Big Bang Deployment involves launching an entire system overhaul or software upgrade at one specific time, replacing the old system entirely. This method minimizes transition periods but demands thorough testing and preparation to avoid critical failures. Explore the article to understand how Big Bang Deployment could impact your project's success and discover best practices for implementation.
Table of Comparison
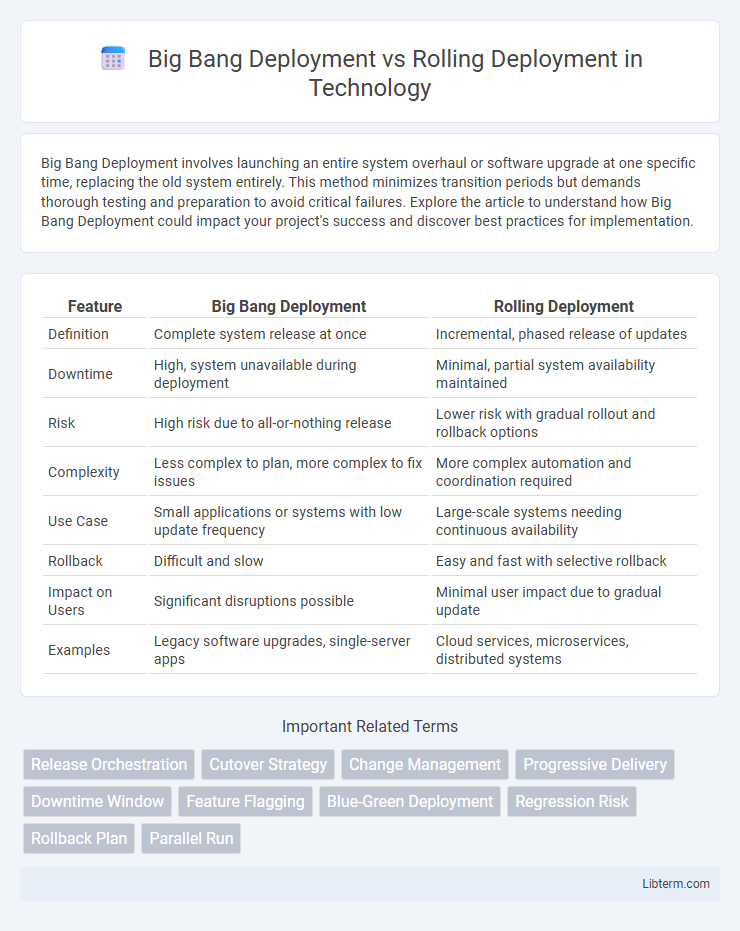
| Feature | Big Bang Deployment | Rolling Deployment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Complete system release at once | Incremental, phased release of updates |
| Downtime | High, system unavailable during deployment | Minimal, partial system availability maintained |
| Risk | High risk due to all-or-nothing release | Lower risk with gradual rollout and rollback options |
| Complexity | Less complex to plan, more complex to fix issues | More complex automation and coordination required |
| Use Case | Small applications or systems with low update frequency | Large-scale systems needing continuous availability |
| Rollback | Difficult and slow | Easy and fast with selective rollback |
| Impact on Users | Significant disruptions possible | Minimal user impact due to gradual update |
| Examples | Legacy software upgrades, single-server apps | Cloud services, microservices, distributed systems |
Introduction to Deployment Strategies
Big Bang Deployment involves releasing an entirely new system version in a single, comprehensive update, minimizing transition time but increasing risk due to all changes being implemented simultaneously. Rolling Deployment updates a system incrementally by gradually replacing instances or components, reducing downtime and allowing for easier rollback if issues arise. Choosing the right deployment strategy depends on factors like system complexity, risk tolerance, and the need for continuous availability.
Understanding Big Bang Deployment
Big Bang Deployment involves releasing the entire system or application at once, enabling immediate access to new features and functionalities across the user base. This approach demands thorough testing and preparation to minimize risks, as any failure impacts all users simultaneously. Organizations favor Big Bang Deployment for projects with clear requirements and a controlled environment, where a swift transition is essential.
