Parsing involves analyzing a string of symbols, either in natural language or computer languages, to determine its grammatical structure. It breaks down text into manageable components, facilitating understanding and further processing by computers or linguists. Explore the rest of this article to uncover effective parsing techniques and tools that can enhance your data analysis skills.
Table of Comparison
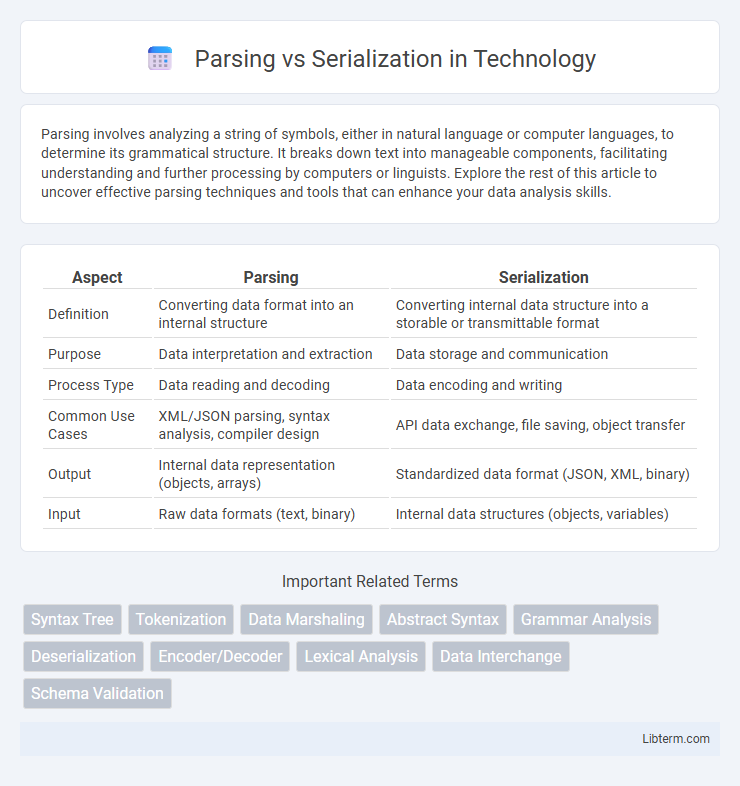
| Aspect | Parsing | Serialization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Converting data format into an internal structure | Converting internal data structure into a storable or transmittable format |
| Purpose | Data interpretation and extraction | Data storage and communication |
| Process Type | Data reading and decoding | Data encoding and writing |
| Common Use Cases | XML/JSON parsing, syntax analysis, compiler design | API data exchange, file saving, object transfer |
| Output | Internal data representation (objects, arrays) | Standardized data format (JSON, XML, binary) |
| Input | Raw data formats (text, binary) | Internal data structures (objects, variables) |
Introduction to Parsing and Serialization
Parsing transforms raw data or code into a structured format that a program can understand, enabling efficient processing and analysis of complex inputs such as JSON, XML, or programming languages. Serialization converts data structures or objects into a format that can be easily stored or transmitted, such as JSON, XML, or binary streams, preserving the original data state for later reconstruction. Both processes are fundamental in data exchange, application development, and communication between systems.
What is Parsing?
Parsing is the process of analyzing a string of data to convert it into a structured format that a computer can interpret and manipulate. It involves breaking down raw input, such as JSON, XML, or HTML, into meaningful components like tokens, syntax trees, or objects. Parsing is essential in programming languages, data processing, and web development to transform unstructured text into usable data structures.
What is Serialization?
Serialization is the process of converting complex data structures or objects into a format that can be easily stored or transmitted, such as JSON, XML, or binary. It enables seamless data exchange between different systems or components by transforming in-memory representations into a standardized format. Effective serialization is crucial for data persistence, remote procedure calls, and inter-process communication in software development.
Key Differences Between Parsing and Serialization
Parsing involves analyzing and converting data from a specific format, such as JSON or XML, into a usable in-memory structure like an object or a tree. Serialization is the process of transforming these in-memory data structures into a storable or transmittable format, often for saving to disk or sending over a network. Key differences include parsing as an input-oriented operation that interprets raw data, whereas serialization is output-oriented, focusing on data encoding for storage or communication.
Parsing: Use Cases and Applications
Parsing is essential in programming languages, compilers, and data processing to convert strings or data streams into structured formats for interpretation or manipulation. Common use cases include JSON and XML parsing in web development, enabling efficient data exchange and integration between APIs and applications. In natural language processing, parsing helps analyze sentence structures to improve machine understanding and semantic analysis.
Serialization: Use Cases and Applications
Serialization converts complex data structures into a format suitable for storage or transmission, enabling seamless data exchange between different systems or programming languages. Common use cases include saving application state, caching objects to improve performance, and facilitating communication in distributed systems through protocols like JSON, XML, or Protocol Buffers. Serialization is essential in web development for API payloads, in game development for saving progress, and in big data frameworks where data serialization formats optimize storage and processing efficiency.
Common Data Formats for Parsing and Serialization
Parsing and serialization are critical processes in data handling, involving the conversion between structured data formats and in-memory objects. Common data formats for parsing include JSON, XML, and YAML, which offer flexible, human-readable structures ideal for data interchange and configuration files. Serialization often uses these same formats to convert objects into strings or byte streams, with JSON favored for web APIs due to its lightweight nature, XML valued for complex hierarchical data, and YAML preferred for configuration due to its readability.
Performance Considerations
Parsing speed depends on the complexity of the data format and the efficiency of the parsing algorithm, with binary formats typically offering faster parsing than text-based formats like JSON or XML. Serialization performance is influenced by the overhead of converting data structures into a storable or transmittable format, where compact binary serialization often outperforms verbose text serialization in both speed and size. Memory usage during parsing and serialization also impacts overall performance, as inefficient memory handling can lead to increased latency and reduced throughput in high-demand applications.
Security Implications
Parsing vulnerabilities often lead to injection attacks, allowing attackers to manipulate input data and execute malicious code. Serialization processes can expose sensitive data if objects are not properly encrypted or validated, creating risks of data tampering or unauthorized access. Secure handling requires rigorous validation, use of safe serialization formats, and implementation of strict access controls to prevent exploitation.
Choosing Between Parsing and Serialization
Choosing between parsing and serialization depends on the data processing needs and application context. Parsing involves interpreting and converting data from formats like JSON or XML into usable structures, crucial for data analysis and validation. Serialization transforms objects into formats for storage or transmission, optimizing performance and compatibility in distributed systems or persistent storage scenarios.
Parsing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com