Certification validates your skills and expertise, enhancing your professional credibility and career opportunities. Earning recognized certifications demonstrates commitment to quality and continuous learning in your field. Explore the full article to discover how certification can benefit your career growth and industry standing.
Table of Comparison
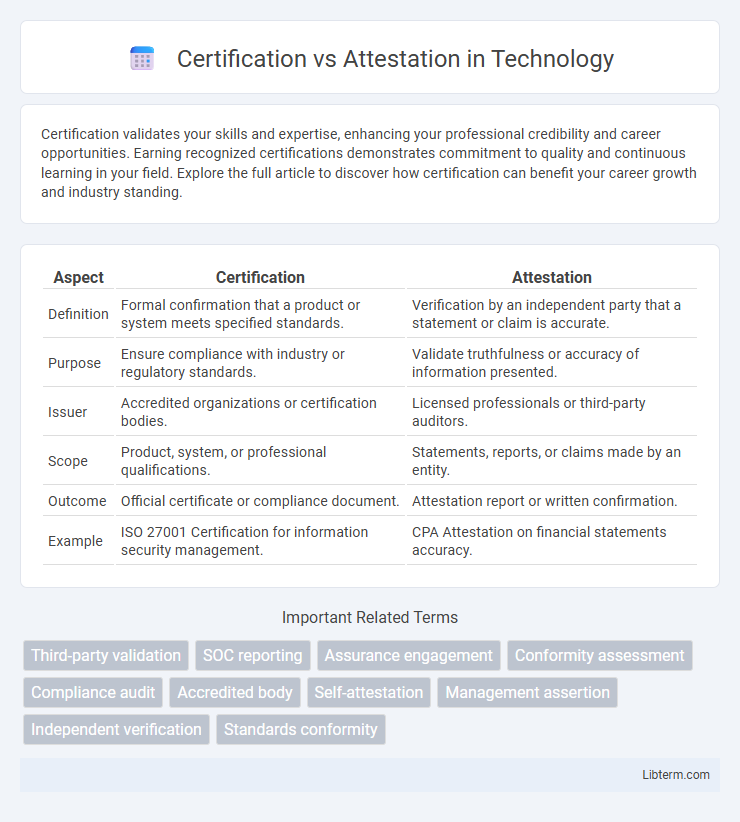
| Aspect | Certification | Attestation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal confirmation that a product or system meets specified standards. | Verification by an independent party that a statement or claim is accurate. |
| Purpose | Ensure compliance with industry or regulatory standards. | Validate truthfulness or accuracy of information presented. |
| Issuer | Accredited organizations or certification bodies. | Licensed professionals or third-party auditors. |
| Scope | Product, system, or professional qualifications. | Statements, reports, or claims made by an entity. |
| Outcome | Official certificate or compliance document. | Attestation report or written confirmation. |
| Example | ISO 27001 Certification for information security management. | CPA Attestation on financial statements accuracy. |
Understanding Certification and Attestation
Certification verifies that a product, service, or system meets specific standards through a formal process conducted by an accredited body, ensuring compliance and quality assurance. Attestation involves a professional providing a written statement or report confirming the accuracy, validity, or truthfulness of information, typically based on an evaluation or audit. Understanding the distinction highlights certification as a conformity assessment, while attestation centers on validation or affirmation of factual data.
Key Definitions: Certification vs Attestation
Certification is a formal process where an authorized body verifies that a product, service, or system meets specified standards or criteria, often resulting in a certificate. Attestation involves providing a written statement or declaration confirming the truth or authenticity of certain information, typically based on evidence or examination. Certification emphasizes compliance with established standards, while attestation focuses on validating specific claims or data.
Legal Frameworks and Standards
Certification involves a formal process where an authorized body verifies that a product, service, or system meets specific legal standards and regulatory requirements, such as ISO 9001 or GDPR compliance. Attestation refers to the issuance of a statement by an independent party confirming that certain facts or conditions are true, often used in financial audits under frameworks like SSAE 18 or SOC reports. Legal frameworks such as the Sarbanes-Oxley Act and international standards guide both practices, ensuring transparency, accountability, and adherence to statutory obligations.
Purposes and Use Cases
Certification verifies compliance with established standards or regulations, often used in quality management, environmental standards, and professional qualifications to ensure credibility and trustworthiness. Attestation provides formal affirmation of the authenticity or accuracy of specific information, such as financial statements, identity verification, or legal documents, primarily for accountability and validation purposes. Businesses rely on certification to demonstrate industry competence, while attestation is crucial for legal compliance and stakeholder assurance.
Process Overview: Certification Steps
Certification involves a systematic process beginning with a thorough assessment of compliance against established standards or criteria by an accredited body. The steps include application submission, documentation review, on-site audits or inspections, followed by evaluation and issuance of the certification if all requirements are met. This process ensures verified adherence to quality, safety, or performance benchmarks specified within the certification framework.
Process Overview: Attestation Steps
The attestation process involves verifying the authenticity of documents through a series of steps including notarization, submission to relevant government authorities, and endorsement by designated officials or agencies. Each step ensures the document's validity for legal or official use, often requiring the original document, proof of identity, and payment of fees. Attestation serves as a critical compliance measure, especially for international document acceptance and legal transactions.
Roles and Responsibilities
Certification involves an authoritative body verifying that a product, service, or system meets specific standards, ensuring compliance and quality assurance through objective evaluation. Attestation requires a professional, often an auditor or a certified public accountant, to provide a formal statement confirming the accuracy or validity of information, typically related to financial statements or compliance reports. Roles in certification emphasize testing and validation, while attestation focuses on independent verification and reporting of factual representations.
Documentation and Evidence Required
Certification requires comprehensive documentation including formal reports, verified data, and compliance records to confirm that standards or specifications have been met. Attestation primarily involves the provision of evidence such as statements, declarations, or summaries that validate the accuracy and reliability of specific information or processes. Both processes demand rigorous evidence, but certification emphasizes exhaustive documentation while attestation focuses on affirmation through documented proof.
Benefits and Limitations of Each Approach
Certification provides formal recognition by an authoritative body, enhancing credibility and trust for individuals or organizations, but it often requires rigorous examinations and ongoing compliance, which can be time-consuming and costly. Attestation offers verification of specific facts or documents, promoting transparency and accuracy without extensive testing, yet it may lack the comprehensive validation found in certification processes. Both approaches improve reliability in different contexts, with certification emphasizing proven competence and attestation focusing on the authenticity of information.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Needs
Certification provides formal validation by an authoritative body confirming compliance with specific standards, ideal for organizations seeking recognized credentials. Attestation involves a professional confirming the accuracy or truthfulness of information, suited for situations requiring verified statements without formal certification. Assess your specific requirements, compliance goals, and stakeholder expectations to choose between certification's rigorous standards or attestation's factual confirmation.
Certification Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com