A data catalog organizes and indexes an organization's data assets to improve data discovery, governance, and management. By creating a centralized inventory of data sources, metadata, and usage, it enables faster access and better decision-making. Explore the article to learn how a data catalog can transform Your data strategy and operational efficiency.
Table of Comparison
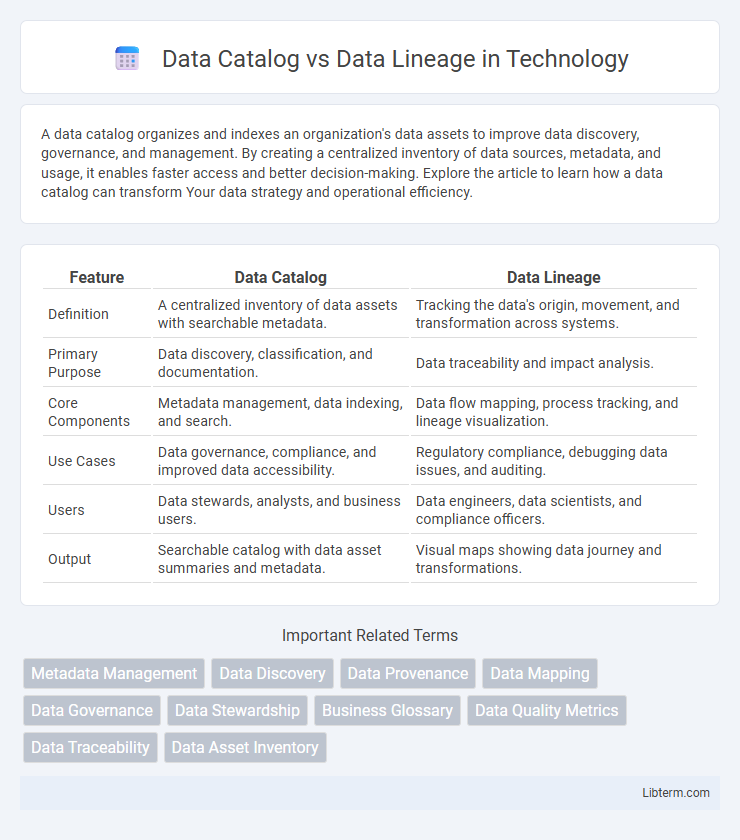
| Feature | Data Catalog | Data Lineage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A centralized inventory of data assets with searchable metadata. | Tracking the data's origin, movement, and transformation across systems. |
| Primary Purpose | Data discovery, classification, and documentation. | Data traceability and impact analysis. |
| Core Components | Metadata management, data indexing, and search. | Data flow mapping, process tracking, and lineage visualization. |
| Use Cases | Data governance, compliance, and improved data accessibility. | Regulatory compliance, debugging data issues, and auditing. |
| Users | Data stewards, analysts, and business users. | Data engineers, data scientists, and compliance officers. |
| Output | Searchable catalog with data asset summaries and metadata. | Visual maps showing data journey and transformations. |
Introduction to Data Catalogs and Data Lineage
Data Catalogs organize and index enterprise data assets, enabling users to quickly discover, understand, and access datasets through metadata management. Data Lineage provides a detailed record of data's origin, movement, and transformation across systems, ensuring transparency and traceability for data governance. Both tools are essential for data management, with catalogs focusing on data discovery and lineage emphasizing data provenance and impact analysis.
Defining Data Catalog: Purpose and Key Features
A Data Catalog serves as a centralized inventory of an organization's data assets, designed to improve data discovery, governance, and management by providing metadata, data classification, and user access controls. Its key features include searchable metadata repositories, automated data profiling, and detailed data documentation to enhance data understanding and usability. Unlike Data Lineage, which tracks the data flow and transformation pathways, the Data Catalog primarily focuses on organizing and indexing data for efficient retrieval and compliance.
What is Data Lineage? Understanding the Basics
Data lineage refers to the detailed tracking and visualization of data's flow from its original source through various processing steps to its final destination, ensuring transparency and data integrity. It provides a comprehensive map of data transformations, movements, and dependencies within an organization's data ecosystem. Understanding data lineage is crucial for data governance, debugging data issues, and complying with regulatory requirements.
Core Differences Between Data Catalog and Data Lineage
Data Catalog organizes and indexes metadata to create a searchable inventory of data assets, enhancing data discovery and governance. Data Lineage tracks the data's origin, transformations, and flow across systems to ensure data quality and compliance. The core difference lies in Data Catalog's focus on metadata management versus Data Lineage's emphasis on tracing data movement and transformations.
Business Value: Why Data Catalogs Matter
Data catalogs enhance business value by providing a centralized inventory of data assets, enabling faster data discovery and improved decision-making through better data governance. Data lineage complements this by tracing data origins and transformations, ensuring data accuracy, compliance, and auditability critical for risk management. Together, they empower organizations to derive insights confidently, reduce operational costs, and accelerate digital transformation initiatives.
Business Value: Importance of Data Lineage
Data lineage provides a critical business value by offering transparency into the data lifecycle, enabling organizations to track the origin, movement, and transformation of data across systems, which enhances data trust and compliance. Unlike data catalogs that primarily function as organized metadata repositories, data lineage helps identify data quality issues and supports impact analysis, reducing operational risks and improving decision-making accuracy. This traceability is vital for regulatory adherence, auditing processes, and efficient troubleshooting, making data lineage indispensable for leveraging data as a strategic asset.
Use Cases: When to Use Data Catalog vs Data Lineage
Data Catalogs are essential for data discovery, organization, and governance, enabling users to quickly find and understand datasets across an enterprise. Data Lineage is critical for tracking data flow, transformations, and dependencies, ensuring accuracy in compliance, impact analysis, and troubleshooting data quality issues. Use Data Catalogs when prioritizing metadata management and data accessibility, while Data Lineage is best suited for transparency in data processing and auditability requirements.
Integration: How Data Catalogs and Data Lineage Work Together
Data catalogs and data lineage integrate by providing a comprehensive view of data assets and their transformations across systems, enabling organizations to enhance data governance and quality. Data catalogs index and classify metadata, while data lineage traces data's origin, movement, and changes, ensuring transparency and compliance throughout data workflows. Together, they support seamless data discovery, impact analysis, and regulatory auditing by linking descriptive metadata with detailed data flow paths.
Challenges in Adopting Data Catalogs and Data Lineage
Adopting data catalogs faces challenges such as data integration complexity, inconsistent metadata standards, and user resistance due to inadequate training or unclear ROI. Data lineage implementation struggles with capturing comprehensive, end-to-end data flow in complex environments, ensuring real-time updates, and maintaining accuracy amid frequent data transformations. Both require significant organizational change management and continuous governance to realize their full potential in enhancing data transparency and trust.
Choosing the Right Solution: Key Considerations for Organizations
Choosing between a data catalog and data lineage solution depends on the organization's primary goals, such as metadata management or tracking data flow for compliance and impact analysis. Data catalogs optimize data discovery, governance, and collaboration by organizing metadata across systems, while data lineage solutions provide detailed visualization of data origins, transformations, and movement. Effective decision-making requires evaluating factors like regulatory requirements, data complexity, user roles, and integration capabilities to ensure alignment with business objectives and data governance strategies.
Data Catalog Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com