Continuous Data Protection (CDP) ensures that every change to your data is saved in real-time, minimizing the risk of data loss and enabling quick recovery from any point in time. This advanced backup solution offers superior protection compared to traditional scheduled backups by maintaining an ongoing, automatic data backup process. Explore the rest of the article to understand how CDP can safeguard your critical data and enhance your disaster recovery strategy.
Table of Comparison
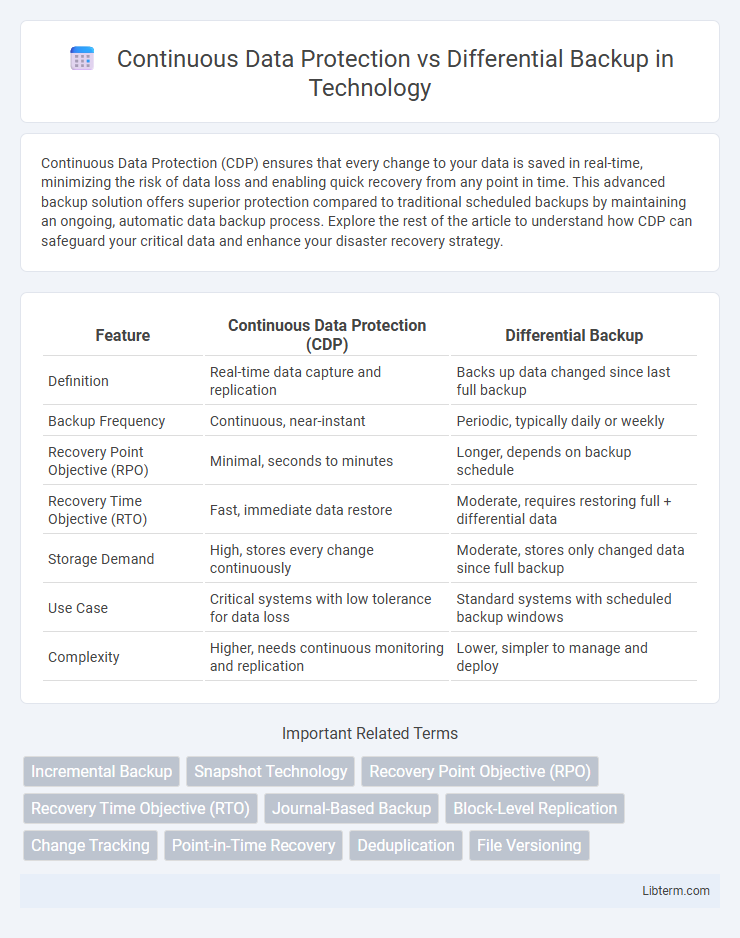
| Feature | Continuous Data Protection (CDP) | Differential Backup |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time data capture and replication | Backs up data changed since last full backup |
| Backup Frequency | Continuous, near-instant | Periodic, typically daily or weekly |
| Recovery Point Objective (RPO) | Minimal, seconds to minutes | Longer, depends on backup schedule |
| Recovery Time Objective (RTO) | Fast, immediate data restore | Moderate, requires restoring full + differential data |
| Storage Demand | High, stores every change continuously | Moderate, stores only changed data since full backup |
| Use Case | Critical systems with low tolerance for data loss | Standard systems with scheduled backup windows |
| Complexity | Higher, needs continuous monitoring and replication | Lower, simpler to manage and deploy |
Understanding Continuous Data Protection
Continuous Data Protection (CDP) continuously captures and saves every change made to data in real time, enabling near-instant recovery points. Unlike differential backup, which only stores data changes since the last full backup at scheduled intervals, CDP ensures minimal data loss and quick restoration by maintaining a comprehensive history of all data modifications. CDP's real-time approach is ideal for environments requiring high data availability and minimal recovery time objectives (RTO).
What is Differential Backup?
Differential backup saves only the data that has changed since the last full backup, reducing storage space and backup time compared to full backups. It creates a cumulative copy of modified files, enabling faster recovery than incremental backups by requiring just the last full backup and the latest differential backup. This method balances efficient data protection with quicker restoration, making it ideal for businesses needing regular but manageable backup routines.
Key Differences Between CDP and Differential Backup
Continuous Data Protection (CDP) captures and saves every change to data in real-time or near real-time, ensuring minimal data loss. Differential Backup records only the changes made since the last full backup, requiring periodic full backups to restore data completely. CDP offers more granular recovery points compared to differential backup's less frequent snapshots, affecting recovery speed and storage demands.
How Continuous Data Protection Works
Continuous Data Protection (CDP) captures and saves data changes in real-time or near-real-time, ensuring every version of the data is stored immediately after any modification occurs. This method uses journal-based logging to record each write operation continuously, allowing for granular recovery points and minimizing the risk of data loss. Unlike differential backups, which periodically save all changes since the last full backup, CDP provides instant recovery to any specific point in time.
How Differential Backup Operates
Differential backup operates by copying all data that has changed since the last full backup, capturing incremental changes without resetting the archive bit, which distinguishes it from incremental backup methods. This approach reduces recovery time compared to incremental backups because only the last full backup and the most recent differential backup are needed for restoration. Continuous Data Protection (CDP), in contrast, captures data changes in real-time or near-real-time, offering more comprehensive data recovery options but requiring more storage and network resources than differential backups.
Recovery Speed: CDP vs Differential Backup
Continuous Data Protection (CDP) offers near-instantaneous recovery speed by continuously capturing and saving every data change, allowing restoration to any specific point in time with minimal data loss. Differential Backup requires restoring the last full backup followed by the most recent differential backup, resulting in slower recovery times compared to CDP due to the additional data processing steps. CDP's granular data capture significantly reduces downtime, making it more efficient for organizations prioritizing rapid recovery.
Storage Requirements and Efficiency
Continuous Data Protection (CDP) stores every data change instantly, requiring substantial storage capacity due to the high frequency of backups, but ensures minimal data loss and rapid recovery. Differential backup saves only changes made since the last full backup, reducing storage needs compared to full backups but potentially increasing storage over time as changes accumulate. CDP offers higher efficiency in recovery point objectives, while differential backup balances storage efficiency with simpler restoration processes.
Impact on System Performance
Continuous Data Protection (CDP) constantly captures data changes in real-time, which can lead to higher resource utilization and potential system slowdowns during peak activity. Differential Backup, performed at scheduled intervals, impacts performance only briefly by copying data modified since the last full backup, resulting in lower sustained resource consumption. Choosing between CDP and differential backup depends on balancing the need for recovery granularity with acceptable system performance overhead.
Use Cases for Continuous Data Protection
Continuous Data Protection (CDP) is ideal for environments requiring near-zero data loss, such as financial institutions, healthcare systems, and e-commerce platforms that handle real-time transactions. It offers real-time backup by capturing changes continuously, ensuring data integrity during unexpected outages or ransomware attacks. Differential backup suits scenarios where periodic recovery points are sufficient, making CDP preferable for mission-critical applications demanding instantaneous data recovery.
When to Choose Differential Backup
Differential backup is ideal for organizations seeking a balance between backup frequency and storage efficiency, especially when data changes daily but immediate recovery is not critical. It captures all changes since the last full backup, enabling quicker restoration than incremental methods while conserving storage compared to continuous data protection (CDP). Businesses with limited bandwidth or those requiring scheduled backups rather than real-time data capture benefit significantly from differential backups.
Continuous Data Protection Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com