Effective IT operations ensure seamless management of an organization's technology infrastructure, optimizing performance, security, and reliability. By integrating automation and monitoring tools, businesses minimize downtime and enhance service delivery. Explore the full article to discover strategies for streamlining your IT operations and boosting organizational efficiency.
Table of Comparison
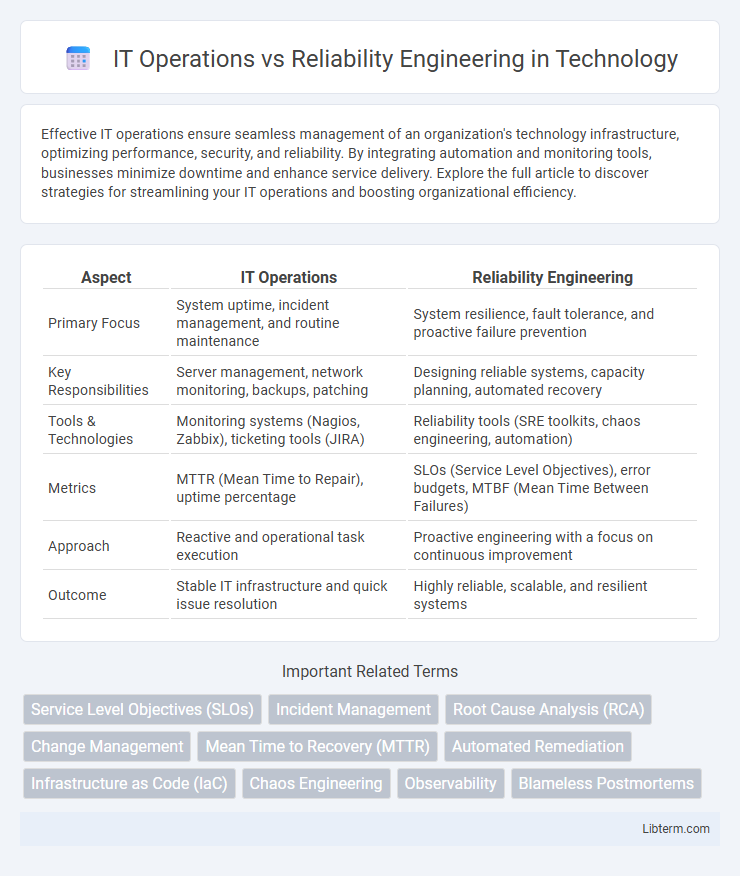
| Aspect | IT Operations | Reliability Engineering |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | System uptime, incident management, and routine maintenance | System resilience, fault tolerance, and proactive failure prevention |
| Key Responsibilities | Server management, network monitoring, backups, patching | Designing reliable systems, capacity planning, automated recovery |
| Tools & Technologies | Monitoring systems (Nagios, Zabbix), ticketing tools (JIRA) | Reliability tools (SRE toolkits, chaos engineering, automation) |
| Metrics | MTTR (Mean Time to Repair), uptime percentage | SLOs (Service Level Objectives), error budgets, MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures) |
| Approach | Reactive and operational task execution | Proactive engineering with a focus on continuous improvement |
| Outcome | Stable IT infrastructure and quick issue resolution | Highly reliable, scalable, and resilient systems |
Introduction to IT Operations and Reliability Engineering
IT Operations involves managing and maintaining IT infrastructure to ensure seamless service delivery, including monitoring, incident management, and system administration. Reliability Engineering focuses on designing and improving systems to maximize uptime, reduce failures, and enhance overall system resilience through practices like fault tolerance and proactive failure analysis. Both disciplines aim to optimize system performance but approach it from operational management and engineering reliability perspectives.
Defining IT Operations: Roles and Responsibilities
IT Operations encompasses the management, maintenance, and support of an organization's IT infrastructure to ensure systems run efficiently. Key roles include system administrators, network engineers, and help desk technicians responsible for monitoring performance, troubleshooting issues, and implementing security protocols. Responsibilities focus on uptime maintenance, incident response, patch management, and optimizing hardware and software resources to support business continuity.
