Obfuscation is the practice of deliberately making code, text, or data difficult to understand to protect intellectual property or enhance security. By obscuring logic and structure, it prevents unauthorized access and reverse engineering. Discover how obfuscation techniques can safeguard your software by exploring the strategies detailed in this article.
Table of Comparison
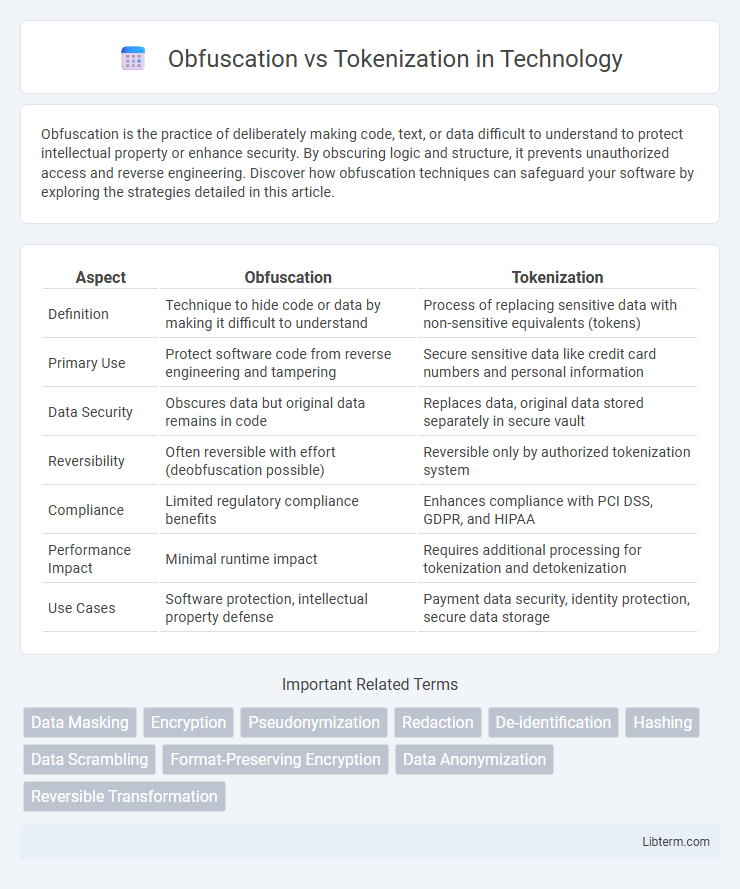
| Aspect | Obfuscation | Tokenization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Technique to hide code or data by making it difficult to understand | Process of replacing sensitive data with non-sensitive equivalents (tokens) |
| Primary Use | Protect software code from reverse engineering and tampering | Secure sensitive data like credit card numbers and personal information |
| Data Security | Obscures data but original data remains in code | Replaces data, original data stored separately in secure vault |
| Reversibility | Often reversible with effort (deobfuscation possible) | Reversible only by authorized tokenization system |
| Compliance | Limited regulatory compliance benefits | Enhances compliance with PCI DSS, GDPR, and HIPAA |
| Performance Impact | Minimal runtime impact | Requires additional processing for tokenization and detokenization |
| Use Cases | Software protection, intellectual property defense | Payment data security, identity protection, secure data storage |
Introduction to Obfuscation and Tokenization
Obfuscation transforms sensitive data into a disguised format to prevent unauthorized access, often employing techniques like encryption, masking, or hashing. Tokenization replaces sensitive information with non-sensitive equivalents called tokens, which retain data format without exposing actual values. Both methods enhance data security in compliance with privacy regulations such as GDPR and PCI DSS, but differ in implementation and use cases.
Defining Obfuscation
Obfuscation refers to the deliberate process of making data unintelligible or difficult to interpret by using techniques such as encryption, masking, or scrambling to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. It differs from tokenization, which replaces sensitive data elements with non-sensitive equivalents called tokens, maintaining data format and usability. Obfuscation is commonly used in software development and cybersecurity to safeguard intellectual property and sensitive data from reverse engineering and data breaches.
Defining Tokenization
Tokenization is a data protection technique that replaces sensitive information with non-sensitive placeholders called tokens, preserving the original data's format and usability without exposing actual values. Unlike obfuscation, which alters data to make it unreadable but still visible, tokenization ensures data cannot be reverse-engineered, enhancing security in payment processing and personal data management. Effective tokenization systems use secure token vaults or deterministic algorithms to maintain data integrity and compliance with regulations like PCI DSS.
Key Differences Between Obfuscation and Tokenization
Obfuscation alters data to make it unreadable or unintelligible by using techniques like masking or encryption, whereas tokenization replaces sensitive data with non-sensitive tokens that have no meaningful value outside the system. Obfuscation maintains the original data format but alters its appearance, while tokenization generates tokens unrelated to the original data to ensure security. The key difference lies in obfuscation's reversible transformation methods versus tokenization's creation of non-reversible identifiers.
Use Cases for Obfuscation
Obfuscation is primarily used for protecting sensitive data in software development environments by making code or data difficult to understand or reverse-engineer, which is essential for safeguarding intellectual property and thwarting cyberattacks. It is effective in scenarios involving mobile app development, where source code needs protection from unauthorized access and tampering, as well as in securing code libraries and APIs exposed to third parties. Obfuscation also plays a critical role in preventing data leakage during runtime in applications that handle confidential information without compromising functionality.
Use Cases for Tokenization
Tokenization is widely used in payment processing to replace sensitive credit card information with non-sensitive tokens, enhancing security and reducing PCI DSS scope. It is also crucial in healthcare for protecting patient data under HIPAA compliance by substituting personal identifiers with tokens. Furthermore, tokenization supports secure data sharing in cloud environments by ensuring sensitive data is never exposed during transmission or storage.
Security Implications of Obfuscation
Obfuscation transforms code or data to make it difficult for unauthorized users to understand, providing a layer of protection against reverse engineering and code tampering. However, it does not eliminate sensitive information, as skilled attackers can potentially de-obfuscate and access the original content. Unlike tokenization, which replaces sensitive data with non-sensitive equivalents, obfuscation's security relies heavily on the complexity of algorithms and is less effective for protecting high-risk personal or financial information.
Security Benefits of Tokenization
Tokenization enhances data security by replacing sensitive information with non-sensitive tokens, reducing the risk of exposure during data processing and storage. Unlike obfuscation, tokenization ensures that tokens cannot be reverse-engineered to reveal original data, providing stronger protection against data breaches. This method complies with stringent regulatory standards such as PCI DSS and GDPR, making it a preferred choice for securing payment and personal data.
Choosing the Right Approach: Obfuscation or Tokenization
Choosing the right approach between obfuscation and tokenization depends on the data security requirements and operational needs. Obfuscation hides sensitive data through methods like encryption or masking to prevent unauthorized access while preserving data format, ideal for development environments. Tokenization replaces sensitive data with non-sensitive placeholders, ensuring strong protection and easy reversibility, making it suitable for payment processing and compliance with regulations like PCI DSS.
Conclusion: Making Data Protection Decisions
Choosing between obfuscation and tokenization for data protection depends on the specific security requirements and compliance standards of an organization. Tokenization is ideal for reducing risk by replacing sensitive data with non-sensitive tokens, especially in payment and healthcare industries. Obfuscation, while useful for hiding data within code, does not provide the same level of compliance assurance but can complement tokenization in layered security strategies.
Obfuscation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com