Log monitoring captures and analyzes system logs in real-time to detect anomalies and ensure operational stability. Efficient log monitoring helps identify security threats, troubleshoot errors, and optimize performance across IT infrastructure. Explore the rest of this article to learn how your organization can benefit from advanced log monitoring techniques.
Table of Comparison
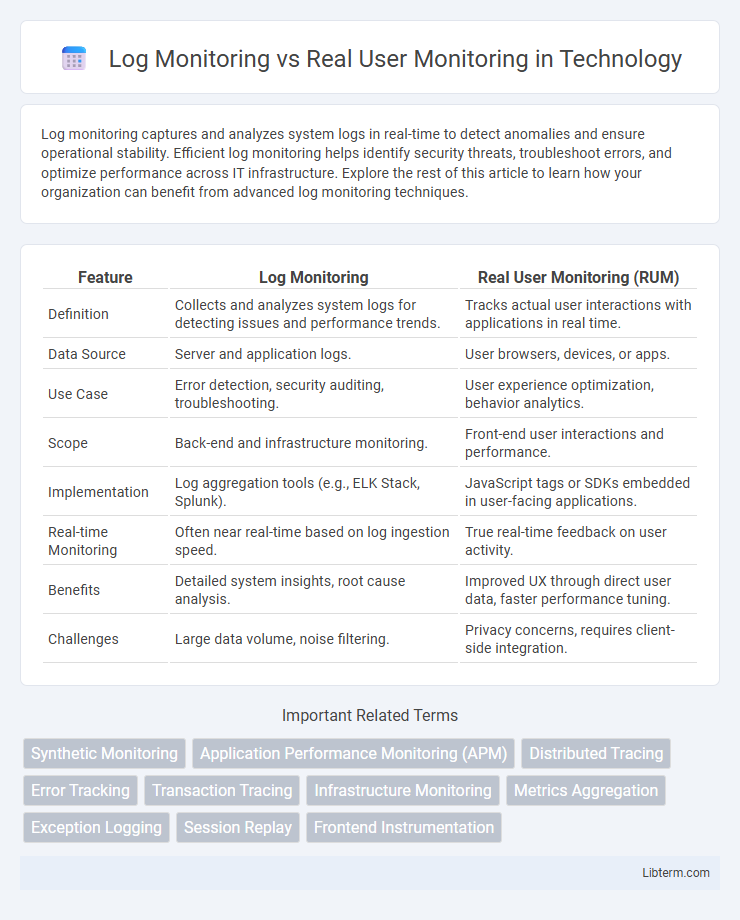
| Feature | Log Monitoring | Real User Monitoring (RUM) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collects and analyzes system logs for detecting issues and performance trends. | Tracks actual user interactions with applications in real time. |
| Data Source | Server and application logs. | User browsers, devices, or apps. |
| Use Case | Error detection, security auditing, troubleshooting. | User experience optimization, behavior analytics. |
| Scope | Back-end and infrastructure monitoring. | Front-end user interactions and performance. |
| Implementation | Log aggregation tools (e.g., ELK Stack, Splunk). | JavaScript tags or SDKs embedded in user-facing applications. |
| Real-time Monitoring | Often near real-time based on log ingestion speed. | True real-time feedback on user activity. |
| Benefits | Detailed system insights, root cause analysis. | Improved UX through direct user data, faster performance tuning. |
| Challenges | Large data volume, noise filtering. | Privacy concerns, requires client-side integration. |
Introduction to Log Monitoring and Real User Monitoring
Log Monitoring involves tracking and analyzing server and application logs to detect errors, performance issues, and security threats in real-time, providing deep technical insights into backend operations. Real User Monitoring (RUM) captures actual user interactions and experiences on websites or applications, measuring metrics such as page load times, transaction success rates, and user behavior patterns. These complementary monitoring techniques enable comprehensive performance management by combining backend system data with end-user experience analysis.
