Concreteness enhances communication by using vivid, specific details that make ideas clear and relatable. It bridges the gap between abstract concepts and practical understanding, helping your audience grasp the message more effectively. Discover how concreteness can transform your writing by exploring the rest of this article.
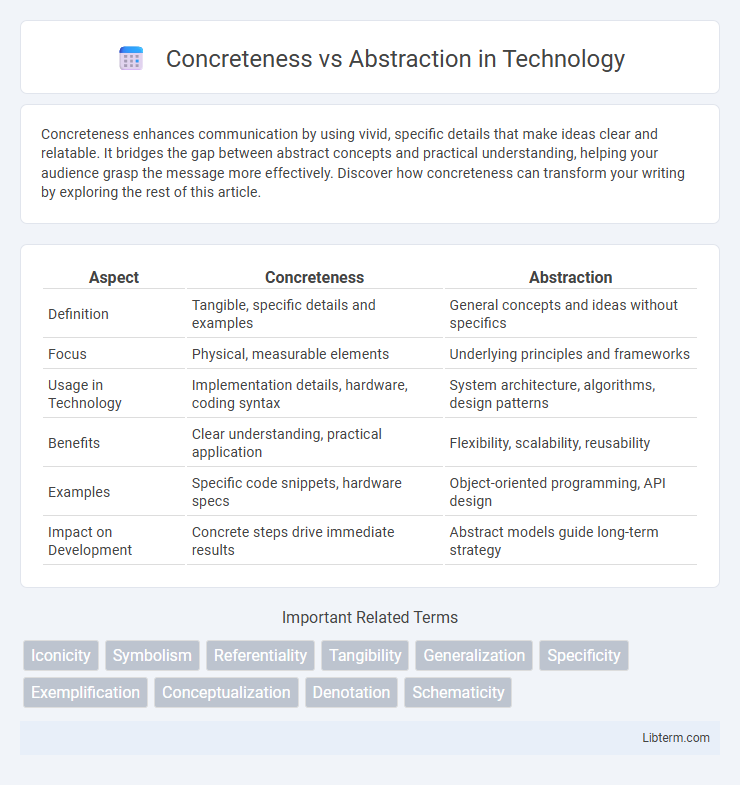
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Concreteness | Abstraction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tangible, specific details and examples | General concepts and ideas without specifics |
| Focus | Physical, measurable elements | Underlying principles and frameworks |
| Usage in Technology | Implementation details, hardware, coding syntax | System architecture, algorithms, design patterns |
| Benefits | Clear understanding, practical application | Flexibility, scalability, reusability |
| Examples | Specific code snippets, hardware specs | Object-oriented programming, API design |
| Impact on Development | Concrete steps drive immediate results | Abstract models guide long-term strategy |
Introduction to Concreteness and Abstraction
Concreteness refers to the quality of being specific, tangible, and easily visualized, often linked to physical objects or direct experiences. Abstraction involves generalizing concepts beyond immediate sensory details, focusing on ideas, principles, or categories that are not physically present. Understanding the distinction between concreteness and abstraction is essential for effective communication, as it shapes how information is perceived and processed.
Defining Concreteness: Clarity in Communication
Concreteness in communication refers to the use of specific, tangible details that create clear and vivid images in the audience's mind, enhancing understanding and retention. By employing precise nouns, active verbs, and sensory language, concrete communication eliminates ambiguity and fosters direct comprehension. This clarity reduces misinterpretation, making messages more effective across various contexts such as marketing, education, and everyday interactions.
Unpacking Abstraction: The Power of Generalization
Unpacking abstraction reveals the power of generalization by simplifying complex concepts into broader categories that apply across multiple contexts. This cognitive process enables efficient problem-solving and transfer of knowledge by identifying underlying patterns rather than focusing on specific details. Mastering abstraction accelerates learning and innovation through enhanced conceptual clarity and adaptability.
Cognitive Differences: How the Brain Processes Each
The brain processes concreteness by activating sensory and perceptual areas associated with vivid, detailed experiences, enhancing memory retention and comprehension through tangible information. In contrast, abstraction engages higher-order cortical regions such as the prefrontal cortex, facilitating complex reasoning, generalization, and conceptual thinking beyond immediate sensory input. Neuroimaging studies reveal distinct neural pathways for concrete versus abstract information, highlighting cognitive differences in how individuals process and integrate varied types of knowledge.
Concreteness in Education and Learning Strategies
Concreteness in education enhances comprehension by grounding abstract concepts in tangible examples, promoting better retention and application of knowledge. Learning strategies that incorporate concrete materials, such as visual aids, manipulatives, or real-world scenarios, foster active engagement and deeper understanding among students. Emphasizing concreteness supports cognitive development by linking new information to sensory experiences and practical contexts, which facilitates meaningful learning.
The Role of Abstraction in Problem-Solving
Abstraction plays a crucial role in problem-solving by allowing individuals to focus on essential features while ignoring irrelevant details, thereby simplifying complex problems. This cognitive process enables the formation of generalized concepts and models, which can be applied across various domains to find effective solutions. Effective use of abstraction enhances algorithm design, system architecture, and decision-making by promoting scalable and adaptable approaches.
Balancing Concreteness and Abstraction in Writing
Balancing concreteness and abstraction in writing enhances clarity and engagement by grounding abstract ideas with specific examples and vivid details. Employing concrete language such as tangible objects, sensory descriptions, and precise data helps readers visualize and understand complex concepts more effectively. Incorporating abstract language strategically connects these examples to broader themes and theories, fostering deeper comprehension without overwhelming the reader with ambiguity.
Real-World Applications: Science, Art, and Technology
Concreteness in science enables precise experimentation and empirical validation, driving innovations like medical imaging technologies and renewable energy systems. In art, abstraction fosters creativity by allowing artists to express complex emotions and concepts through symbolism and non-representational forms. Technology leverages both concreteness and abstraction to design intuitive user interfaces and develop advanced algorithms for artificial intelligence, enhancing functionality and user experience.
Common Pitfalls: When Too Much of Either Fails
Excessive concreteness limits creative thinking by anchoring ideas in specific details, while excessive abstraction causes loss of practical relevance, leading to vague or impractical concepts. Common pitfalls include overfitting solutions to narrow scenarios or producing ambiguous theories with little real-world application. Balancing concreteness and abstraction enhances clarity and innovation in problem-solving and communication.
Practical Tips for Achieving the Right Balance
Finding the right balance between concreteness and abstraction enhances communication effectiveness by making ideas clear yet flexible. Use specific examples and sensory details to ground abstract concepts in reality, aiding understanding and retention. Tailor the level of detail to your audience's knowledge, providing enough context without overwhelming, ensuring practical and relatable messaging.
Concreteness Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com