Protocol Buffer and MessagePack are efficient serialization formats designed for fast data exchange and compact storage. These technologies minimize data size and improve transmission speed, making them ideal for network communication and cross-platform applications. Discover how implementing Protocol Buffer and MessagePack can enhance your data handling by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
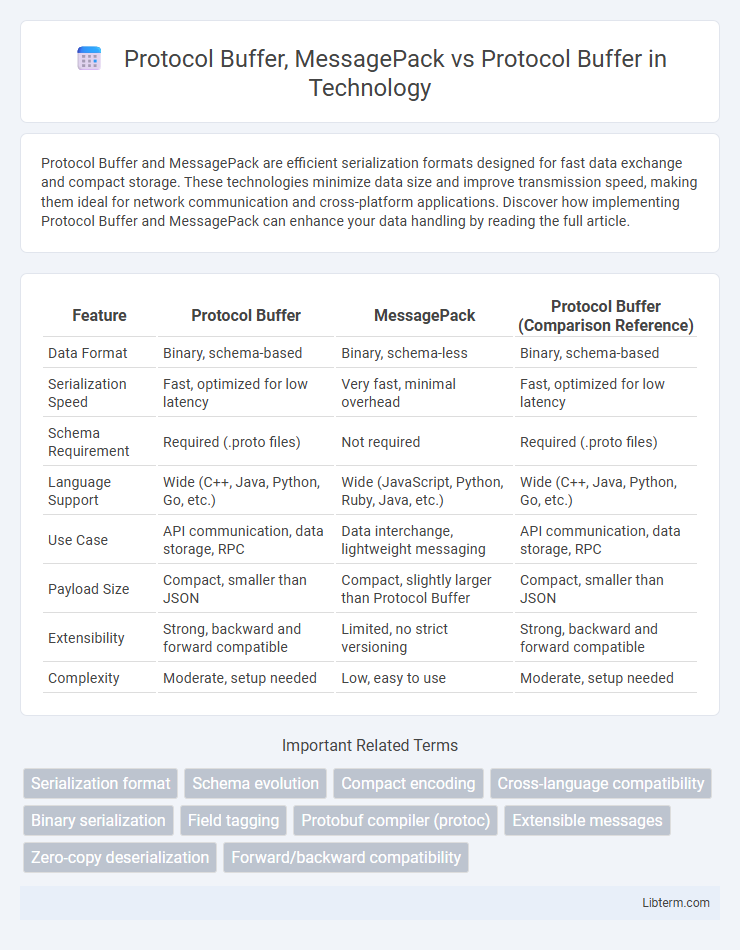
| Feature | Protocol Buffer | MessagePack | Protocol Buffer (Comparison Reference) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Format | Binary, schema-based | Binary, schema-less | Binary, schema-based |
| Serialization Speed | Fast, optimized for low latency | Very fast, minimal overhead | Fast, optimized for low latency |
| Schema Requirement | Required (.proto files) | Not required | Required (.proto files) |
| Language Support | Wide (C++, Java, Python, Go, etc.) | Wide (JavaScript, Python, Ruby, Java, etc.) | Wide (C++, Java, Python, Go, etc.) |
| Use Case | API communication, data storage, RPC | Data interchange, lightweight messaging | API communication, data storage, RPC |
| Payload Size | Compact, smaller than JSON | Compact, slightly larger than Protocol Buffer | Compact, smaller than JSON |
| Extensibility | Strong, backward and forward compatible | Limited, no strict versioning | Strong, backward and forward compatible |
| Complexity | Moderate, setup needed | Low, easy to use | Moderate, setup needed |
Introduction to Data Serialization
Protocol Buffer and MessagePack are efficient data serialization formats designed for compact data encoding and fast processing. Protocol Buffer, developed by Google, uses a schema-based approach with strong typing, enabling backward compatibility and optimized parsing. MessagePack offers a schema-less, binary JSON-like format that prioritizes simplicity and cross-language support for transmitting structured data.
What is Protocol Buffer?
