common software development standards emphasize modularity, readability, and maintainability, ensuring code quality and team collaboration efficiency. Adhering to these standards like consistent naming conventions, proper documentation, and thorough testing mitigates risks posed by anti-patterns such as spaghetti code, magic numbers, and premature optimization. Integrating standard design principles, including SOLID and DRY, prevents common pitfalls and fosters scalable, robust software architectures.
Identifying Common Anti-patterns
Common anti-patterns include Spaghetti Code, characterized by tangled and unstructured code that hinders maintenance and scaling. Another frequent anti-pattern is the God Object, where a single class handles excessive responsibilities, violating the single responsibility principle and increasing complexity. Recognizing these anti-patterns enables developers to adhere to coding standards that promote modularity, readability, and efficient debugging.
Impact of Anti-patterns on Project Success
Anti-patterns significantly undermine project success by introducing inefficient practices that increase technical debt, reduce code maintainability, and escalate development costs. These recurring poor solutions often lead to project delays, decreased software quality, and higher failure rates compared to adherence to established standards. Emphasizing standards ensures consistent coding, better collaboration, and optimized resource allocation, mitigating risks associated with anti-patterns.
Best Practices for Implementing Standards
Implementing standards involves adhering to established best practices such as consistent naming conventions, modular design, and thorough documentation to ensure code maintainability and scalability. Emphasizing automated testing and continuous integration supports compliance with standards while reducing defects and improving software quality. Organizations achieve higher productivity and interoperability by fostering a culture that prioritizes standards over anti-patterns like code duplication and poor error handling.
Strategies for Avoiding Anti-patterns
Effective strategies for avoiding anti-patterns include adopting coding standards such as SOLID principles and design patterns like MVC to ensure maintainability and scalability. Conducting regular code reviews and pair programming facilitates early detection and correction of undesirable practices. Leveraging automated static analysis tools and continuous integration pipelines enhances adherence to best practices, reducing the risk of introducing anti-patterns into the codebase.
Case Studies: Standards vs Anti-patterns in Real-world Scenarios
Case studies comparing standards and anti-patterns in real-world scenarios reveal the impact of best practices on project success and maintainability. Organizations adhering to coding standards report improved code quality, easier collaboration, and reduced technical debt, while those following anti-patterns often face increased bugs, delayed timelines, and higher maintenance costs. Analyzing these case studies highlights the importance of enforcing design patterns, documentation standards, and testing protocols to avoid common pitfalls and enhance software reliability.
Future Trends in Standards and Anti-pattern Prevention
Emerging future trends in standards emphasize integrating AI-driven automation to enhance compliance and adaptability across industries, promoting dynamic updates in real-time. Anti-pattern prevention increasingly relies on predictive analytics and machine learning models to identify and mitigate recurring design flaws before they become entrenched. Embracing modular, flexible standards will enable organizations to proactively address evolving challenges while reducing the prevalence of anti-patterns in software development and system architecture.
Standards Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com