A gateway serves as a crucial connection point between different networks, enabling seamless communication and data transfer. It plays a vital role in managing traffic, security, and compatibility across diverse protocols and systems. Explore the rest of this article to understand how a gateway can enhance your network infrastructure.
Table of Comparison
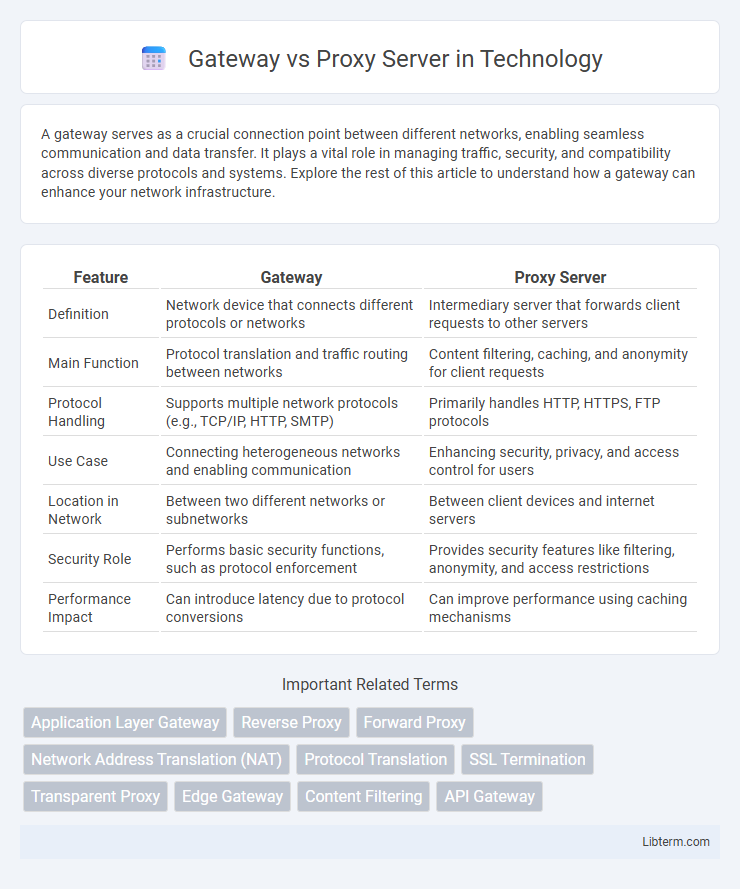
| Feature | Gateway | Proxy Server |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Network device that connects different protocols or networks | Intermediary server that forwards client requests to other servers |
| Main Function | Protocol translation and traffic routing between networks | Content filtering, caching, and anonymity for client requests |
| Protocol Handling | Supports multiple network protocols (e.g., TCP/IP, HTTP, SMTP) | Primarily handles HTTP, HTTPS, FTP protocols |
| Use Case | Connecting heterogeneous networks and enabling communication | Enhancing security, privacy, and access control for users |
| Location in Network | Between two different networks or subnetworks | Between client devices and internet servers |
| Security Role | Performs basic security functions, such as protocol enforcement | Provides security features like filtering, anonymity, and access restrictions |
| Performance Impact | Can introduce latency due to protocol conversions | Can improve performance using caching mechanisms |
Introduction to Gateway and Proxy Server
A gateway acts as an entry point connecting different networks and translating communication protocols to enable data exchange. A proxy server functions as an intermediary for client requests, masking IP addresses and enhancing security by filtering traffic and caching responses. Both serve crucial roles in network management, with gateways focusing on protocol translation and proxies on client-server interaction control.
What is a Gateway?
A gateway is a network point that acts as an entry or exit between different networks, facilitating communication by translating protocols and data formats. It operates at various layers of the OSI model, often handling tasks like routing, protocol conversion, and security enforcement for data traffic crossing network boundaries. Gateways are essential in connecting heterogeneous networks, enabling seamless interoperability and efficient data exchange.
What is a Proxy Server?
A proxy server acts as an intermediary that forwards client requests to other servers, masking the original IP address to enhance privacy and security. It helps control internet usage, filter content, and cache data to improve performance and reduce bandwidth. Businesses often use proxy servers to monitor employee activity and protect internal networks from external threats.
Key Differences Between Gateway and Proxy Server
Gateways operate at multiple layers of the OSI model and perform protocol conversions between different networks, enabling communication across diverse systems. Proxy servers function primarily as intermediaries that filter, cache, and control user requests within the same network protocol, enhancing security and access management. Unlike proxy servers, gateways handle traffic between distinct network architectures, while proxies manage client-server interactions within a homogeneous environment.
Core Functions of Gateway
A gateway serves as a critical network node that connects different networks using distinct protocols, enabling seamless communication and data translation between heterogeneous systems. It performs protocol conversion, data filtering, and routing to ensure interoperability, often managing traffic between internal networks and external environments. Unlike proxy servers, which primarily act as intermediaries for client requests to external resources, gateways facilitate complex protocol mediation and enable comprehensive network integration.
Core Functions of Proxy Server
Proxy servers primarily act as intermediaries between client devices and the internet, managing requests to enhance security, control access, and improve performance. They mask client IP addresses, cache content for faster response times, and filter traffic to block malicious sites or enforce organizational policies. While gateways facilitate protocol translation and connectivity between different networks, proxy servers focus on traffic regulation, privacy, and resource optimization within network segments.
Use Cases: When to Choose a Gateway
Gateways are ideal for connecting disparate networks that use different protocols, enabling seamless communication in complex environments like enterprise integrations and IoT systems. They facilitate protocol translation, security enforcement, and data filtering, making them essential for bridging cloud services with on-premises infrastructure. Organizations should choose gateways when requirements include multi-protocol interoperability, secure data routing, and centralized control across heterogeneous networks.
Use Cases: When to Choose a Proxy Server
Proxy servers are ideal for users seeking to enhance online privacy, bypass geo-restrictions, or cache web content to improve browsing speed. Organizations often deploy proxy servers to control employee internet access, monitor usage, and block malicious sites. In scenarios requiring simple content filtering or anonymous browsing without complex routing, a proxy server offers an efficient and cost-effective solution compared to gateway devices.
Security Implications: Gateway vs Proxy
Gateways provide a robust security layer by inspecting and filtering traffic at the application level, effectively blocking malicious data before it reaches internal networks. Proxies primarily anonymize and control user access, monitoring outbound traffic and preventing unauthorized connections but offer limited protection against diverse threats entering the system. Understanding these distinctions is critical for implementing a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy that leverages gateways for deep threat inspection and proxies for access management and content filtering.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Solution
Choosing between a gateway and a proxy server depends on the specific network requirements and security needs. Gateways excel in protocol translation and connecting different network architectures, while proxy servers primarily enhance privacy, content control, and caching efficiency. Understanding the operational context and desired functionalities ensures selecting the most appropriate solution for optimal network performance and security.
Gateway Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com