Encryption safeguards your data by converting information into a coded format that unauthorized users cannot access. This technology is essential for protecting sensitive communications, financial transactions, and personal information across digital platforms. Discover how encryption works and why it is crucial for maintaining your online security in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
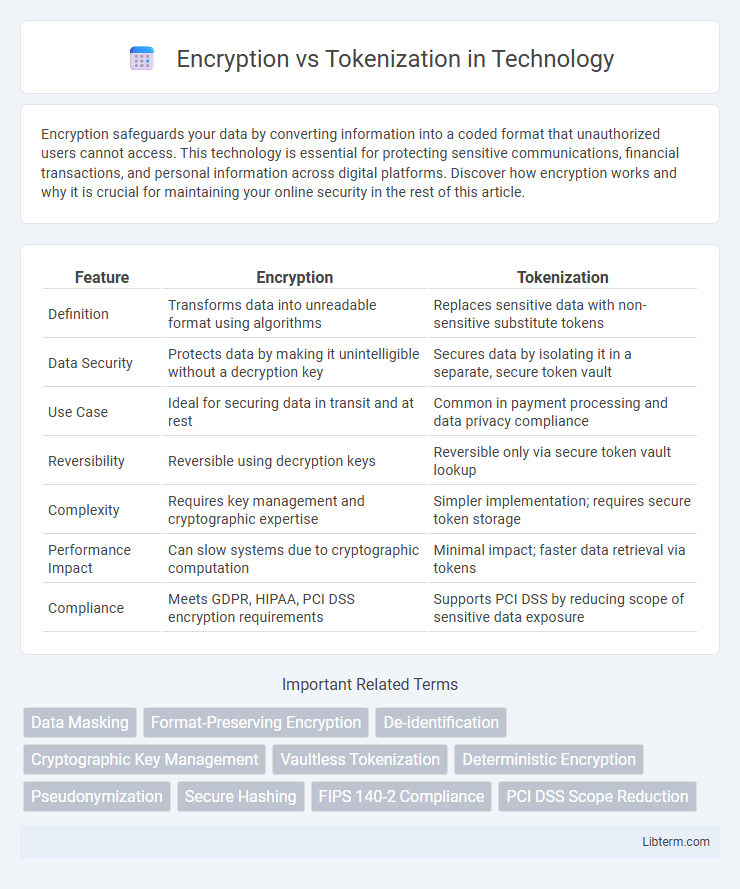
| Feature | Encryption | Tokenization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transforms data into unreadable format using algorithms | Replaces sensitive data with non-sensitive substitute tokens |
| Data Security | Protects data by making it unintelligible without a decryption key | Secures data by isolating it in a separate, secure token vault |
| Use Case | Ideal for securing data in transit and at rest | Common in payment processing and data privacy compliance |
| Reversibility | Reversible using decryption keys | Reversible only via secure token vault lookup |
| Complexity | Requires key management and cryptographic expertise | Simpler implementation; requires secure token storage |
| Performance Impact | Can slow systems due to cryptographic computation | Minimal impact; faster data retrieval via tokens |
| Compliance | Meets GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS encryption requirements | Supports PCI DSS by reducing scope of sensitive data exposure |
Introduction to Encryption vs Tokenization
Encryption converts sensitive data into a coded format using algorithms and keys, ensuring confidentiality by making information unreadable without the decryption key. Tokenization replaces sensitive data with unique, non-sensitive placeholders or tokens, which have no exploitable value outside the system. Both methods enhance data security but serve different purposes: encryption protects data in transit and storage, while tokenization minimizes exposure by substituting data elements within specific environments.
Defining Encryption
Encryption is a process that transforms readable data into a coded format using algorithms and cryptographic keys, ensuring that only authorized parties can access the original information. It plays a critical role in securing sensitive data by converting plaintext into ciphertext, which appears as random characters without the decryption key. Encryption protocols such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and RSA provide robust protection for data in transit and at rest across various digital platforms.
Understanding Tokenization
Tokenization replaces sensitive data with unique identification symbols retaining essential information without compromising security, unlike encryption which encodes data into a cipher. Tokenization minimizes exposure to data breaches by storing tokens instead of actual data, making it ideal for credit card processing and personal information protection. This approach enhances compliance with standards such as PCI DSS by reducing the scope of sensitive data environments.
Key Differences Between Encryption and Tokenization
Encryption transforms data into a coded format using algorithms and encryption keys, ensuring confidentiality by making the data unreadable without the decryption key. Tokenization replaces sensitive data with non-sensitive placeholders called tokens, which have no meaningful value outside the tokenization system, thus reducing risk without altering the original data format. Unlike encryption, tokenization does not require complex key management but relies heavily on secure token vaults to prevent unauthorized data retrieval.
Use Cases for Encryption
Encryption is essential for protecting sensitive data in transit and at rest, commonly used in securing online communications, such as emails and VPN connections. It is widely implemented in financial services to safeguard credit card information and personal identification details during transactions. Healthcare systems rely on encryption to comply with regulations like HIPAA by protecting patients' medical records from unauthorized access.
Use Cases for Tokenization
Tokenization is essential for securing sensitive payment card data, enabling compliance with PCI DSS by replacing card numbers with non-sensitive tokens during transactions. It simplifies data security in healthcare by protecting patient information while allowing authorized access to necessary details. E-commerce platforms rely on tokenization to safeguard customer payment details, reducing the risk of data breaches and fraud in online purchases.
Security Benefits of Encryption
Encryption transforms data into an unreadable format using algorithms and cryptographic keys, ensuring confidentiality during storage and transmission. It provides strong protection against unauthorized access by making encrypted data indecipherable without the proper decryption key. Encryption also supports data integrity and authentication through techniques like hashing and digital signatures, enhancing overall cybersecurity.
Security Benefits of Tokenization
Tokenization enhances security by replacing sensitive data with unique, non-sensitive tokens that have no exploitable value outside the specific system, reducing exposure to data breaches. Unlike encryption, tokenization eliminates the risk of decryption keys being compromised, as tokens are irreversible and unrelated to the original data. This method significantly minimizes the scope of PCI-DSS compliance and mitigates the impact of data theft incidents.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Encryption and tokenization both enhance data security but differ in compliance applications, as encryption protects data through algorithms making it unreadable without keys, often required by regulations like GDPR and HIPAA for securing personal information. Tokenization replaces sensitive data with unique tokens, minimizing the exposure of actual data, which aligns with PCI DSS standards by reducing the scope of regulated data environments. Organizations must assess specific regulatory frameworks and data types to determine whether encryption or tokenization best supports compliance and risk management strategies.
Choosing the Right Data Protection Method
Choosing the right data protection method depends on specific security requirements and compliance standards. Encryption transforms sensitive data into unreadable ciphertext, ensuring confidentiality and enabling secure data transmission or storage. Tokenization replaces sensitive data with non-sensitive tokens, often used to reduce the scope of compliance by minimizing exposure of actual data during processing.
Encryption Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com