OpenID Connect is a secure authentication protocol that enables users to verify their identity across multiple applications using a single set of credentials. It builds on the OAuth 2.0 framework, adding an identity layer to facilitate seamless and trusted user sign-ins. Dive into the rest of the article to understand how OpenID Connect can enhance your digital security and user experience.
Table of Comparison
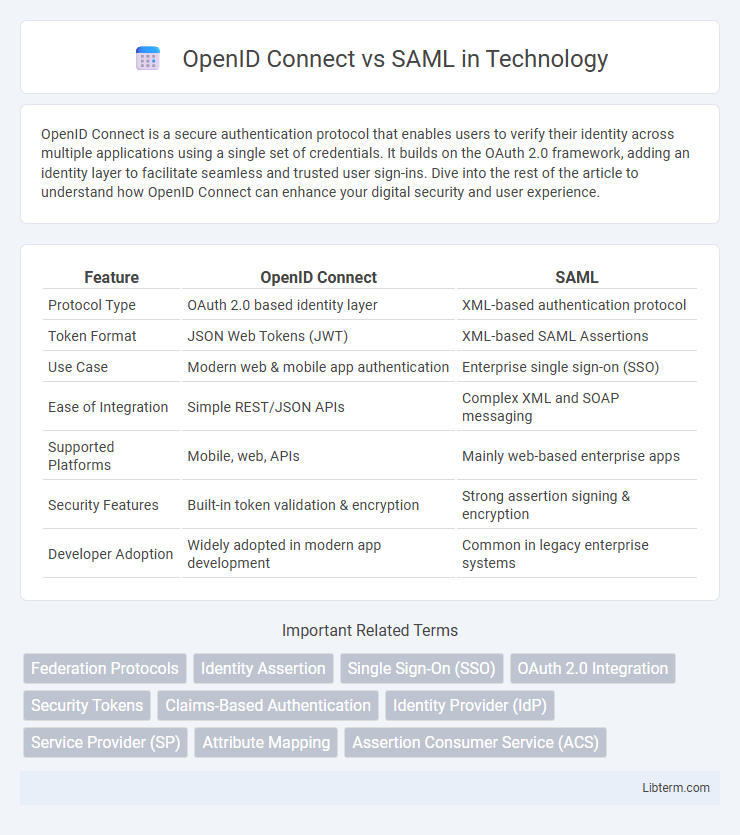
| Feature | OpenID Connect | SAML |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol Type | OAuth 2.0 based identity layer | XML-based authentication protocol |
| Token Format | JSON Web Tokens (JWT) | XML-based SAML Assertions |
| Use Case | Modern web & mobile app authentication | Enterprise single sign-on (SSO) |
| Ease of Integration | Simple REST/JSON APIs | Complex XML and SOAP messaging |
| Supported Platforms | Mobile, web, APIs | Mainly web-based enterprise apps |
| Security Features | Built-in token validation & encryption | Strong assertion signing & encryption |
| Developer Adoption | Widely adopted in modern app development | Common in legacy enterprise systems |
Introduction to OpenID Connect and SAML
OpenID Connect is a modern identity layer built on the OAuth 2.0 protocol, designed for single sign-on (SSO) and identity federation in web and mobile applications, providing lightweight and scalable authentication. Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) is an XML-based framework for exchanging authentication and authorization data between identity providers and service providers, commonly used in enterprise SSO solutions. OpenID Connect uses JSON and RESTful APIs for token exchange, while SAML relies on XML and SOAP, reflecting their design optimization for internet-scale applications versus legacy enterprise environments.
Core Concepts and Terminology
OpenID Connect (OIDC) uses OAuth 2.0 as its underlying protocol and introduces lightweight authentication through ID tokens and userinfo endpoints, enabling seamless single sign-on (SSO) with JSON Web Tokens (JWT). Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) is an XML-based framework that exchanges authentication and authorization data via assertions, relying on a browser redirect flow between identity providers and service providers. While OIDC emphasizes modern web and mobile app compatibility with RESTful APIs, SAML is traditionally used in enterprise SSO with detailed assertion statements and SOAP messages.
