Data obfuscation protects sensitive information by disguising it through techniques such as masking, encryption, and tokenization, ensuring unauthorized users cannot interpret the data. This approach is crucial for maintaining privacy, complying with regulations, and securing intellectual property in various applications. Discover how implementing data obfuscation can safeguard your information by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
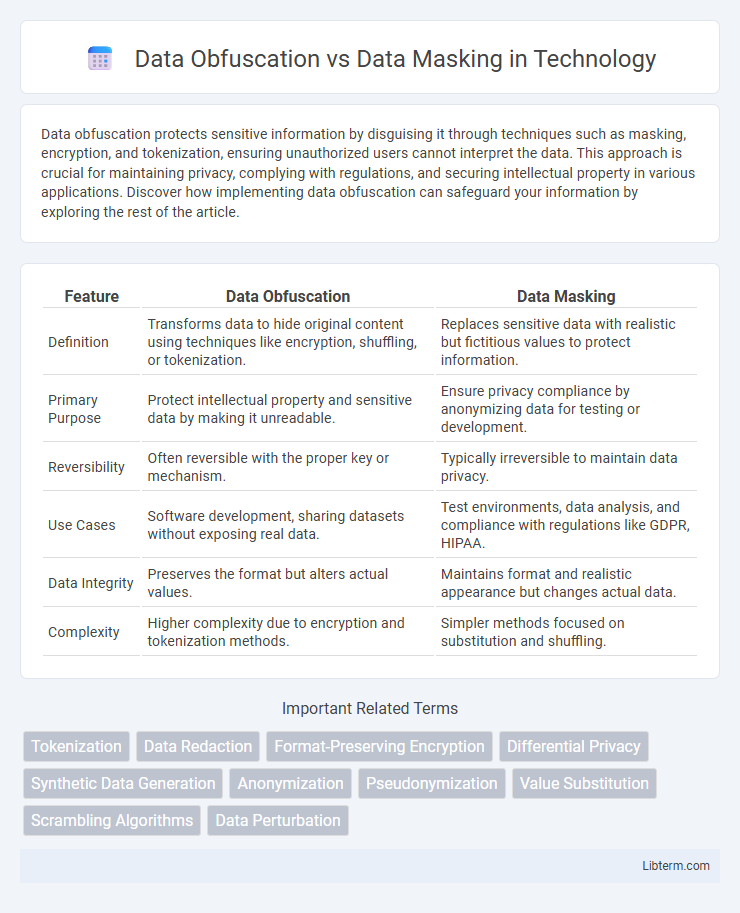
| Feature | Data Obfuscation | Data Masking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transforms data to hide original content using techniques like encryption, shuffling, or tokenization. | Replaces sensitive data with realistic but fictitious values to protect information. |
| Primary Purpose | Protect intellectual property and sensitive data by making it unreadable. | Ensure privacy compliance by anonymizing data for testing or development. |
| Reversibility | Often reversible with the proper key or mechanism. | Typically irreversible to maintain data privacy. |
| Use Cases | Software development, sharing datasets without exposing real data. | Test environments, data analysis, and compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA. |
| Data Integrity | Preserves the format but alters actual values. | Maintains format and realistic appearance but changes actual data. |
| Complexity | Higher complexity due to encryption and tokenization methods. | Simpler methods focused on substitution and shuffling. |
Introduction to Data Obfuscation and Data Masking
Data obfuscation involves transforming sensitive data into a scrambled or encrypted form to prevent unauthorized access while maintaining its usability for testing or analysis. Data masking replaces original data with fictitious but realistic values to protect personal or confidential information during non-production processes. Both methods are essential for data privacy compliance, with obfuscation focusing on encryption techniques and masking emphasizing data substitution.
