Polling gathers public opinion through structured surveys, providing critical insights into voter preferences and social trends. Accurate polling techniques and data analysis ensure reliable results that inform political strategies and business decisions. Discover how polling shapes decision-making and why understanding its nuances can enhance your perspective in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
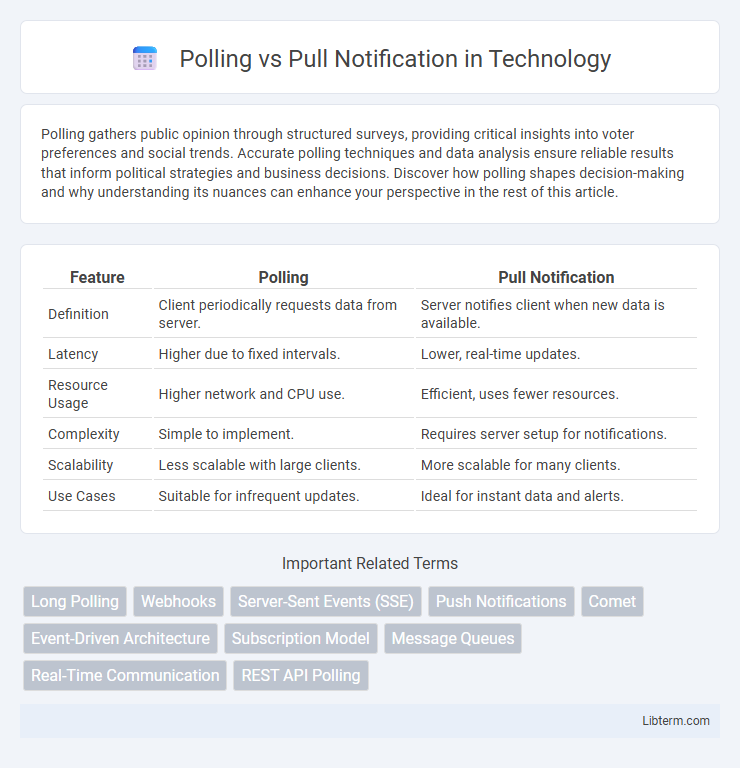
| Feature | Polling | Pull Notification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Client periodically requests data from server. | Server notifies client when new data is available. |
| Latency | Higher due to fixed intervals. | Lower, real-time updates. |
| Resource Usage | Higher network and CPU use. | Efficient, uses fewer resources. |
| Complexity | Simple to implement. | Requires server setup for notifications. |
| Scalability | Less scalable with large clients. | More scalable for many clients. |
| Use Cases | Suitable for infrequent updates. | Ideal for instant data and alerts. |
Introduction to Polling and Pull Notification
Polling is a communication method where a client repeatedly requests data from a server at regular intervals, ensuring it checks for updates continuously. Pull Notification, on the other hand, allows the server to push notifications to the client only when new data is available, reducing unnecessary network traffic. Both methods are essential for managing real-time data synchronization in web applications and services.
Definitions: Polling vs Pull Notification
Polling is a method where a client repeatedly requests data from a server at regular intervals to check for updates. Pull notification refers to the process by which a client sends a request to a server specifically to retrieve new or updated information since the last check. Both techniques rely on client-initiated communication but differ in implementation, with polling being time-based and pull notification being event-driven or state-based.
How Polling Works
Polling operates by repeatedly sending requests at fixed intervals from a client to a server to check for new data or updates, ensuring the client remains synchronized with the server state. The server processes each request regardless of whether new information is available, which may lead to unnecessary network traffic and increased latency in receiving updates. This method is straightforward to implement but can strain system resources, especially with high-frequency polling or many clients.
How Pull Notification Works
Pull notification works by having a client periodically send requests to a server to check for new data or updates. The server responds only when new information is available, reducing unnecessary data transmission compared to constant data streaming. This method improves bandwidth efficiency and minimizes server load by ensuring communication occurs only when changes are detected.
Key Differences Between Polling and Pull Notification
Polling requires the client to repeatedly request information from the server at regular intervals, leading to potential latency and increased network traffic, whereas pull notification enables the server to send updates only when new data is available, improving efficiency and reducing unnecessary data transmission. Polling often results in wasted resources due to empty responses if no update is present, while pull notifications provide real-time or near-real-time data delivery, enhancing user experience. In terms of scalability, pull notification systems handle high-volume, event-driven environments more effectively than polling mechanisms, which can strain server resources under heavy load.
Pros and Cons of Polling
Polling offers simplicity and ease of implementation by repeatedly requesting data from a server at fixed intervals, making it suitable for applications with predictable update frequencies. However, it can lead to increased network traffic and server load due to frequent unnecessary requests, resulting in inefficiency and potential latency in data updates. Polling may also cause delayed responsiveness since the client only receives new data during scheduled polls, potentially impacting real-time data applications.
Pros and Cons of Pull Notification
Pull notification offers the advantage of reducing unnecessary data transfers by allowing clients to request updates only when needed, which conserves bandwidth and processing power. However, its main drawback lies in potential latency, as clients might not receive real-time information promptly, leading to delays in data synchronization. Furthermore, pull notifications can increase server load due to frequent client requests, especially in applications requiring high responsiveness.
Use Cases: When to Use Polling or Pull Notification
Polling is ideal for applications requiring regular status updates without server-initiated alerts, such as monitoring system health or retrieving data at fixed intervals. Pull notifications work best in scenarios needing immediate updates on demand, like chat applications or financial trading platforms where latency and real-time information are critical. Choosing between polling and pull notification depends on factors like network efficiency, update frequency, and the necessity for real-time data delivery.
Performance and Scalability Considerations
Polling requires frequent client requests to the server, causing increased network traffic and higher latency, which can degrade performance under high load. Pull notifications reduce unnecessary requests by delivering updates only when changes occur, improving scalability and resource efficiency. Implementing pull notifications with event-driven architecture supports better load distribution and faster response times in large-scale applications.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Application
Polling involves regularly requesting data from a server at set intervals, ensuring updated information but potentially leading to increased latency and higher bandwidth usage. Pull notification uses a server-initiated approach to push updates immediately, reducing unnecessary network traffic and improving real-time responsiveness. Selecting the right method depends on application needs: polling suits scenarios with intermittent updates, while pull notification excels in environments requiring instant data delivery and efficient resource utilization.
Polling Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com