Refresh Token Grant enables secure and seamless user authentication by allowing your application to request a new access token without requiring the user to re-enter credentials. This mechanism enhances user experience by maintaining continuous access while adhering to OAuth 2.0 security standards. Discover how Refresh Token Grant works and why it's essential for your application's authentication flow in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
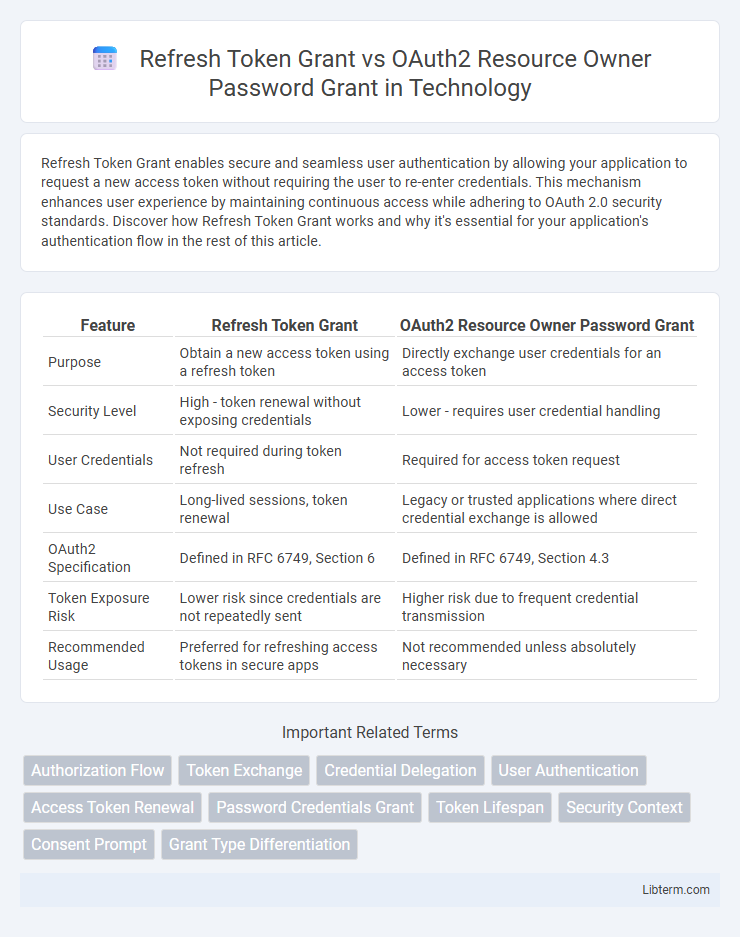
| Feature | Refresh Token Grant | OAuth2 Resource Owner Password Grant |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Obtain a new access token using a refresh token | Directly exchange user credentials for an access token |
| Security Level | High - token renewal without exposing credentials | Lower - requires user credential handling |
| User Credentials | Not required during token refresh | Required for access token request |
| Use Case | Long-lived sessions, token renewal | Legacy or trusted applications where direct credential exchange is allowed |
| OAuth2 Specification | Defined in RFC 6749, Section 6 | Defined in RFC 6749, Section 4.3 |
| Token Exposure Risk | Lower risk since credentials are not repeatedly sent | Higher risk due to frequent credential transmission |
| Recommended Usage | Preferred for refreshing access tokens in secure apps | Not recommended unless absolutely necessary |
Introduction to OAuth2 Grant Types
OAuth2 grant types define different methods for a client to obtain an access token, with the Refresh Token Grant enabling clients to request new tokens without re-authenticating, thereby improving user experience and security. The Resource Owner Password Credentials Grant involves exchanging a user's username and password directly for an access token, which can pose higher security risks and is typically recommended only for highly trusted applications. Understanding these grant types is essential for implementing OAuth2 authorization flows that balance convenience, security, and user experience.
What is a Refresh Token Grant?
Refresh Token Grant is an OAuth2 mechanism that allows clients to obtain a new access token by exchanging a refresh token without requiring the resource owner's credentials again. This grant type enhances security and user experience by enabling long-lived sessions while minimizing exposure of sensitive credentials. Unlike the Resource Owner Password Grant, which directly uses user credentials, Refresh Token Grant relies on previously issued tokens, reducing the risk of credential theft.