Protocol Buffer is a language-neutral, platform-neutral serialization format developed by Google for efficient data interchange. It uses a compact binary format that is faster and smaller than traditional text-based formats like JSON or XML. Compared to MessagePack, Protocol Buffer offers a more strictly defined schema, enabling better backward and forward compatibility in data serialization.
Key Features of Protocol Buffer
Protocol Buffer offers efficient serialization with compact binary format and excellent schema definition support, enabling backward and forward compatibility across different versions. Its key features include automatic code generation for multiple languages, fast parsing performance, and strong data validation through well-defined message structures. Compared to MessagePack, Protocol Buffer emphasizes strict schema enforcement and extensive tool support, making it ideal for large-scale, cross-platform communication systems.
Overview of MessagePack
MessagePack is a binary serialization format designed for efficient data exchange, offering compact encoding similar to Protocol Buffer but without requiring a predefined schema. It supports a wide range of data types including integers, strings, arrays, and maps, enabling flexibility for dynamic data structures. Unlike Protocol Buffer's strict schema enforcement, MessagePack facilitates rapid serialization and deserialization with minimal overhead, making it ideal for applications needing fast and lightweight communication.
Key Features of MessagePack
MessagePack is a binary serialization format designed for efficient data exchange, known for its compact size and high performance in encoding and decoding. Unlike Protocol Buffer, MessagePack does not require a predefined schema, allowing it to serialize dynamic or evolving data structures with greater flexibility. Its key features include support for multiple programming languages, seamless integration with JSON-compatible data, and fast serialization speeds, making it ideal for lightweight messaging and real-time applications.
Protocol Buffer vs MessagePack: Performance Comparison
Protocol Buffer and MessagePack are both efficient serialization formats designed for performance and compact data representation. Protocol Buffer generally offers faster serialization and deserialization speeds due to its compiled schema and optimized binary format, while MessagePack provides slightly smaller payload sizes by allowing schema-less serialization, which can add overhead during parsing. Benchmarks indicate Protocol Buffer excels in environments requiring high throughput and strict schema validation, whereas MessagePack is preferred when dynamic data structures and minimal size are critical.
Data Format and Compatibility Differences
Protocol Buffer employs a compact, binary data serialization format designed for efficient cross-platform communication, supporting schema evolution through backward and forward compatibility. MessagePack also uses a binary format but emphasizes simplicity and minimal overhead, allowing seamless data exchange without requiring a predefined schema. Protocol Buffer's strict schema enforcement enables more robust data validation and versioning, while MessagePack offers greater flexibility and ease of integration with dynamic data structures.
Platform and Language Support
Protocol Buffer offers extensive platform and language support, including C++, Java, Python, Go, and many others, making it highly versatile for cross-platform development. MessagePack also supports numerous languages such as JavaScript, Ruby, and C#, with efficient serialization but slightly fewer official libraries compared to Protocol Buffer. Both formats excel in multi-language environments, but Protocol Buffer's broader ecosystem ensures deeper integration across diverse platforms and frameworks.
Use Cases: When to Choose Protocol Buffer or MessagePack
Protocol Buffer excels in scenarios requiring strict schema enforcement, efficient serialization for complex data structures, and strong backward compatibility, making it ideal for large-scale distributed systems and microservices communication. MessagePack is preferred for lightweight, schema-less serialization tasks, providing faster performance for simple, dynamic data exchange such as real-time messaging and mobile applications. Choosing between Protocol Buffer and MessagePack depends on the need for schema validation, performance constraints, and the complexity of data being serialized.
Conclusion and Recommendation
Protocol Buffer offers efficient binary serialization with strong schema enforcement, ideal for complex data structures and long-term API compatibility. MessagePack provides fast serialization with minimal overhead, suitable for lightweight applications requiring flexible schema. Choose Protocol Buffer for strict data validation and structured environments; opt for MessagePack when prioritizing speed and simplicity in dynamic data scenarios.
Protocol Buffer, MessagePack Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com