Key Differences Between Data Obfuscation and Data Masking
Data obfuscation transforms data into a non-readable format to protect sensitive information while maintaining its usability for testing or analysis, whereas data masking replaces sensitive data with realistic but fictitious values to prevent exposure. Obfuscation techniques often involve encryption, tokenization, or shuffling, ensuring data cannot be reverse-engineered, while masking employs substitution or scrambling methods that preserve data type and format for functional use. The key difference lies in obfuscation's focus on making data unintelligible versus masking's goal of protecting data privacy by concealing actual data with deceptive equivalents.
Use Cases for Data Obfuscation
Data obfuscation is primarily used in software development and testing environments to protect sensitive data while maintaining realistic datasets for functional testing. It is ideal for use cases where intellectual property and business logic must be hidden from unauthorized users, such as in development teams working with customer information or proprietary algorithms. By transforming data into a non-reversible format, data obfuscation ensures compliance with data privacy regulations while allowing developers to work with structurally similar but non-sensitive data.
Use Cases for Data Masking
Data masking is primarily used to protect sensitive information in non-production environments such as development, testing, and training, ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. It allows organizations to share realistic but anonymized data sets with third-party vendors and internal teams without exposing actual personal or confidential information. Data obfuscation, while similar, typically applies to source code protection rather than broad data privacy scenarios.
Techniques Used in Data Obfuscation
Data obfuscation employs techniques such as tokenization, substitution, shuffling, and encryption to transform sensitive data into a non-readable or unusable format while preserving its original structure. These methods ensure that data remains functional for testing or analysis without exposing confidential information. Unlike data masking, which typically replaces data with realistic but fictitious values, obfuscation often involves more complex algorithms to protect the integrity and privacy of the data.
Methods Employed in Data Masking
Data masking employs techniques such as substitution, shuffling, number variance, encryption, and nulling to obscure sensitive data while preserving its format and usability for testing or analysis. Substitution replaces real data with realistic but fictitious values, and shuffling rearranges existing data within a dataset to break direct associations. Number variance adjusts numerical values slightly, encryption secures data by encoding it, and nulling replaces sensitive values with nulls to prevent exposure.
Security Benefits of Data Obfuscation
Data obfuscation enhances security by transforming sensitive information into a format that is unintelligible and resistant to unauthorized access, thereby protecting data during development and testing environments. Unlike data masking, which hides data by replacing it with fictitious but realistic values, obfuscation employs complex algorithms to alter data structure, making reverse engineering significantly more difficult. This method safeguards intellectual property and reduces the risk of data breaches by ensuring that even if data is intercepted, it remains unusable to attackers.
Privacy Advantages of Data Masking
Data masking enhances privacy by replacing sensitive information with realistic but fictitious data, ensuring that unauthorized users cannot access the original confidential details while maintaining data utility for testing or analysis. Unlike data obfuscation, which modifies data to hinder interpretation but may still expose patterns, data masking guarantees a higher level of privacy by consistently protecting personally identifiable information (PII) and compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA. This method reduces the risk of data breaches and supports secure data handling across development, testing, and operational environments.
Regulatory Compliance: Obfuscation vs Masking
Data obfuscation and data masking both enhance regulatory compliance by protecting sensitive information but serve different purposes in data security frameworks. Data obfuscation alters data to make it unintelligible while preserving usability for testing or development, aligning with GDPR and HIPAA requirements for minimizing exposure of personally identifiable information (PII). Data masking, often used in production environments, replaces sensitive data with realistic but fictitious values, ensuring compliance with PCI-DSS standards by preventing unauthorized access to credit card information during processing.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Organization
Data obfuscation transforms sensitive information into a scrambled format to prevent unauthorized access, while data masking replaces original data with realistic but fictional values to maintain usability. Selecting the right approach depends on your organization's security requirements, compliance standards, and the intended use of the data--obfuscation suits environments demanding high security with minimal data utility, whereas masking is ideal for testing and development scenarios requiring functional data. Assessing data sensitivity, user access levels, and regulatory obligations will guide the decision between these two critical data protection techniques.
Data Obfuscation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com