Replication ensures the accurate copying of data across multiple systems to enhance reliability and availability. This process minimizes downtime and protects against data loss by creating consistent, real-time duplicates. Explore the rest of the article to understand how replication can strengthen your data management strategy.
Table of Comparison
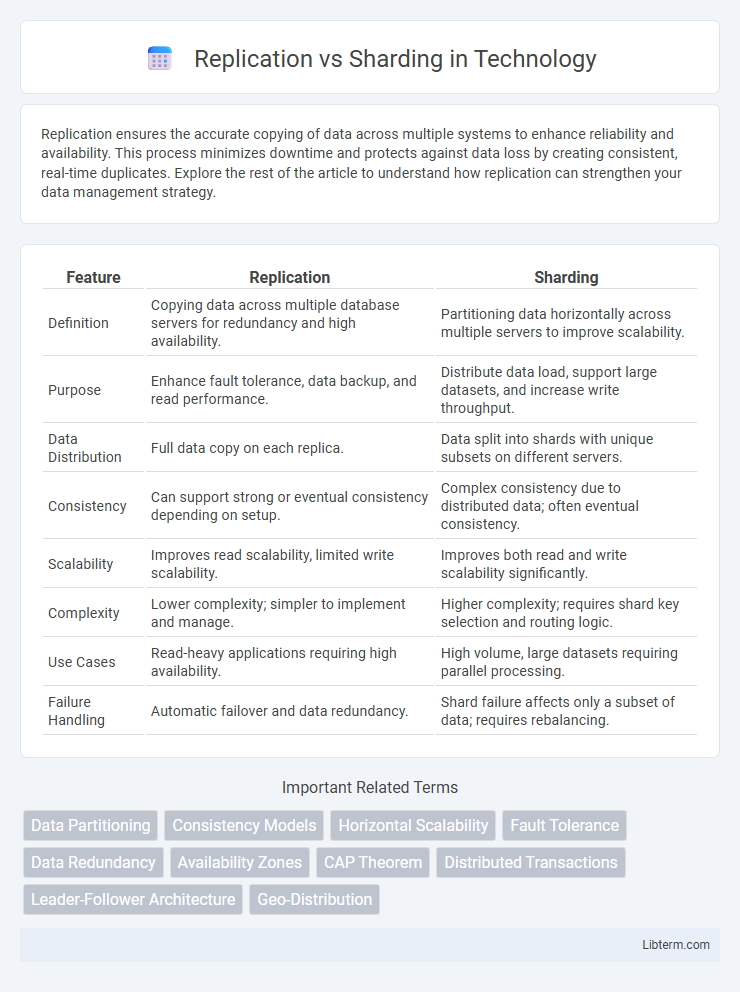
| Feature | Replication | Sharding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Copying data across multiple database servers for redundancy and high availability. | Partitioning data horizontally across multiple servers to improve scalability. |
| Purpose | Enhance fault tolerance, data backup, and read performance. | Distribute data load, support large datasets, and increase write throughput. |
| Data Distribution | Full data copy on each replica. | Data split into shards with unique subsets on different servers. |
| Consistency | Can support strong or eventual consistency depending on setup. | Complex consistency due to distributed data; often eventual consistency. |
| Scalability | Improves read scalability, limited write scalability. | Improves both read and write scalability significantly. |
| Complexity | Lower complexity; simpler to implement and manage. | Higher complexity; requires shard key selection and routing logic. |
| Use Cases | Read-heavy applications requiring high availability. | High volume, large datasets requiring parallel processing. |
| Failure Handling | Automatic failover and data redundancy. | Shard failure affects only a subset of data; requires rebalancing. |
Introduction to Data Management Strategies
Replication involves copying data across multiple servers to enhance availability and fault tolerance, while sharding partitions a database into smaller, independent segments to improve performance and scalability. Both strategies address different challenges in data management: replication ensures data redundancy and quick recovery from failures, whereas sharding distributes workload to manage massive datasets efficiently. Effective data management employs these techniques based on application needs, balancing consistency, availability, and partition tolerance.
Understanding Replication: Definition and Purpose
Replication involves creating exact copies of a database across multiple servers to ensure data availability and fault tolerance. This process enhances read performance by distributing query loads while providing redundancy to protect against hardware failures. By maintaining synchronized replicas, replication supports disaster recovery and high availability in distributed database systems.
Sharding Explained: What It Is and How It Works
Sharding is a database partitioning technique that splits large datasets across multiple servers to improve performance and scalability by distributing the load. Each shard operates as an independent database, containing a subset of the data, enabling faster query processing and reduced latency for high-traffic applications. This approach contrasts with replication, which duplicates data for redundancy but does not distribute workload, making sharding ideal for managing massive, growing data volumes efficiently.
Key Differences Between Replication and Sharding
Replication involves copying the same dataset across multiple servers to ensure high availability and fault tolerance, while sharding partitions the dataset into smaller, distinct segments distributed across different servers to improve scalability and performance. Replication enhances read performance and data redundancy by maintaining multiple copies of data, whereas sharding optimizes write and query efficiency by splitting the data based on a shard key. Key differences include replication's focus on data duplication for resilience versus sharding's emphasis on horizontal scaling through data distribution.
Advantages of Data Replication
Data replication enhances system reliability by creating multiple copies of data across different servers, ensuring high availability and fault tolerance. It improves read performance by allowing queries to be distributed and served from replicas, reducing the load on the primary database. Replication also facilitates disaster recovery by maintaining up-to-date backups of critical data in geographically diverse locations.
Benefits of Implementing Sharding
Sharding enhances database performance by distributing data across multiple servers, allowing for parallel processing and faster query responses in large-scale applications. It improves scalability by enabling seamless horizontal growth, accommodating increasing data volumes without compromising system efficiency. Sharding also increases fault tolerance, as the failure of one shard does not affect the entire database, ensuring higher availability and reliability.
Common Challenges with Replication
Replication challenges often include data consistency issues due to latency between master and replica nodes, leading to potential stale reads. Managing failover mechanisms without data loss and ensuring synchronized backups are complex tasks in distributed replication setups. Scaling writes remains difficult since replicas copy data but do not distribute write loads like sharding.
Potential Issues in Sharding Architectures
Sharding architectures can encounter potential issues such as uneven data distribution leading to hotspot formation and degraded performance. Cross-shard transactions pose complexity challenges, increasing latency and complicating consistency guarantees. Fault tolerance difficulties arise from shard failures, potentially causing partial data unavailability without adequate replication or failover mechanisms.
Choosing Between Replication and Sharding
Choosing between replication and sharding depends on workload characteristics and scaling needs. Replication enhances data availability and read performance by copying data across multiple nodes, ideal for read-heavy applications requiring fault tolerance. Sharding distributes data across partitions to improve write scalability and manage large datasets, suitable for applications needing horizontal scaling and high write throughput.
Best Practices for Scalable Database Solutions
Replication enhances database availability and fault tolerance by creating exact copies of data across multiple nodes, ensuring high read throughput and data redundancy. Sharding partitions data horizontally across multiple servers, improving write performance and accommodating large datasets by distributing load. Combining replication with sharding is a best practice for scalable database solutions, as it balances high availability, fault tolerance, and efficient data distribution.
Replication Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com