Load balancing distributes network or application traffic across multiple servers to ensure optimal resource use, maximize throughput, and minimize response time. Effective load balancing enhances system reliability by preventing any single server from becoming a bottleneck or point of failure. Discover how implementing load balancing can improve your infrastructure's performance and reliability by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
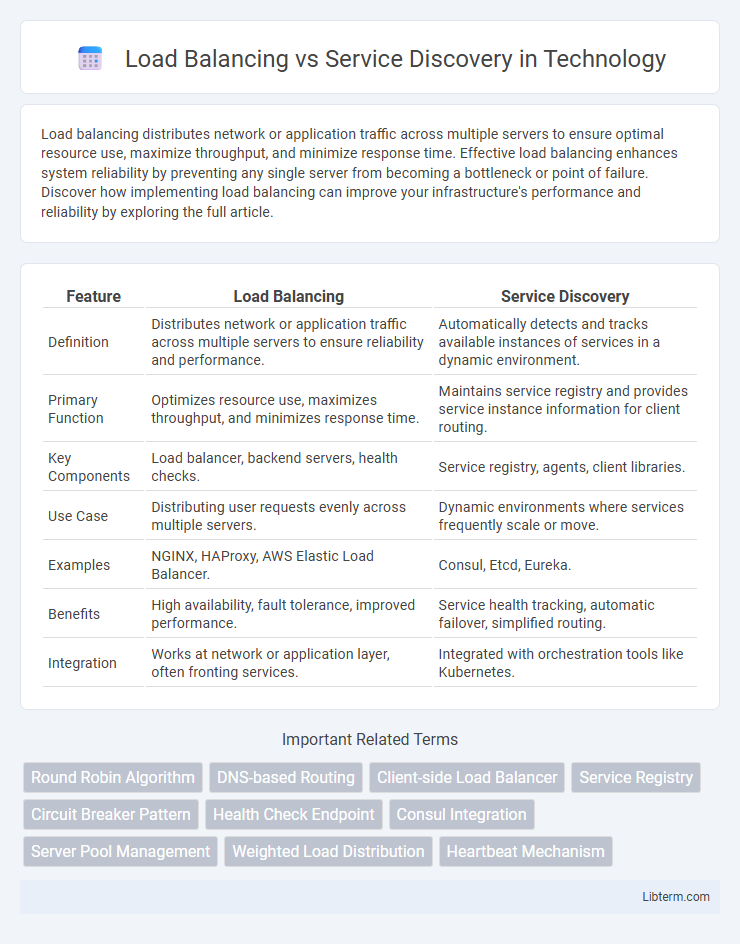
| Feature | Load Balancing | Service Discovery |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Distributes network or application traffic across multiple servers to ensure reliability and performance. | Automatically detects and tracks available instances of services in a dynamic environment. |
| Primary Function | Optimizes resource use, maximizes throughput, and minimizes response time. | Maintains service registry and provides service instance information for client routing. |
| Key Components | Load balancer, backend servers, health checks. | Service registry, agents, client libraries. |
| Use Case | Distributing user requests evenly across multiple servers. | Dynamic environments where services frequently scale or move. |
| Examples | NGINX, HAProxy, AWS Elastic Load Balancer. | Consul, Etcd, Eureka. |
| Benefits | High availability, fault tolerance, improved performance. | Service health tracking, automatic failover, simplified routing. |
| Integration | Works at network or application layer, often fronting services. | Integrated with orchestration tools like Kubernetes. |
Introduction to Load Balancing and Service Discovery
Load balancing distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers to ensure reliability and optimal resource utilization, enhancing application performance and scalability. Service discovery automates the detection of available services within a system, enabling dynamic connection between components without manual configuration. Both techniques are essential in microservices architectures to maintain high availability and seamless communication between services.
Core Concepts: What is Load Balancing?
Load balancing is a method used to distribute network traffic or application requests across multiple servers to ensure optimal resource use, minimize response time, and avoid overload on any single server. It improves availability and reliability by rerouting traffic to healthy servers in cases of failure. Core types include hardware-based and software-based load balancers, as well as algorithms like round-robin, least connections, and IP hash for traffic distribution.
Core Concepts: What is Service Discovery?
Service Discovery is a core component in microservices architectures that enables automatic detection of network locations for service instances, facilitating dynamic communication between distributed services. It maintains an up-to-date registry of available service instances and their network details, allowing clients or load balancers to query and locate services without hardcoded IP addresses or endpoints. By automating the process of tracking service availability and addressing changes in scaling or failures, Service Discovery enhances system resilience and scalability.
Key Differences Between Load Balancing and Service Discovery
Load balancing distributes network or application traffic across multiple servers to ensure reliability and optimal resource use, while service discovery enables microservices to locate and communicate with each other dynamically in distributed systems. Load balancing typically operates at the transport or application layer, managing client requests and optimizing response times, whereas service discovery functions at the service level, maintaining an updated registry of available services and their endpoints. Key differences include load balancing's focus on traffic management and fault tolerance versus service discovery's role in service registry maintenance and dynamic endpoint resolution.
How Load Balancing Works in Modern Architectures
Load balancing in modern architectures distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers to ensure reliability and high performance, using algorithms like round-robin, least connections, and IP hash for optimal resource utilization. It operates at various layers, including Layer 4 (transport) and Layer 7 (application), allowing for advanced routing based on request content, session persistence, and health checks. Integration with container orchestration platforms and service meshes enhances dynamic scaling and fault tolerance by automatically redirecting traffic to healthy instances in microservices environments.
Service Discovery Mechanisms Explained
Service discovery mechanisms enable microservices to locate each other dynamically by registering service instances with a centralized registry or using DNS-based approaches, facilitating efficient communication in distributed systems. These mechanisms support real-time updates of service availability, allowing load balancers to route requests to healthy instances based on metrics like latency, instance health, or geographic location. Common service discovery protocols include Consul, Eureka, and DNS-SD, each providing dynamic service registration, health monitoring, and query capabilities essential for scalable cloud-native applications.
Pros and Cons of Load Balancing
Load balancing optimizes resource use by distributing incoming network traffic across multiple servers, enhancing reliability and scalability but may introduce single points of failure if not properly configured. It effectively improves application availability and reduces response time, though complexity increases with dynamic scaling and can lead to uneven load distribution without fine-tuned algorithms. Unlike service discovery, which dynamically identifies service instances, load balancing requires constant monitoring to adapt to changes in service health and demand.
Pros and Cons of Service Discovery
Service discovery automates the detection of network locations for services, enhancing scalability and dynamic environment adaptability but can introduce complexity and additional latency in request routing. It enables microservices to communicate seamlessly without hard-coded IP addresses, improving fault tolerance and reducing manual configuration errors. However, reliance on a service registry creates a potential single point of failure and requires maintaining consistency and availability, which can complicate infrastructure management.
Use Cases: When to Use Load Balancing vs Service Discovery
Load balancing is ideal for distributing incoming network traffic evenly across multiple servers to enhance application availability and performance, particularly in web services and high-traffic environments. Service discovery excels in dynamic microservices architectures where services need to locate each other automatically, enabling seamless communication and scaling without manual configuration. Use load balancing when optimizing resource utilization and managing requests at scale, while service discovery is essential for maintaining connectivity and adaptability in constantly changing service topologies.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Application
Load balancing optimizes application performance by distributing network traffic across multiple servers, while service discovery dynamically identifies available service instances within a distributed system. Choosing the right solution depends on factors such as application architecture, scalability requirements, and fault tolerance needs. Combining both load balancing and service discovery often results in enhanced reliability and efficient resource utilization for microservices-based applications.
Load Balancing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com