Automation enhances efficiency by streamlining repetitive tasks and reducing human error in various industries. It integrates advanced technologies such as AI and robotics to optimize workflows and increase productivity. Discover how automation can transform your operations by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
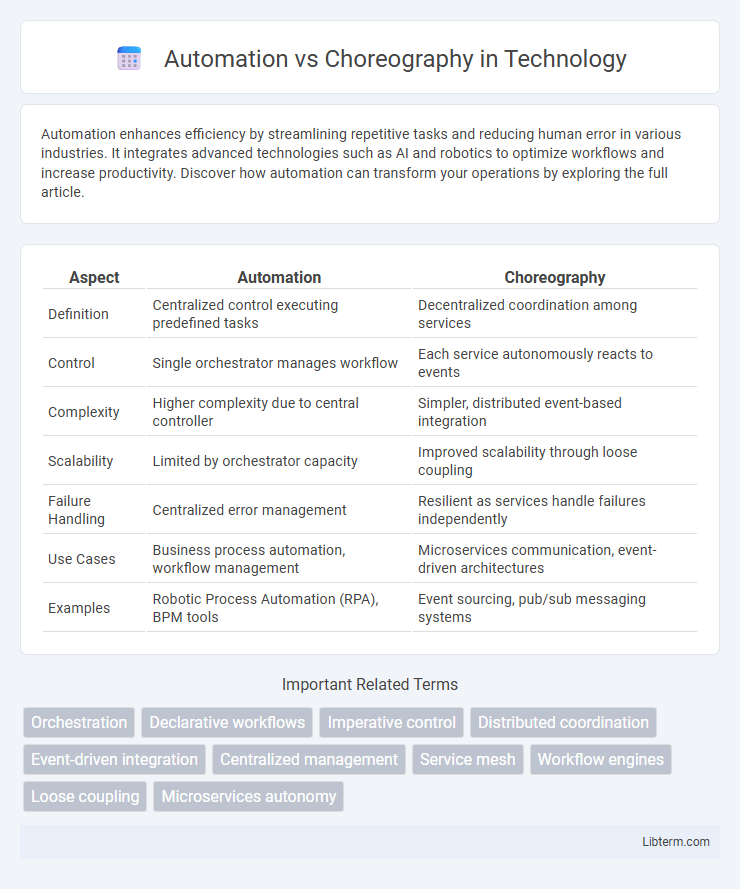
| Aspect | Automation | Choreography |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Centralized control executing predefined tasks | Decentralized coordination among services |
| Control | Single orchestrator manages workflow | Each service autonomously reacts to events |
| Complexity | Higher complexity due to central controller | Simpler, distributed event-based integration |
| Scalability | Limited by orchestrator capacity | Improved scalability through loose coupling |
| Failure Handling | Centralized error management | Resilient as services handle failures independently |
| Use Cases | Business process automation, workflow management | Microservices communication, event-driven architectures |
| Examples | Robotic Process Automation (RPA), BPM tools | Event sourcing, pub/sub messaging systems |
Introduction to Automation and Choreography
Automation involves executing predefined tasks through scripts or software to improve efficiency and reduce manual intervention, commonly used in IT and business processes. Choreography, in contrast, coordinates multiple autonomous services or systems to collaborate seamlessly without a central controller, emphasizing decentralized communication. Both approaches optimize workflows but differ in control mechanisms and integration strategies.
Defining Automation in Modern Workflows
Automation in modern workflows refers to the use of technology to execute repetitive tasks and processes with minimal human intervention, improving efficiency and accuracy. It leverages tools such as robotic process automation (RPA), AI-driven software, and integration platforms to streamline operations and reduce manual effort. These automated systems enable seamless data exchange, real-time monitoring, and consistent task execution across diverse business functions.
Understanding Choreography in System Integration
Choreography in system integration defines a decentralized approach where services communicate through a predefined protocol, enabling autonomous service interactions without a central coordinator. This method enhances scalability by allowing each service to manage its behavior and state independently while adhering to global interaction rules. Understanding choreography is crucial for developing flexible, resilient integrations in complex distributed systems, as it promotes loose coupling and asynchronous message exchanges across diverse platforms.
Key Differences Between Automation and Choreography
Automation centralizes control by using a single system or tool to execute predefined tasks and workflows, ensuring consistency and efficiency in repetitive processes. Choreography distributes control across multiple services or components, enabling them to interact and coordinate independently through event-driven communication and decentralized decision-making. Key differences include control structure--centralized in automation versus decentralized in choreography--and the level of coupling, with automation often tightly coupled and choreography promoting loose coupling for greater flexibility and scalability.
Use Cases for Automation
Automation excels in repetitive, rule-based tasks such as invoice processing, customer onboarding, and IT infrastructure management, where predefined workflows streamline operations. It enables increased efficiency and accuracy in areas like robotic process automation (RPA) for data entry and automated testing in software development. Use cases often include error reduction in financial reporting, accelerating supply chain processes, and improving compliance through standardized procedures.
Use Cases for Choreography
Choreography excels in use cases involving distributed systems where multiple services need to communicate asynchronously without a central controller, such as microservices architectures managing order processing or supply chain workflows. It enables autonomous services to emit and listen to events, facilitating loosely coupled interactions that improve system scalability and fault tolerance. Event-driven choreography is particularly effective for real-time data synchronization and complex business processes requiring dynamic, independent decision-making across components.
Benefits of Automation
Automation increases operational efficiency by enabling repetitive tasks to be executed faster and with higher accuracy, reducing human error. It supports scalability by allowing systems to handle growing workloads without additional manual intervention. Automation also enhances consistency and reliability, ensuring standardized processes and improved compliance across various business functions.
Advantages of Choreography
Choreography offers enhanced scalability by allowing multiple services to interact directly without a central coordinator, reducing bottlenecks and increasing system resilience. It promotes flexibility as each service autonomously manages its own process logic, simplifying updates and maintenance. Real-time adaptability and fault tolerance improve since services can independently respond to events, leading to more robust distributed applications.
Choosing Between Automation and Choreography
Choosing between automation and choreography depends on the complexity and flexibility required in a system's workflow. Automation centralizes control, enabling streamlined, rule-based task execution ideal for repetitive and predictable processes. Choreography distributes control among services, fostering dynamic interactions and scalability suited for complex, event-driven architectures.
Future Trends in Automation and Choreography
Future trends in automation and choreography emphasize increased integration of AI-powered decision-making and real-time data processing, enabling dynamic and adaptive workflows. The rise of event-driven architectures supports more scalable and resilient choreographed systems, reducing dependencies on centralized control. Advances in distributed ledger technologies and microservices further enhance transparency and coordination in both automated and choreographed processes.
Automation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com