Push notifications deliver timely and relevant updates directly to your device, enhancing user engagement and retention. They provide instant communication for promotions, alerts, or personalized messages, ensuring your audience stays informed without actively checking your app or website. Explore the full article to discover effective strategies for optimizing push notification campaigns.
Table of Comparison
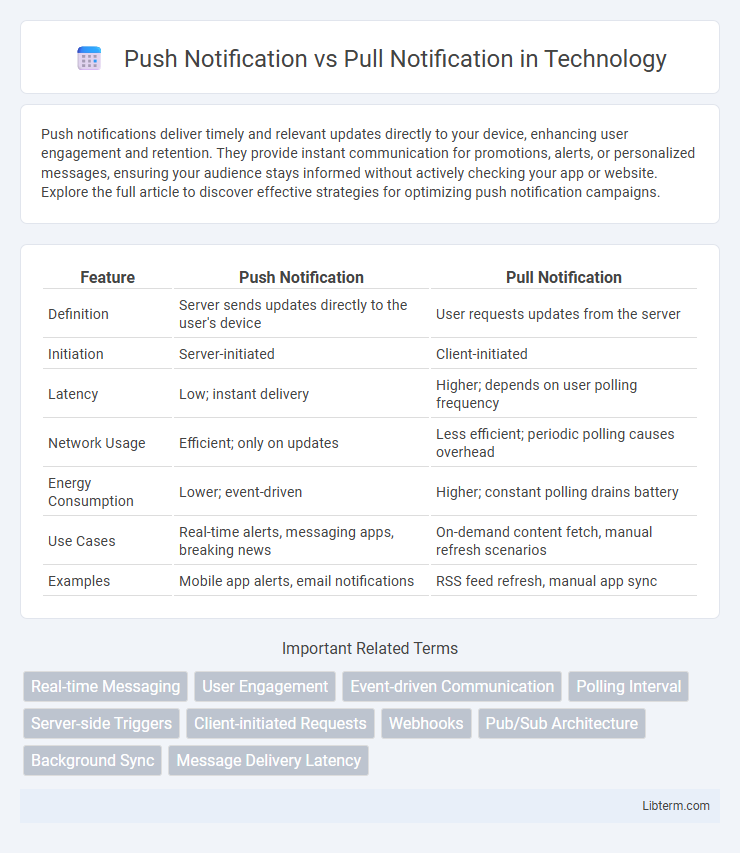
| Feature | Push Notification | Pull Notification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Server sends updates directly to the user's device | User requests updates from the server |
| Initiation | Server-initiated | Client-initiated |
| Latency | Low; instant delivery | Higher; depends on user polling frequency |
| Network Usage | Efficient; only on updates | Less efficient; periodic polling causes overhead |
| Energy Consumption | Lower; event-driven | Higher; constant polling drains battery |
| Use Cases | Real-time alerts, messaging apps, breaking news | On-demand content fetch, manual refresh scenarios |
| Examples | Mobile app alerts, email notifications | RSS feed refresh, manual app sync |
Introduction to Push and Pull Notifications
Push notifications deliver real-time updates directly to a user's device without requiring a request, enhancing immediate engagement for apps and websites. Pull notifications rely on the user or client application to initiate communication by requesting data from the server, often resulting in delayed information delivery. Understanding the distinction between push and pull notifications is essential for optimizing user interaction and system responsiveness in digital communication strategies.
Understanding Push Notifications
Push notifications are messages sent directly from a server to a user's device, enabling real-time updates without requiring the user to request information. These notifications are essential for delivering timely alerts, such as social media updates, news, or transactional information, enhancing user engagement and app retention. Understanding push notification technology includes grasping concepts like device tokens, payload size limits, and delivery protocols used by platforms like APNs (Apple Push Notification service) and FCM (Firebase Cloud Messaging).
Exploring Pull Notifications
Pull notifications require the client device to actively request updates from the server, enabling greater control over data retrieval timing and bandwidth use. These notifications reduce unnecessary data transfer by allowing users to fetch information only when needed, making them ideal for applications with intermittent connectivity or limited battery life. Pull notifications are commonly used in email clients and social media apps where users manually refresh content, contrasting with push notifications that automatically deliver updates instantly.
Key Differences Between Push and Pull Notifications
Push notifications are messages sent directly from a server to a user's device without a prior request, enabling real-time updates and immediate engagement. Pull notifications require the user or client device to request information from the server, resulting in delayed data retrieval based on user action or predefined intervals. Key differences include immediacy, server initiation in push versus client initiation in pull, and resource efficiency, with push being more proactive and pull requiring periodic polling.
Advantages of Push Notifications
Push notifications enable real-time communication by automatically delivering timely updates, alerts, or promotional messages directly to users' devices without requiring user initiation. This immediate engagement increases user retention and conversion rates by providing relevant information at the right moment. Push notifications also reduce server load compared to pull methods by minimizing constant data requests, resulting in more efficient bandwidth usage and improved app performance.
Benefits of Pull Notifications
Pull notifications enhance user control by allowing individuals to retrieve information at their convenience, reducing the risk of unwanted interruptions. This method conserves device resources and bandwidth because data is only fetched when explicitly requested by the user. Pull notifications also enable more efficient data management by minimizing unnecessary network traffic and improving battery life on mobile devices.
Use Cases for Push and Pull Notifications
Push notifications are ideal for real-time alerts such as breaking news, weather updates, or appointment reminders where immediate user attention is crucial. Pull notifications excel in scenarios requiring user-initiated content retrieval, such as checking for new emails, social media feeds, or app updates on demand. Both methods optimize user experience by balancing timely information delivery with user control over data consumption.
Security Considerations in Notification Systems
Push notifications deliver information directly from the server to the user's device, which requires robust encryption methods such as SSL/TLS to prevent interception or unauthorized access during transmission. Pull notifications rely on the client device requesting updates from the server, necessitating strong authentication protocols to ensure data is retrieved only by authorized users, mitigating risks like man-in-the-middle attacks or data leakage. Implementing security measures such as end-to-end encryption, token-based authentication, and regular updates are crucial to protecting both push and pull notification systems against common vulnerabilities like spoofing and unauthorized data access.
Choosing the Right Notification Strategy
Choosing the right notification strategy depends on the context and user engagement goals; push notifications actively deliver timely alerts to users without requiring a request, ideal for urgent updates or promotions, while pull notifications rely on users to initiate data retrieval, suitable for less time-sensitive information. Push notifications often increase user interaction rates due to their proactive nature but require careful management to avoid notification fatigue. Pull notifications provide a more user-controlled experience, ensuring information is accessed only when desired, thus maintaining user satisfaction in scenarios prioritizing user autonomy.
Future Trends in Notification Technology
Push notifications are evolving with AI-driven personalization and real-time context awareness, enhancing user engagement through proactive and relevant alerts. Pull notifications are integrating advanced user-initiated data retrieval systems, leveraging machine learning to optimize timing and content delivery based on user behavior. Future trends emphasize hybrid models combining push and pull mechanisms, ensuring seamless, adaptive communication that anticipates user needs across IoT devices and smart ecosystems.
Push Notification Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com