Big Data refers to the vast volumes of structured and unstructured data generated daily from various sources, requiring advanced tools and techniques for effective processing and analysis. Understanding its applications can transform how businesses make decisions, optimize operations, and gain competitive advantages. Explore this article to discover how Big Data can unlock new opportunities for your organization.
Table of Comparison
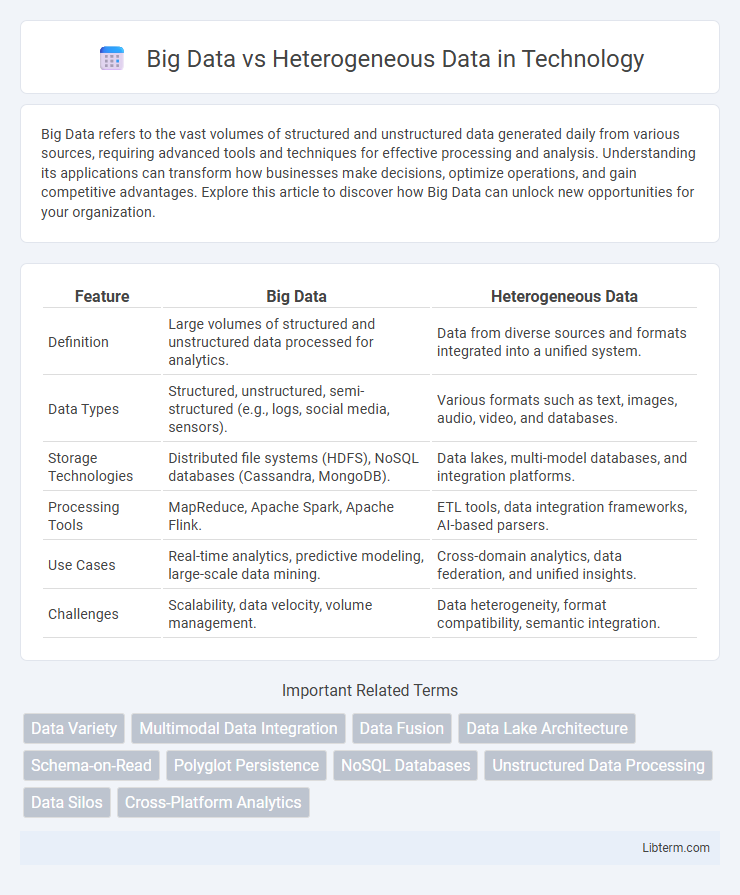
| Feature | Big Data | Heterogeneous Data |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Large volumes of structured and unstructured data processed for analytics. | Data from diverse sources and formats integrated into a unified system. |
| Data Types | Structured, unstructured, semi-structured (e.g., logs, social media, sensors). | Various formats such as text, images, audio, video, and databases. |
| Storage Technologies | Distributed file systems (HDFS), NoSQL databases (Cassandra, MongoDB). | Data lakes, multi-model databases, and integration platforms. |
| Processing Tools | MapReduce, Apache Spark, Apache Flink. | ETL tools, data integration frameworks, AI-based parsers. |
| Use Cases | Real-time analytics, predictive modeling, large-scale data mining. | Cross-domain analytics, data federation, and unified insights. |
| Challenges | Scalability, data velocity, volume management. | Data heterogeneity, format compatibility, semantic integration. |
Understanding Big Data: Definition and Key Characteristics
Big Data refers to massive volumes of structured and unstructured data characterized by the three Vs: volume, velocity, and variety, enabling complex analytics and decision-making. Heterogeneous data encompasses diverse types and sources, including text, images, and sensor data, which require integration and advanced processing techniques. Understanding Big Data involves recognizing its ability to handle heterogeneous datasets at scale through distributed computing and real-time analysis.
