Traditional coding involves writing software using programming languages like C, Java, or Python, requiring detailed knowledge of syntax and logic to build functional applications. This method emphasizes manual debugging and optimization, ensuring precise control over software behavior and performance. Explore the rest of the article to discover how traditional coding compares to modern development approaches and what it means for your programming journey.
Table of Comparison
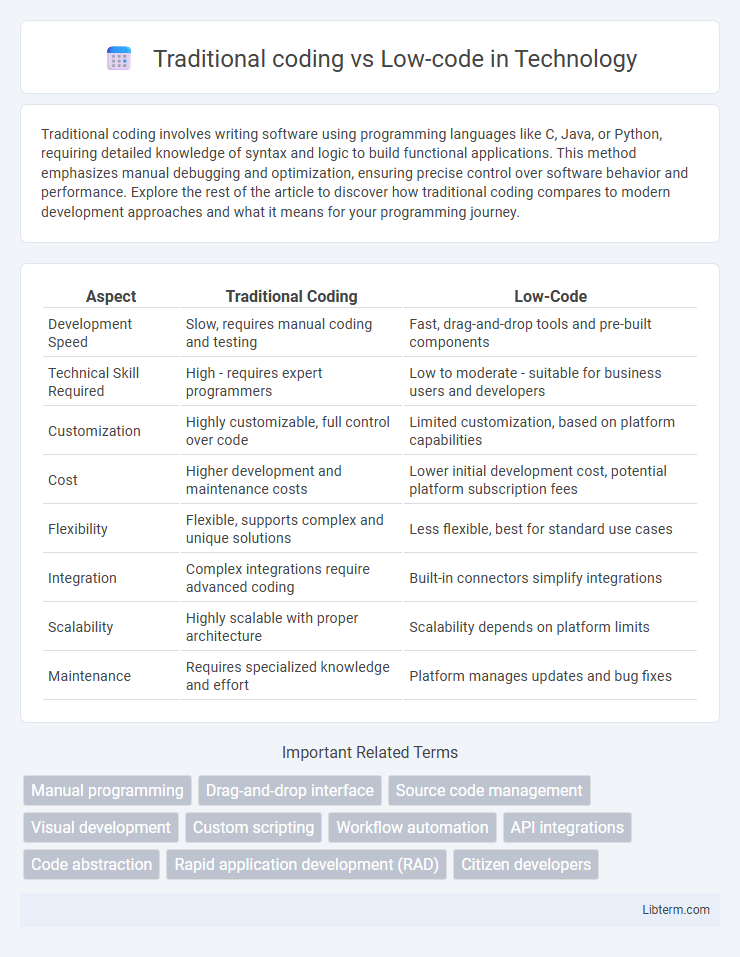
| Aspect | Traditional Coding | Low-Code |
|---|---|---|
| Development Speed | Slow, requires manual coding and testing | Fast, drag-and-drop tools and pre-built components |
| Technical Skill Required | High - requires expert programmers | Low to moderate - suitable for business users and developers |
| Customization | Highly customizable, full control over code | Limited customization, based on platform capabilities |
| Cost | Higher development and maintenance costs | Lower initial development cost, potential platform subscription fees |
| Flexibility | Flexible, supports complex and unique solutions | Less flexible, best for standard use cases |
| Integration | Complex integrations require advanced coding | Built-in connectors simplify integrations |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with proper architecture | Scalability depends on platform limits |
| Maintenance | Requires specialized knowledge and effort | Platform manages updates and bug fixes |
Introduction to Traditional Coding and Low-Code
Traditional coding involves writing detailed, manual code using programming languages like Java, Python, or C++, requiring extensive developer expertise and time investment. Low-code platforms utilize visual interfaces and pre-built components to accelerate application development, enabling users with minimal coding skills to create functional software rapidly. These platforms significantly reduce development cycles while maintaining sufficient customization for many business applications.
Key Differences Between Traditional Coding and Low-Code
Traditional coding requires extensive programming knowledge and involves writing complex code manually, which offers complete control but demands significant time and resources. Low-code platforms provide visual development tools and pre-built components that accelerate application deployment with minimal hand-coding, enabling faster innovation and easier collaboration between technical and non-technical users. The key differences lie in development speed, required expertise, and flexibility, with traditional coding suited for highly customized solutions and low-code optimized for rapid prototyping and standard workflows.
Benefits of Traditional Coding
Traditional coding offers unparalleled flexibility and control, enabling developers to create highly customized and complex applications tailored to specific business needs. It supports integration with a wide range of platforms, languages, and frameworks, ensuring scalability and optimization for performance-intensive tasks. Developers can leverage full access to source code, facilitating advanced debugging, security enhancements, and continuous improvement of software systems.
Advantages of Low-Code Development
Low-code development accelerates application delivery by using visual interfaces and pre-built components, reducing the need for extensive hand-coding. This approach enhances collaboration between business users and developers, facilitating faster iteration and innovation. It also minimizes development costs and lowers the barrier to entry by enabling non-technical users to contribute to software creation.
Limitations of Traditional Coding
Traditional coding often faces limitations such as increased development time, higher costs, and the need for specialized programming skills, which can slow down project delivery. It also presents challenges in scalability and maintenance, requiring continuous manual updates and debugging efforts. These constraints hinder rapid innovation and agility in software development compared to low-code platforms.
Challenges Faced in Low-Code Platforms
Low-code platforms often face challenges such as limited customization options, which restrict developers from implementing complex, highly specific features. Integration with legacy systems can be problematic, leading to compatibility issues and increased maintenance efforts. Furthermore, governance and security concerns arise due to the abstraction of code, making it harder to enforce stringent controls and audit trails.
Use Cases: When to Choose Traditional Coding
Traditional coding is ideal for complex, customized software solutions requiring full control over functionality and performance, such as enterprise-level applications, embedded systems, and security-critical software. It provides greater flexibility for integrating unique algorithms, handling large-scale data processing, and optimizing resource-intensive operations. Enterprises with dedicated development teams often prefer traditional coding to meet specific business requirements that low-code platforms cannot fully support.
Use Cases: When to Opt for Low-Code Solutions
Low-code solutions excel in rapid application development for business process automation, customer portals, and internal tools where quick deployment and iterative changes are crucial. Enterprises prioritize low-code platforms to empower citizen developers and reduce IT backlogs for routine or standardized applications. Complex, highly customized software with stringent security requirements typically remains better suited for traditional coding approaches.
Cost and Time Comparison
Traditional coding typically involves higher development costs due to the need for specialized programmers and longer project timelines, often extending several months or even years. Low-code platforms significantly reduce both expenses and time by enabling faster deployment through visual interfaces and pre-built components, cutting development cycles by up to 70%. Enterprises adopting low-code solutions report average cost savings of 40-50% and accelerated time-to-market, enhancing overall business agility.
Future Trends in Application Development
Future trends in application development indicate a growing integration of low-code platforms with traditional coding to enhance agility and accelerate deployment. Enterprises increasingly leverage low-code solutions to empower citizen developers while maintaining complex backend processes through traditional coding. This hybrid approach optimizes efficiency, scalability, and innovation in evolving digital landscapes.
Traditional coding Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com