What is the Resource Owner Password Grant?
The Resource Owner Password Grant in OAuth2 allows a user to provide their username and password directly to a client application, which then exchanges these credentials for an access token. This grant type is typically used when the client is highly trusted, such as official applications, because it exposes user credentials to the client. Compared to the Refresh Token Grant that refreshes access tokens without user credentials, the Resource Owner Password Grant poses higher security risks and is discouraged in favor of more secure flows like Authorization Code Grant.
Core Differences between Refresh Token and Password Grant
The Refresh Token Grant in OAuth2 allows clients to obtain a new access token using a refresh token without requiring user credentials again, enhancing security and user experience by minimizing password exposure. In contrast, the Resource Owner Password Grant directly exchanges the user's username and password for an access token, which can increase risk by exposing credentials to the client application. Core differences include the refresh token's role in token renewal and improved security versus the Password Grant's straightforward credential use and potential vulnerability.
Security Implications of Each Grant Type
Refresh Token Grant enhances security by minimizing the exposure of user credentials, allowing clients to obtain new access tokens without repeatedly requesting user credentials, thereby reducing attack surfaces. OAuth2 Resource Owner Password Grant requires users to provide their credentials directly to the client, increasing risks of credential leakage and trust issues, especially in untrusted or third-party applications. The use of Refresh Token Grant aligns better with modern security best practices by supporting token revocation and expiration mechanisms, limiting long-term token misuse compared to the Resource Owner Password Grant.
When to Use Refresh Token Grant
The Refresh Token Grant is ideal when maintaining long-lived user sessions without requiring repeated authentication, typically in mobile or web applications where user experience depends on seamless access token renewal. It enhances security by limiting exposure of user credentials, unlike the OAuth2 Resource Owner Password Grant, which should only be used in highly trusted applications due to its direct handling of user credentials. Choose Refresh Token Grant when needing to preserve session continuity while minimizing security risks associated with credential handling.
When to Use Resource Owner Password Grant
Resource Owner Password Grant is suitable when the application is highly trusted, such as first-party apps, and requires direct access to user credentials to authenticate securely. It should be used in scenarios with limited user interface capabilities and where collecting credentials is necessary for legacy or internal systems. Refresh Token Grant is preferred for maintaining long-term access without re-prompting users for credentials, enhancing security and user experience in most OAuth2 implementations.
Use Cases and Real-World Applications
Refresh Token Grant is primarily used to maintain user sessions without repeatedly prompting for credentials, making it ideal for applications requiring long-term access like mobile apps and web services. OAuth2 Resource Owner Password Grant suits trusted applications needing direct access to user credentials, often found in legacy systems or internal enterprise apps where security risks are minimized. Real-world applications favor Refresh Token Grant for improving user experience and security by enabling seamless token renewal, while Resource Owner Password Grant is less common due to higher exposure of user credentials.
Best Practices for Secure Implementation
Refresh Token Grant enhances security by allowing clients to obtain new access tokens without exposing user credentials, minimizing the risk of credential leakage, and supporting token revocation and rotation to limit token lifespan. OAuth2 Resource Owner Password Grant requires direct handling of user credentials, increasing exposure risk, and should be avoided in favor of more secure flows unless absolutely necessary with stringent controls like secure storage and transmission. Best practices emphasize leveraging Refresh Token Grant for long-lived sessions, enforcing HTTPS, implementing strict token scopes and expiration, and using mechanisms such as Proof Key for Code Exchange (PKCE) to prevent token interception and replay attacks.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Grant for Your Needs
Refresh Token Grant provides enhanced security by allowing long-term access without exposing user credentials, ideal for maintaining sessions in modern applications. OAuth2 Resource Owner Password Grant, while simpler, requires direct handling of user credentials, making it less secure and suitable mainly for trusted applications or legacy systems. Selecting the proper grant depends on the application's security requirements, user experience priorities, and the trust level between client and resource owner.
Refresh Token Grant Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com