What is Reliability Engineering? Core Concepts
Reliability Engineering focuses on ensuring systems perform consistently over time by minimizing failures through proactive design, testing, and maintenance strategies. Core concepts include fault tolerance, failure mode analysis, and continuous monitoring to predict and prevent downtime. This discipline emphasizes scalability and resiliency to enhance system reliability beyond traditional IT Operations, which primarily manage day-to-day infrastructure and incident response.
Key Differences Between IT Operations and Reliability Engineering
IT Operations centers on maintaining IT infrastructure and ensuring systems run smoothly through monitoring, incident management, and routine maintenance, emphasizing immediate problem resolution. Reliability Engineering focuses on designing systems for long-term stability, emphasizing proactive measures like automation, fault tolerance, and performance optimization to minimize downtime. While IT Operations reacts to system failures, Reliability Engineering aims to predict and prevent them, driving continuous improvement in system reliability.
Overlapping Responsibilities: Where IT Ops and Reliability Meet
IT Operations and Reliability Engineering both focus on maintaining system performance and uptime, with IT Ops managing infrastructure, deployment, and incident response while Reliability Engineering emphasizes system design, monitoring, and automation to prevent failures. Shared responsibilities include capacity planning, incident management, root cause analysis, and continuous improvement of processes to enhance system reliability. Collaboration between these teams ensures seamless service delivery, minimizing downtime and improving overall operational efficiency.
Tools and Technologies Used in Each Discipline
IT Operations primarily utilizes monitoring systems like Nagios, Zabbix, and SolarWinds to ensure uptime and manage infrastructure performance, often integrating configuration management tools such as Ansible, Puppet, and Chef for automation. Reliability Engineering leverages advanced observability platforms including Prometheus, Grafana, and Datadog, emphasizing SRE-specific tools like error budgeting and chaos engineering frameworks such as Gremlin or Chaos Monkey to proactively enhance system resilience. Both disciplines rely heavily on cloud-based services and container orchestration technologies like Kubernetes and Docker to streamline deployment and maintain stability across dynamic environments.
The Evolving Role of IT Operations in Modern Enterprises
IT Operations has shifted from routine infrastructure management to proactive service delivery and system optimization, integrating automation, AI-driven monitoring, and real-time analytics. Reliability Engineering emphasizes designing systems for fault tolerance, scalability, and continuous availability, using practices like Chaos Engineering and Site Reliability Engineering (SRE). Modern enterprises increasingly blend IT Operations with Reliability Engineering to enhance system resilience, reduce downtime, and accelerate software deployment cycles.
How Reliability Engineering Drives Business Value
Reliability engineering enhances business value by proactively identifying and mitigating system failures through continuous monitoring, automation, and root cause analysis. This approach reduces downtime and improves service availability, directly impacting customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. IT operations typically focus on maintaining infrastructure, while reliability engineering ensures long-term system resilience and strategic risk management.
Best Practices for Collaboration Between IT Ops and Reliability Teams
Effective collaboration between IT Operations and Reliability Engineering teams hinges on establishing shared objectives such as system uptime, incident response time, and continuous improvement through post-mortem analyses. Implementing integrated communication channels, synchronized monitoring tools, and joint incident management protocols ensures real-time data sharing and coordinated troubleshooting. Emphasizing a culture of mutual accountability and continuous feedback loops optimizes system reliability and operational efficiency.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Organization
Evaluating IT operations versus reliability engineering depends on your organization's priorities between maintaining system uptime and streamlining incident response. IT operations focus on system management and support to ensure daily functions run smoothly, while reliability engineering emphasizes proactive design, automation, and resilience to prevent failures. Selecting the right approach involves assessing team expertise, business goals, and the criticality of continuous availability to optimize overall system performance and customer satisfaction.
IT Operations Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com