Effective data governance ensures your organization's data is accurate, consistent, and secure, driving better decision-making and regulatory compliance. Implementing clear policies and accountability frameworks helps manage data quality, privacy, and accessibility across all departments. Explore the rest of the article to uncover essential strategies for mastering data governance and maximizing your data's potential.
Table of Comparison
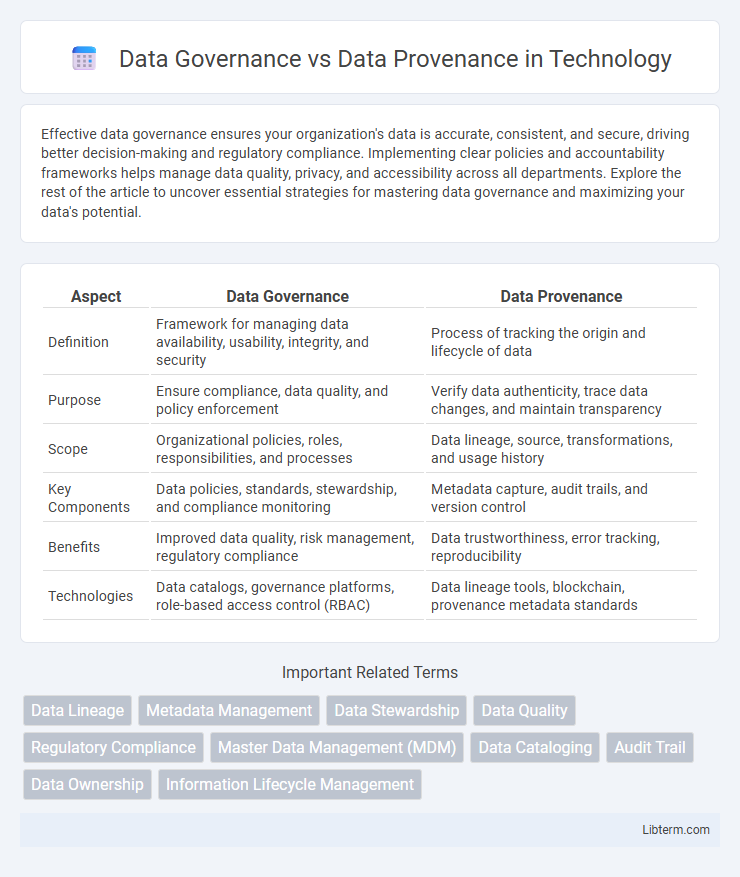
| Aspect | Data Governance | Data Provenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Framework for managing data availability, usability, integrity, and security | Process of tracking the origin and lifecycle of data |
| Purpose | Ensure compliance, data quality, and policy enforcement | Verify data authenticity, trace data changes, and maintain transparency |
| Scope | Organizational policies, roles, responsibilities, and processes | Data lineage, source, transformations, and usage history |
| Key Components | Data policies, standards, stewardship, and compliance monitoring | Metadata capture, audit trails, and version control |
| Benefits | Improved data quality, risk management, regulatory compliance | Data trustworthiness, error tracking, reproducibility |
| Technologies | Data catalogs, governance platforms, role-based access control (RBAC) | Data lineage tools, blockchain, provenance metadata standards |
Introduction to Data Governance and Data Provenance
Data governance establishes the policies, standards, and procedures to ensure data accuracy, security, and compliance throughout its lifecycle within an organization. Data provenance tracks the origin, history, and transformations of data, providing a detailed lineage that supports transparency and trustworthiness. Both concepts are essential for effective data management, with governance focusing on control frameworks and provenance emphasizing traceability.
Defining Data Governance
Data governance establishes the framework of policies, procedures, and standards to ensure the proper management, quality, security, and compliance of organizational data. It involves defining roles, responsibilities, and accountability for data assets to support business objectives and regulatory requirements. Effective data governance enables consistent data usage, risk management, and decision-making across the enterprise.
Understanding Data Provenance
Data provenance refers to the detailed history of data, capturing its origins, transformations, and movement across systems, which enables transparency and trust in data accuracy. Understanding data provenance is crucial for regulatory compliance, auditing, and ensuring data quality by tracing how data was created and modified over time. Unlike broader data governance frameworks that establish policies and roles for managing data, data provenance provides the granular lineage information necessary for accountability and effective decision-making.
Key Differences Between Data Governance and Data Provenance
Data governance encompasses the overall management framework, policies, and procedures ensuring data quality, security, and compliance across an organization, while data provenance specifically tracks the origin, lineage, and transformation history of data sets. Data governance provides accountability and roles for data stewardship, focusing on data access controls and regulatory adherence, whereas data provenance focuses on metadata that details the creation, modification, and movement of data to enhance transparency and traceability. The key difference lies in governance's broad scope for policy enforcement versus provenance's detailed tracking of data's life cycle and source authenticity.
The Role of Data Governance in Modern Organizations
Data governance establishes the framework for managing data quality, security, and compliance across an organization, ensuring reliable and accessible information for decision-making. It defines policies, standards, and responsibilities that enable consistent data handling and accountability. By contrast, data provenance tracks the origin and lifecycle of data, supporting transparency and traceability within the governance structure.
The Importance of Data Provenance for Data Integrity
Data provenance ensures the traceability and origin of data, which is critical for maintaining data integrity in complex data governance frameworks. Accurate provenance records enable organizations to verify data authenticity, detect errors, and prevent tampering throughout the data lifecycle. Robust data provenance supports compliance with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA by providing transparent audit trails essential for trustworthy data management.
Overlapping Areas: Where Governance Meets Provenance
Data governance and data provenance intersect in areas such as data quality, compliance, and traceability, where governance frameworks leverage provenance metadata to ensure data integrity and transparency. Both disciplines emphasize accountability by documenting data origins, transformations, and access patterns to support regulatory requirements and data stewardship. Integration of data provenance within governance processes enhances auditability and decision-making in enterprise data management ecosystems.
Challenges in Implementing Data Governance and Provenance
Implementing data governance faces challenges such as establishing clear data ownership, ensuring regulatory compliance, and managing data quality across disparate systems. Data provenance implementation struggles with capturing detailed audit trails, maintaining data lineage accuracy, and integrating provenance metadata within complex data pipelines. Both require robust policies and advanced technologies to address scalability, security concerns, and cross-departmental coordination effectively.
Best Practices for Integrating Governance and Provenance
Implementing best practices for integrating data governance and data provenance involves establishing clear policies that define data ownership, access controls, and accountability to ensure data integrity and compliance. Leveraging metadata management tools to capture detailed provenance information enhances traceability, enabling organizations to monitor data lineage from origin to consumption effectively. Employing automation and real-time monitoring facilitates continuous auditing and risk mitigation, aligning governance frameworks with provenance tracking for comprehensive data management.
Future Trends in Data Governance and Data Provenance
Future trends in Data Governance emphasize automated policy enforcement, AI-driven data quality monitoring, and enhanced regulatory compliance through blockchain integration. Data Provenance advancements focus on immutable audit trails, improved transparency via decentralized ledger technologies, and scalable metadata management to ensure data integrity across complex ecosystems. Both domains increasingly converge on leveraging machine learning and cryptographic techniques to enhance trust, security, and accountability in enterprise data management.
Data Governance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com