Key Differences Between Log Monitoring and Real User Monitoring
Log monitoring captures and analyzes server-side logs to detect system errors, performance issues, and security events, providing backend operational insights. Real User Monitoring (RUM) tracks actual user interactions in real time, measuring page load times, user behavior, and frontend performance to enhance user experience. The key difference lies in log monitoring focusing on backend infrastructure data while RUM emphasizes frontend user-centric metrics.
How Log Monitoring Works
Log monitoring collects and analyzes log data generated by applications, servers, and network devices to detect errors, security incidents, and performance issues in real-time. It involves aggregating logs from multiple sources, parsing them to extract meaningful information, and setting alerts for anomalies or predefined thresholds. This method provides deep insights into system behavior and helps IT teams troubleshoot problems by examining detailed event histories.
How Real User Monitoring Works
Real User Monitoring (RUM) collects data by tracking actual user interactions with web applications through browser-based scripts or SDKs embedded in the app, capturing metrics like page load times, click rates, and user navigation paths. This data is sent in real-time to monitoring platforms, providing granular insights into end-user experience and performance from the user's perspective. Unlike log monitoring, which analyzes server and application logs for errors and performance issues, RUM offers direct visibility into front-end behavior and user impact, enabling more precise optimization of user experience.
Benefits of Log Monitoring
Log monitoring provides detailed, timestamped records of system events that enable precise troubleshooting and historical analysis, improving overall system reliability. It enhances security by detecting anomalies and unauthorized access through real-time log analysis, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Unlike Real User Monitoring, which primarily focuses on user experience, log monitoring delivers comprehensive insights into backend processes, facilitating proactive maintenance and performance optimization.
Advantages of Real User Monitoring
Real User Monitoring (RUM) captures actual user interactions and experiences in real-time, providing precise insights into application performance and user behavior that log monitoring may overlook. It enables detection of front-end issues, browser-specific errors, and network latency impacting users directly, facilitating targeted performance optimization. RUM's user-centric data supports improved customer satisfaction and proactive problem resolution by aligning technical metrics with user experience.
Use Cases for Log Monitoring
Log monitoring excels in tracking system performance, security events, and troubleshooting by analyzing server logs, application logs, and error reports for anomalies and failures. It is crucial for IT operations teams to detect infrastructure issues, audit compliance, and perform root cause analysis through centralized log aggregation and alerts. Enterprises rely on log monitoring for proactive incident management, capacity planning, and ensuring reliability in complex distributed environments.
Use Cases for Real User Monitoring
Real User Monitoring (RUM) is essential for understanding actual user experiences by capturing real-time data on load times, interactions, and errors directly from end-users, making it ideal for performance optimization and user-centric application improvements. Use cases include pinpointing slow page elements affecting user engagement, tracking conversion bottlenecks in e-commerce sites, and identifying region-specific performance issues that logs alone cannot reveal. In contrast, Log Monitoring primarily supports backend debugging and system health checks through server-generated logs, whereas RUM provides actionable insights into frontend user behavior and performance metrics.
Choosing Between Log Monitoring and Real User Monitoring
Choosing between Log Monitoring and Real User Monitoring depends on the specific needs of your IT infrastructure and user experience goals. Log Monitoring offers detailed insights into system performance, error detection, and backend issues by analyzing server and application logs. Real User Monitoring provides a direct view of end-user interactions, measuring performance metrics like page load times and user behavior to optimize front-end experiences.
Integrating Log Monitoring and Real User Monitoring for Optimal Insights
Integrating log monitoring and real user monitoring (RUM) creates a comprehensive observability strategy by combining backend system insights with actual user experience data. Log monitoring captures detailed server and application events, enabling rapid issue detection and root cause analysis, while RUM tracks real-time user interactions and performance metrics across browsers and devices. This synergy allows organizations to correlate backend anomalies with frontend user impacts, enhancing troubleshooting accuracy, improving application performance, and delivering optimal digital experiences.
Log Monitoring Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com