Efficient indexing and sorting are crucial for optimizing data retrieval and organization in databases and information systems. Properly implemented sorting algorithms improve search speeds, while indexing structures enhance data accessibility and reduce query time. Explore the rest of the article to understand how these techniques can improve your system's performance.
Table of Comparison
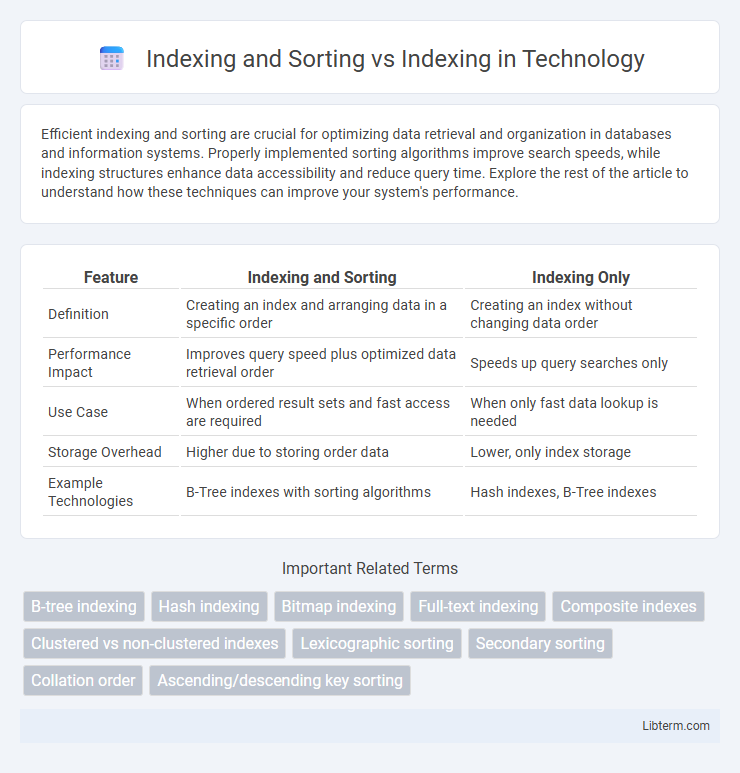
| Feature | Indexing and Sorting | Indexing Only |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Creating an index and arranging data in a specific order | Creating an index without changing data order |
| Performance Impact | Improves query speed plus optimized data retrieval order | Speeds up query searches only |
| Use Case | When ordered result sets and fast access are required | When only fast data lookup is needed |
| Storage Overhead | Higher due to storing order data | Lower, only index storage |
| Example Technologies | B-Tree indexes with sorting algorithms | Hash indexes, B-Tree indexes |
Understanding Indexing: Definition and Purpose
Indexing is a database optimization technique that creates data structures, such as B-trees or hash maps, to accelerate query retrieval by reducing the search space. Sorting organizes data in a specific order, often necessary for effective indexing since certain index types, like B-tree indexes, rely on sorted keys to optimize range queries and improve data access speed. Understanding indexing involves recognizing its primary purpose: to enhance data retrieval efficiency and minimize query execution time by allowing the database engine to quickly locate rows without scanning entire tables.
What is Indexing and Sorting?
Indexing is the process of creating a data structure that improves the speed of data retrieval operations on databases or files by maintaining a sorted list of keys with pointers to the data records. Sorting organizes data elements in a specific order, such as ascending or descending, to optimize search efficiency and enable faster access. While indexing relies on sorted keys to enhance query performance, sorting itself arranges the raw data, making indexed searches more effective.
Key Differences Between Indexing and Sorting
Indexing creates a data structure, such as a B-tree or hash index, to enable fast retrieval of records without scanning the entire dataset, optimizing query performance in databases. Sorting arranges data in a specific order based on keys or values, improving data readability and enabling efficient binary searches but does not reduce search complexity alone. Key differences include that indexing supports quick random lookups and range queries by maintaining pointers to data locations, while sorting only organizes data sequentially without overhead for direct access.
Benefits of Indexing in Databases
Indexing in databases significantly improves query performance by allowing faster data retrieval through optimized structures like B-trees and hash indexes. Unlike sorting, which organizes data temporarily during query execution, indexing maintains a persistent order that reduces disk I/O and minimizes search time. Efficient indexing leads to quicker access to records, enhanced system scalability, and reduced CPU utilization during data operations.
How Sorting Enhances Data Retrieval
Sorting organizes data within indexes to improve search efficiency by enabling faster lookups through ordered structures like B-trees or sorted arrays. Indexing alone creates references to data locations, but when combined with sorting, it significantly reduces the time complexity of queries by allowing binary search techniques. This enhancement leads to quicker data retrieval, optimized query performance, and reduced I/O operations in database management systems.
Indexing and Sorting: Complementary or Conflicting?
Indexing and sorting are complementary processes that enhance data retrieval efficiency by organizing data in a structured manner. Indexing creates a data structure, such as a B-tree or hash index, allowing rapid search operations, while sorting arranges data records in a specific order, improving the performance of range queries and enabling faster sequential access. Combining indexing with sorted data enables optimized query execution plans, reduces I/O operations, and boosts overall database performance.
Use Cases for Indexing Alone
Indexing alone optimizes data retrieval by creating structured pointers to the location of data, significantly enhancing query performance in read-heavy applications such as databases and search engines. Use cases include rapid lookup of records, efficient filtering based on indexed fields, and supporting unique constraints to maintain data integrity. This approach reduces the need for full dataset scans, making it crucial for real-time data access scenarios and large-scale data analytics.
When to Combine Indexing with Sorting
Combining indexing with sorting is essential when query performance demands efficient retrieval of ordered data, such as in range queries or pagination. Indexes alone speed up data lookup, but sorting integrated within the index structure eliminates costly sorting operations during query execution. Utilizing combined indexing and sorting optimizes database access patterns by reducing execution time and improving responsiveness in large-scale applications.
Performance Considerations: Indexing vs Indexing and Sorting
Indexing improves data retrieval speed by creating a structured map of the data, reducing query response time significantly compared to full table scans, while indexing combined with sorting enhances query efficiency when ordered results are frequently requested. Sorting during indexing incurs additional computation overhead, potentially affecting insert and update performance but benefits read-heavy workloads by minimizing runtime sorting operations. Performance trade-offs depend on workload characteristics where indexing alone favors faster writes and indexing with sorting favors optimized read and ordered data retrieval.
Best Practices for Efficient Data Management
Indexing and sorting enhance query performance by organizing data for faster retrieval, with indexing creating a data structure that allows quick lookups and sorting arranging data in a specific order to optimize search operations. Best practices for efficient data management include using appropriate index types like B-tree or hash indexes based on query patterns and maintaining sorted indexes when range queries are frequent, minimizing index overhead by indexing only necessary columns. Regularly monitoring and updating indexes, alongside leveraging composite indexes for multi-column filters, ensures optimal database performance and resource utilization.
Indexing and Sorting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com