AES-NI (Advanced Encryption Standard New Instructions) is a set of hardware instructions that accelerate the encryption and decryption processes using the AES algorithm, enhancing both security and performance. Leveraging AES-NI can significantly reduce CPU overhead during data protection, making it ideal for securing sensitive information in real-time applications. Discover how AES-NI can optimize your security solutions by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
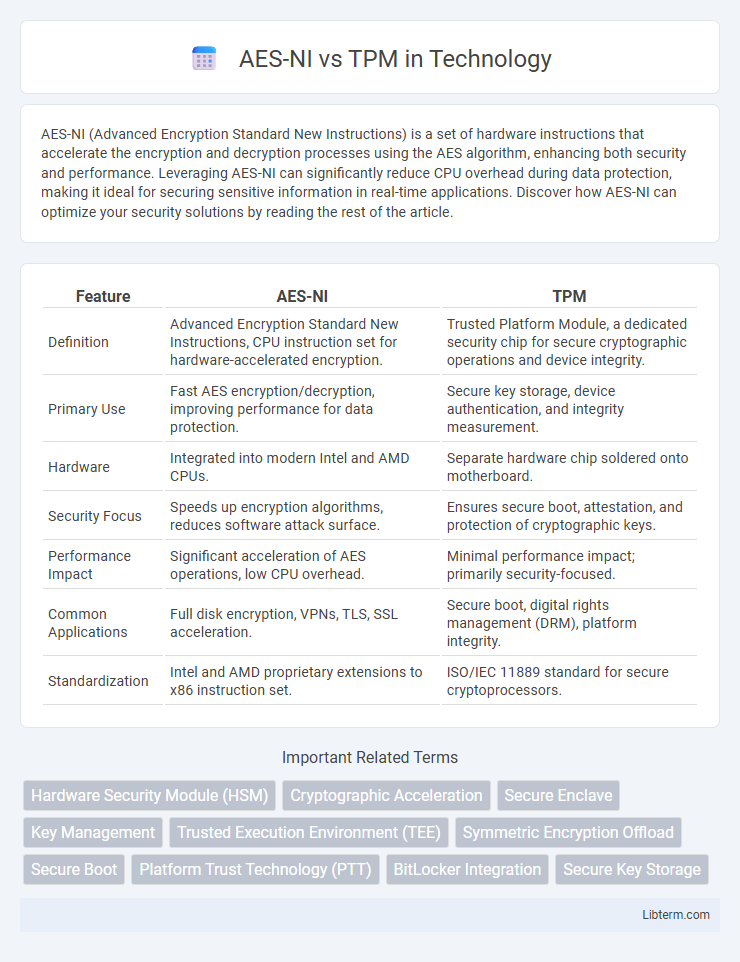
| Feature | AES-NI | TPM |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Advanced Encryption Standard New Instructions, CPU instruction set for hardware-accelerated encryption. | Trusted Platform Module, a dedicated security chip for secure cryptographic operations and device integrity. |
| Primary Use | Fast AES encryption/decryption, improving performance for data protection. | Secure key storage, device authentication, and integrity measurement. |
| Hardware | Integrated into modern Intel and AMD CPUs. | Separate hardware chip soldered onto motherboard. |
| Security Focus | Speeds up encryption algorithms, reduces software attack surface. | Ensures secure boot, attestation, and protection of cryptographic keys. |
| Performance Impact | Significant acceleration of AES operations, low CPU overhead. | Minimal performance impact; primarily security-focused. |
| Common Applications | Full disk encryption, VPNs, TLS, SSL acceleration. | Secure boot, digital rights management (DRM), platform integrity. |
| Standardization | Intel and AMD proprietary extensions to x86 instruction set. | ISO/IEC 11889 standard for secure cryptoprocessors. |
Introduction to AES-NI and TPM
AES-NI (Advanced Encryption Standard New Instructions) is a set of hardware instructions that accelerates encryption and decryption processes directly within the CPU, enhancing data security and performance. TPM (Trusted Platform Module) is a dedicated hardware chip designed to securely store cryptographic keys, digital certificates, and ensure platform integrity through secure boot and attestation. While AES-NI boosts cryptographic operations speed, TPM provides a hardware-based root of trust for system security and device authentication.
Core Functions: AES-NI vs TPM
AES-NI (Advanced Encryption Standard New Instructions) accelerates cryptographic operations by providing hardware-based instructions for fast and secure encryption and decryption, primarily enhancing AES algorithm performance directly within the CPU. TPM (Trusted Platform Module) serves as a dedicated hardware security chip that securely generates, stores cryptographic keys, and ensures platform integrity through hardware-based root of trust, supporting secure boot, attestation, and key management. While AES-NI optimizes bulk data encryption speed and efficiency in software, TPM focuses on key security and platform authentication, offering complementary security functions rather than overlapping capabilities.