What is Heterogeneous Data? Concepts and Examples
Heterogeneous data refers to information coming from diverse sources and formats, such as structured databases, unstructured text, images, videos, and sensor data, which vary in type, schema, and origin. Unlike big data, which emphasizes volume, velocity, and variety, heterogeneous data highlights the complexity of integrating and analyzing multiple data formats and sources simultaneously. Examples include combining social media posts, GPS coordinates, medical records, and multimedia files to gain comprehensive insights in fields like healthcare, finance, and smart cities.
Core Differences: Big Data vs Heterogeneous Data
Big Data refers to extremely large datasets characterized by the three Vs: volume, velocity, and variety, requiring advanced processing techniques to extract meaningful insights. Heterogeneous Data emphasizes the diversity in data types and sources, encompassing structured, semi-structured, and unstructured formats from multiple origins. The core difference lies in Big Data's focus on scale and speed of data processing, while Heterogeneous Data centers on the complexity and integration challenges posed by varied data formats and sources.
Sources and Types of Big Data
Big Data originates from diverse sources including social media platforms, sensors, transactional records, and multimedia files, generating vast volumes of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. Heterogeneous Data emphasizes the variety and complexity inherent in Big Data, encompassing text, images, videos, logs, and geospatial data that require advanced integration and processing techniques. Understanding the sources and types of Big Data is crucial for leveraging analytics, machine learning, and data management strategies effectively.
Diversity and Complexity in Heterogeneous Data
Heterogeneous data encompasses diverse formats, structures, and sources, including text, images, videos, and sensor readings, which amplify its complexity compared to traditional big data. Managing this diversity requires advanced integration techniques and scalable algorithms capable of handling varying data types and inconsistent schemas. The interplay between this data variety and the complexity of processing challenges distinguishes heterogeneous data from conventional big data systems.
Storage Solutions for Big Data and Heterogeneous Data
Big Data storage solutions prioritize scalability and high-throughput architectures such as distributed file systems like Hadoop HDFS and cloud object storage, enabling efficient handling of massive volumes of structured and unstructured data. Heterogeneous data storage requires flexible, schema-agnostic databases like NoSQL, multi-model databases, and data lakes that support diverse data formats including images, text, video, and sensor data. Selecting storage technologies involves balancing performance, schema flexibility, and integration capabilities to effectively manage the variety and velocity inherent in disparate data sources.
Challenges in Processing Big Data vs Heterogeneous Data
Processing big data presents challenges such as managing vast volumes, ensuring data quality, and maintaining high velocity and variety within a unified framework. Heterogeneous data processing struggles with integrating diverse data formats, schemas, and sources, requiring advanced data normalization and transformation techniques. Scalability issues and real-time analytics further complicate both big data and heterogeneous data handling in distributed computing environments.
Analytical Techniques: Comparing Approaches
Big Data analytical techniques often leverage distributed computing frameworks like Apache Hadoop and Spark to process vast structured and unstructured datasets efficiently. In contrast, heterogeneous data analysis requires specialized integration methods such as data fusion, schema matching, and ontological mapping to harmonize diverse data formats and sources. Machine learning algorithms and advanced statistical models are adapted differently in each approach, optimizing for scalability in Big Data and interoperability in heterogeneous data environments.
Real-World Applications: Use Cases and Industries
Big Data enables industries like finance, healthcare, and retail to analyze massive datasets for predictive analytics, fraud detection, and customer behavior insights, driving data-driven decision-making. Heterogeneous Data, consisting of diverse data types including text, images, and sensor data, is crucial in sectors such as autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and personalized medicine, where integration of varied data sources enhances situational awareness and tailored solutions. Real-world applications harness both Big Data and Heterogeneous Data to improve operational efficiency, innovation, and strategic planning across dynamic environments.
Future Trends: The Evolving Landscape of Data Management
Future trends in data management emphasize the integration of big data technologies with heterogeneous data sources to enhance analytics and decision-making. Advances in AI-driven data harmonization and real-time processing frameworks enable seamless handling of structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data across diverse platforms. The evolving landscape prioritizes scalable storage solutions and interoperability standards to support complex, multi-source datasets critical for AI, IoT, and edge computing applications.
Big Data Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com