An IDE (Integrated Development Environment) combined with a code compiler streamlines the software development process by providing tools for writing, testing, and debugging code all in one place. This setup enhances productivity by allowing you to quickly compile and run your programs without switching between different applications. Discover how choosing the right IDE and compiler can transform your coding experience in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
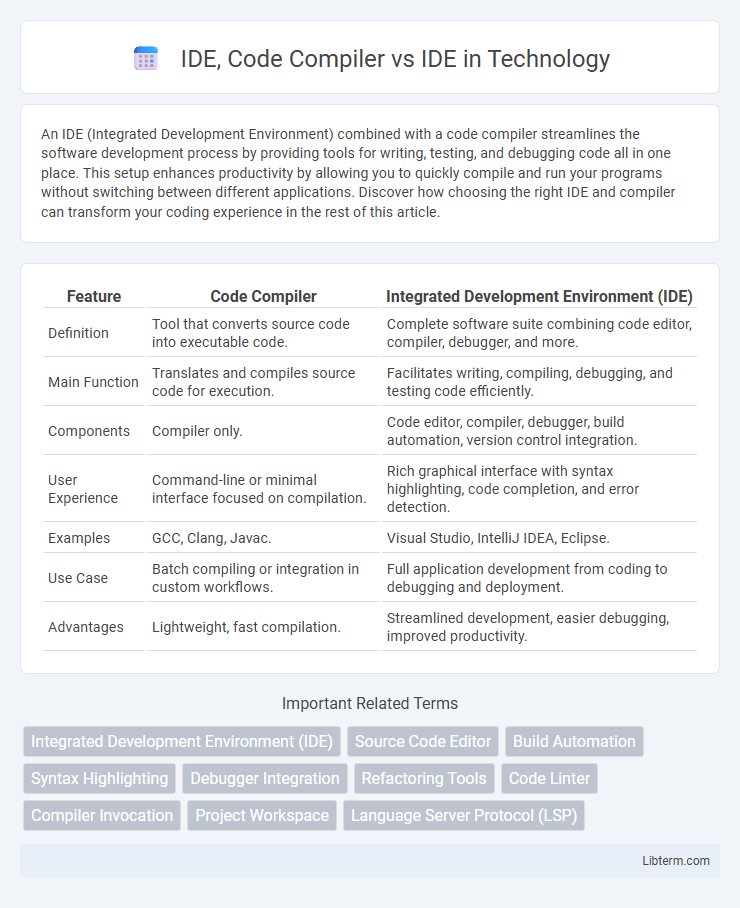
| Feature | Code Compiler | Integrated Development Environment (IDE) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tool that converts source code into executable code. | Complete software suite combining code editor, compiler, debugger, and more. |
| Main Function | Translates and compiles source code for execution. | Facilitates writing, compiling, debugging, and testing code efficiently. |
| Components | Compiler only. | Code editor, compiler, debugger, build automation, version control integration. |
| User Experience | Command-line or minimal interface focused on compilation. | Rich graphical interface with syntax highlighting, code completion, and error detection. |
| Examples | GCC, Clang, Javac. | Visual Studio, IntelliJ IDEA, Eclipse. |
| Use Case | Batch compiling or integration in custom workflows. | Full application development from coding to debugging and deployment. |
| Advantages | Lightweight, fast compilation. | Streamlined development, easier debugging, improved productivity. |
Introduction to IDEs and Code Compilers
Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) are comprehensive software suites designed to facilitate software development by combining source code editors, debugging tools, and build automation into a single interface. Code compilers are specialized programs within or separate from IDEs that translate high-level programming languages into machine code or bytecode, enabling program execution. Understanding the distinction between IDEs and code compilers is essential for developers to optimize coding efficiency, as IDEs provide an interactive environment while compilers focus solely on code translation and error detection.
What is an IDE?
An Integrated Development Environment (IDE) is a software application that combines code editing, compiling, and debugging tools into a single interface, streamlining the software development process. Unlike standalone code compilers that solely translate source code into executable programs, IDEs offer features such as syntax highlighting, code completion, version control integration, and real-time error detection. Popular IDEs like Visual Studio, Eclipse, and IntelliJ IDEA enhance developer productivity by providing a comprehensive environment tailored for coding, testing, and project management.
What is a Code Compiler?
A code compiler is a software tool that translates high-level programming language into machine code executable by a computer's processor, enabling efficient program execution. Unlike an Integrated Development Environment (IDE), which provides a comprehensive interface including editing, debugging, and compiling, a compiler specifically handles the conversion of source code into binary or executable files. Compilers perform syntax analysis, optimization, and code generation, crucial for languages like C, C++, and Java to ensure accurate and performant software.
Key Features of IDEs
Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) provide comprehensive tools including code editors, debuggers, and version control integration, unlike standalone code compilers that primarily translate source code into executable programs. Key features of IDEs encompass intelligent code completion, real-time error highlighting, and seamless integration with build systems, which enhance developer productivity and code quality. IDEs also support project management and collaboration capabilities, making them essential for modern software development workflows.
Key Features of Code Compilers
Code compilers translate high-level programming languages into machine code, enabling direct execution by a computer's processor, which improves performance and efficiency. Key features include syntax analysis, error detection, optimization of code, and generation of executable files. Unlike IDEs, which provide comprehensive tools like code editing, debugging, and project management, compilers focus specifically on converting source code into runnable programs.
Differences Between a Code Compiler and an IDE
An IDE (Integrated Development Environment) combines a code editor, compiler or interpreter, debugger, and other tools into a single application to streamline software development. A code compiler specifically translates source code written in programming languages like C++ or Java into executable machine code, without providing editing or debugging features. Key differences lie in functionality: IDEs offer comprehensive development support including syntax highlighting and version control, while compilers focus solely on converting code for execution.
Advantages of Using an IDE
An Integrated Development Environment (IDE) offers a comprehensive platform that combines code editing, compiling, debugging, and testing tools, streamlining the software development process. Unlike standalone code compilers, IDEs provide features like syntax highlighting, code completion, and version control integration, enhancing developer productivity and reducing errors. The all-in-one nature of IDEs accelerates development cycles and facilitates collaboration in complex projects.
When to Use a Code Compiler Instead of an IDE
Use a code compiler instead of an IDE when you need faster performance and minimal resource consumption for simple, single-file projects. Compilers provide direct translation of source code to executable files without the overhead of integrated debugging or development tools found in IDEs. Opt for a code compiler in environments where automation, build scripts, or continuous integration pipelines prioritize speed and efficiency over comprehensive code editing features.
Popular IDEs and Code Compilers
Popular IDEs like Visual Studio Code, IntelliJ IDEA, and Eclipse offer integrated features including code editing, debugging, and version control, enhancing developer productivity by combining multiple tools in one environment. Code compilers such as GCC, Clang, and javac specialize in translating source code into executable binaries but lack the extensive interface and tools found in IDEs. Choosing between an IDE and a standalone compiler depends on project complexity and workflow preferences, with many developers favoring IDEs for their comprehensive development support.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Development Needs
An Integrated Development Environment (IDE) combines multiple developer tools such as code editing, debugging, and compiling into a single platform, enhancing productivity by streamlining workflows. A code compiler focuses solely on translating source code into executable programs, offering faster compilation but lacking the comprehensive features of an IDE. Choosing the right tool depends on your project complexity, need for debugging, and preferences for integrated features versus speed and simplicity.
IDE, Code Compiler Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com