Exploring Rolling Deployment
Rolling deployment gradually updates applications across server clusters, minimizing downtime and reducing risks by allowing continuous monitoring and rollback capabilities. This method supports scalability and high availability by incrementally replacing instances without disrupting the entire system. Compared to Big Bang deployment, which updates all components simultaneously, rolling deployment ensures smoother transitions and improved user experience during releases.
Key Differences Between Big Bang and Rolling Deployments
Big Bang deployment involves releasing a complete system update all at once, leading to immediate and widespread changes, while rolling deployment introduces updates in phases across subsets of servers or users, minimizing downtime. Big Bang offers faster launch but carries higher risk due to potential system-wide failures, whereas rolling deployment reduces risk by allowing gradual rollout and easier rollback of problematic changes. The choice between Big Bang and rolling deployment depends on factors like system complexity, user impact tolerance, and the ability to manage incremental updates.
Advantages of Big Bang Deployment
Big Bang Deployment offers the advantage of immediate system availability by launching the entire application or upgrade at once, reducing the complexity of managing multiple versions concurrently. It minimizes the risk of compatibility issues and ensures all users access the new features simultaneously, promoting consistency across the organization. This approach simplifies testing and validation processes by focusing on a single, comprehensive release, accelerating time-to-market for critical updates.
Advantages of Rolling Deployment
Rolling deployment minimizes downtime by updating applications incrementally across servers, ensuring continuous service availability and reducing user disruption. It allows quick rollback on specific instances if issues arise, enhancing system reliability and stability. Resource utilization improves as small batches are deployed, enabling smoother monitoring and testing in production environments.
Risks and Challenges of Each Approach
Big Bang Deployment carries significant risks including potential system downtime, higher complexity in troubleshooting, and a greater chance of introducing critical bugs due to the simultaneous launch of all features. Rolling Deployment reduces immediate risk by gradually releasing updates across servers, but it presents challenges such as managing version compatibility, increased monitoring requirements, and prolonged exposure to partially updated environments. Both approaches require careful planning, with Big Bang demanding comprehensive testing and contingency plans, while Rolling Deployment necessitates robust automation and rollback mechanisms.
Choosing the Right Deployment Strategy for Your Project
Big Bang Deployment involves launching a complete system update at once, which can accelerate time-to-market but poses higher risks of system failure and user disruption if issues arise. Rolling Deployment gradually releases updates to a subset of servers or users, minimizing downtime and allowing for easier rollback in case of errors, making it ideal for projects requiring continuous availability. Choosing the right deployment strategy depends on factors such as project complexity, risk tolerance, infrastructure capabilities, and the need for rapid feedback or minimal service interruption.
Real-World Use Cases and Examples
Big Bang Deployment is often used in large-scale ERP implementations like SAP S/4HANA, where the entire system goes live simultaneously to minimize integration issues and leverage comprehensive testing; for example, Walmart's massive SAP rollout utilized this approach to synchronize operations globally. Rolling Deployment suits cloud service providers like Netflix, allowing incremental updates with minimal disruption by gradually releasing changes across server clusters, maintaining high availability and rapid rollback capabilities. Enterprises prioritize Big Bang in scenarios demanding immediate, organization-wide transformation, while Rolling Deployment excels in continuous delivery environments requiring seamless user experience during frequent updates.
Final Recommendations and Best Practices
Big Bang Deployment requires comprehensive testing and a robust rollback plan to mitigate risks associated with launching all changes simultaneously, making it suitable for smaller, less complex systems. Rolling Deployment supports continuous delivery by gradually updating instances, reducing downtime and enabling quick issue detection, ideal for large-scale, cloud-based applications. Best practices include thorough automated testing, monitoring deployment metrics, and maintaining clear communication channels to ensure smooth transitions regardless of the chosen strategy.
Big Bang Deployment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com