Relational databases organize data into structured tables consisting of rows and columns, making information easy to access and manage efficiently. They use SQL (Structured Query Language) to perform queries, updates, and management tasks, ensuring data integrity and supporting complex relationships between datasets. Explore the rest of the article to understand how relational databases can optimize your data handling and improve business decision-making.
Table of Comparison
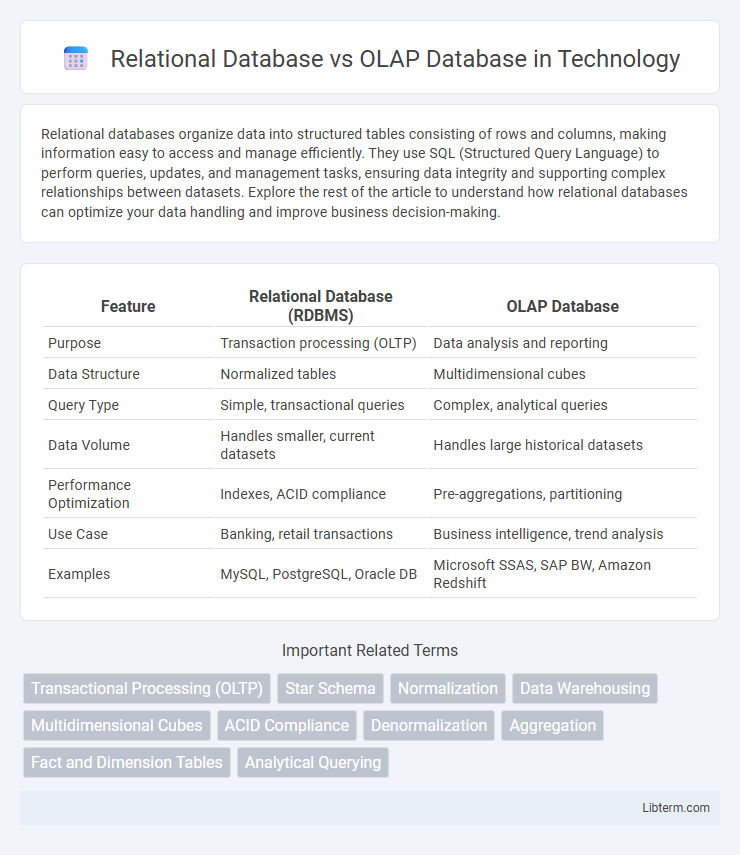
| Feature | Relational Database (RDBMS) | OLAP Database |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Transaction processing (OLTP) | Data analysis and reporting |
| Data Structure | Normalized tables | Multidimensional cubes |
| Query Type | Simple, transactional queries | Complex, analytical queries |
| Data Volume | Handles smaller, current datasets | Handles large historical datasets |
| Performance Optimization | Indexes, ACID compliance | Pre-aggregations, partitioning |
| Use Case | Banking, retail transactions | Business intelligence, trend analysis |
| Examples | MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle DB | Microsoft SSAS, SAP BW, Amazon Redshift |
Introduction to Relational and OLAP Databases
Relational databases organize data into structured tables with rows and columns, supporting transactional processing through SQL queries for efficient data management and integrity. OLAP databases, designed for analytical processing, enable complex multi-dimensional queries that facilitate fast aggregation and trend analysis over large data volumes. Understanding the differences in architecture and use cases helps optimize data storage and retrieval strategies for operational versus analytical needs.
Core Concepts: What is a Relational Database?
A relational database organizes data into tables with rows and columns, using structured query language (SQL) for data management, ensuring data integrity through relationships between tables via primary and foreign keys. It supports transaction processing with ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) properties, making it ideal for day-to-day operations requiring consistent and reliable data handling. In contrast, OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) databases focus on multidimensional data analysis and complex queries for business intelligence rather than transactional efficiency.
Core Concepts: What is an OLAP Database?
An OLAP database is designed specifically for Online Analytical Processing, enabling complex queries and multi-dimensional analysis of large volumes of data. Unlike relational databases that focus on transaction processing (OLTP) and row-based storage, OLAP databases use multi-dimensional data models, such as cubes, to facilitate fast aggregation and slicing of data across different dimensions. This structure supports business intelligence activities like trend analysis, forecasting, and decision-making by optimizing read-heavy workloads and complex computations.
Data Structure Differences: Tables vs. Multidimensional Cubes
Relational databases organize data into two-dimensional tables with rows and columns, optimizing for transactional processing and ensuring data normalization. OLAP databases utilize multidimensional cubes designed to facilitate complex analytical queries by structuring data across multiple dimensions such as time, geography, and products. This multidimensional approach enables fast aggregation, slicing, and dicing of data, supporting advanced business intelligence and decision-making processes.
Performance and Query Optimization
Relational databases excel in transaction processing with optimized indexing and normalization techniques that ensure fast query response times for routine CRUD operations. OLAP databases prioritize complex analytical queries by employing techniques such as columnar storage, aggregation, and precomputed data cubes to enhance performance on large datasets. Query optimization in OLAP environments leverages advanced caching and parallel processing to deliver rapid insights across multidimensional data structures.
Data Modeling Approaches
Relational databases utilize a normalized data modeling approach, organizing data into tables with relationships to minimize redundancy and ensure data integrity, ideal for transactional processing. OLAP databases employ multidimensional data modeling, often using star or snowflake schemas to optimize complex queries and rapid aggregation across multiple dimensions. These approaches serve different purposes: relational models support operational efficiency, while OLAP models enhance analytical performance and decision support.
Use Cases and Application Scenarios
Relational databases excel in transactional applications such as customer relationship management (CRM) systems, e-commerce platforms, and inventory management where data integrity and real-time updates are critical. OLAP databases are optimized for complex analytical queries, supporting business intelligence tasks like sales forecasting, market trend analysis, and financial reporting through multidimensional data models. Use cases for OLAP emphasize data aggregation and rapid query performance over large datasets while relational databases prioritize normalized schemas and consistency for day-to-day operations.
Scalability and Data Volume Handling
Relational databases excel in managing transactional workloads with structured data but face scalability limitations when handling massive data volumes, often requiring vertical scaling or sharding techniques. OLAP databases are designed for high scalability and efficient processing of large, complex analytical queries across vast multidimensional datasets, leveraging distributed architectures and columnar storage. Their ability to handle petabyte-scale data volumes makes OLAP systems optimal for big data analytics and real-time business intelligence.
Security and Data Integrity
Relational databases enforce robust security mechanisms such as role-based access control, encryption at rest and in transit, and rigorous authentication protocols to protect sensitive data, ensuring strong data integrity through ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) compliance. OLAP databases prioritize data integrity by maintaining multidimensional data consistency and support advanced security features tailored for complex query environments, including granular access controls and audit trails to monitor data usage. Both systems implement comprehensive backup and recovery processes, but relational databases excel in transactional data accuracy, while OLAP systems focus on secure analytical data integrity for business intelligence.
Choosing the Right Database for Your Needs
Relational databases excel in managing transactional data with ACID compliance, making them ideal for day-to-day operations requiring consistency and integrity. OLAP databases specialize in multidimensional analysis and complex queries on large datasets, optimizing decision support and business intelligence tasks. Choosing the right database depends on whether your primary need is transaction processing or advanced data analysis and reporting.
Relational Database Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com