Hardware Architecture Differences
AES-NI (Advanced Encryption Standard New Instructions) is a set of CPU instructions that accelerate encryption and decryption processes directly within the processor's core, enhancing cryptographic efficiency at the hardware level. TPM (Trusted Platform Module) is a dedicated microcontroller designed to securely generate, store, and manage cryptographic keys, providing a hardware root of trust separate from the main CPU. While AES-NI embeds cryptographic acceleration inside the CPU's instruction set architecture, TPM operates as an isolated hardware component focused on secure key storage and platform integrity verification.
Cryptographic Operations: Speed and Efficiency
AES-NI enhances cryptographic operations by providing hardware-accelerated encryption and decryption, significantly increasing speed and efficiency in symmetric key algorithms like AES compared to software-based methods. TPM focuses on secure key storage and cryptographic key generation but does not accelerate cryptographic operations, resulting in slower performance for encryption tasks. For high-throughput cryptographic processing, AES-NI offers superior efficiency, whereas TPM prioritizes secure key management over operational speed.
Security Features and Threat Mitigation
AES-NI (Advanced Encryption Standard New Instructions) enhances encryption performance by integrating hardware-accelerated AES algorithms directly into the CPU, significantly reducing cryptographic operation time and mitigating side-channel attacks such as timing attacks. TPM (Trusted Platform Module) provides a dedicated microcontroller for secure key storage, platform integrity validation, and hardware-based root of trust, effectively defending against firmware attacks, unauthorized hardware access, and boot-level threats. Together, AES-NI ensures efficient and robust data encryption, while TPM strengthens system-level security through trusted boot processes and secure key management, addressing complementary layers of threat mitigation.
Use Cases in Modern Computing
AES-NI accelerates encryption and decryption processes by offloading AES algorithm computations directly to hardware, which enhances performance in data-at-rest encryption, secure communications, and virtual private networks (VPNs). TPM provides hardware-based root of trust, securing cryptographic keys, platform integrity, and authentication mechanisms, making it essential for secure boot, disk encryption (BitLocker), and hardware attestation. Modern computing environments leverage AES-NI for high-speed bulk data encryption, while TPM ensures system integrity and trustworthiness, often combining both for comprehensive security solutions.
Integration and Compatibility
AES-NI (Advanced Encryption Standard New Instructions) integrates directly into modern CPUs, enhancing encryption performance by offloading cryptographic calculations to dedicated hardware instructions, ensuring seamless compatibility with a wide range of software frameworks and operating systems. TPM (Trusted Platform Module) functions as a discrete hardware chip designed for secure cryptographic key storage and platform integrity verification, requiring motherboard-level support and BIOS/firmware compatibility. While AES-NI offers low-level processor acceleration broadly compatible with encryption libraries, TPM provides secure key management and attestation features essential for trusted computing environments, with software and hardware integration varying by platform and vendor implementations.
Performance Benchmarks: Real-World Scenarios
AES-NI delivers significant performance boosts by accelerating AES encryption and decryption directly within the CPU, enabling encryption tasks to run up to 10 times faster than software-only solutions. TPM, designed primarily for secure key storage and hardware-based security functions, does not accelerate cryptographic operations, resulting in minimal impact on encryption performance. In real-world scenarios like full-disk encryption and VPN workloads, AES-NI offers superior throughput and reduced latency compared to TPM-based security implementations.
Pros and Cons Comparison
AES-NI enhances encryption performance by providing hardware-accelerated AES encryption, reducing CPU load and improving speed, making it ideal for data-intensive applications. TPM offers secure key storage and hardware-based integrity measurements, boosting system security but typically lacks the encryption acceleration benefits of AES-NI. While AES-NI focuses on fast cryptographic operations, TPM emphasizes secure key management and device attestation, necessitating a complementary approach for comprehensive security solutions.
Choosing Between AES-NI and TPM
Choosing between AES-NI and TPM depends on security needs and hardware capabilities; AES-NI offers hardware-accelerated encryption for faster and more efficient data protection, ideal for high-performance environments. TPM provides a secure cryptoprocessor for cryptographic operations, key storage, and platform integrity verification, enhancing overall device security at the firmware level. Organizations requiring robust encryption speed should prioritize AES-NI, while those emphasizing hardware-based root of trust and secure key management typically opt for TPM.
AES-NI Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com