Authentication Flow Comparison
OpenID Connect uses JSON Web Tokens (JWT) and RESTful APIs to provide a streamlined authentication flow, enabling single sign-on (SSO) with enhanced scalability and mobile support. SAML relies on XML-based assertions exchanged via browser redirects, making it well-suited for enterprise environments with legacy systems requiring robust security. The OpenID Connect flow offers faster token validation and better compatibility with modern applications, whereas SAML provides a mature, widely adopted framework for federated identity management.
Security Mechanisms and Protocols
OpenID Connect employs OAuth 2.0 underlying protocols, offering streamlined token-based authentication with JSON Web Tokens (JWT) that enhance flexibility and support mobile and web applications. SAML relies on XML-based assertions exchanged via browser redirects, providing robust, enterprise-grade Single Sign-On (SSO) suited for legacy systems with strong cryptographic security through XML Signature and XML Encryption standards. OpenID Connect's use of RESTful APIs facilitates easier integration and dynamic client registration, whereas SAML's security depends heavily on established XML frameworks ensuring message integrity and confidentiality across federated identity domains.
Integration and Implementation Scenarios
OpenID Connect offers ease of integration with modern web and mobile applications using RESTful APIs and JSON, making it suitable for cloud-based services and consumer-facing platforms. SAML, relying on XML-based assertions and SOAP, is preferred in enterprise environments for secure single sign-on (SSO) across legacy systems and federated identity scenarios. Developers choose OpenID Connect for its lightweight protocol and better support for OAuth 2.0 flows, while SAML remains dominant in robust, high-security integrations requiring complex attribute handling.
User Experience Differences
OpenID Connect offers a streamlined user experience through native mobile app support and simpler authentication flows, reducing friction during login. SAML typically requires browser redirects and is better suited for enterprise single sign-on within web applications, potentially causing delays and a less seamless interaction. The JSON-based protocol of OpenID Connect enables faster token exchange compared to the XML-based SAML, enhancing responsiveness in modern user interfaces.
Use Cases: Enterprise vs. Modern Applications
OpenID Connect is widely adopted for modern applications requiring seamless user authentication via mobile apps and single-page applications, offering lightweight, JSON-based protocols ideal for cloud-native environments. SAML remains the preferred choice for enterprise settings with legacy systems, providing robust XML-based assertions for secure, federated identity management across complex, on-premises infrastructures. Enterprises often combine both, leveraging OpenID Connect for external web services and SAML for internal enterprise resource access to optimize security and user experience.
Performance and Scalability
OpenID Connect offers faster token issuance and smaller message sizes compared to SAML, resulting in improved performance for web and mobile applications. Its JSON-based tokens enable more efficient parsing and reduced computational overhead, supporting high-throughput environments. SAML, relying on XML, tends to have larger payloads and increased processing demands, which can impact scalability in large-scale or resource-constrained deployments.
Pros and Cons of OpenID Connect and SAML
OpenID Connect offers modern, lightweight authentication with native support for mobile and web applications, making it ideal for cloud-based services, but it relies heavily on JSON and OAuth 2.0, which may increase complexity for legacy systems. SAML provides robust, enterprise-grade single sign-on (SSO) with XML-based security tokens and wide compatibility with existing identity providers, yet it tends to be heavier and less flexible for newer, API-driven environments. OpenID Connect excels in ease of integration and user experience, while SAML remains preferred for traditional enterprise security and federated identity management.
Choosing the Right Protocol for Your Organization
OpenID Connect offers modern, RESTful authentication using JSON and OAuth 2.0, making it ideal for mobile apps and cloud-based services requiring lightweight and flexible identity verification. SAML provides robust, XML-based single sign-on primarily suited for enterprise environments with legacy systems needing comprehensive security and attribute exchange. Evaluate your organization's infrastructure, application types, and security needs to select OpenID Connect for agility or SAML for extensive federation capabilities.
OpenID Connect Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com