DevOps integrates development and operations teams to enhance software delivery speed and quality through automation, collaboration, and continuous improvement. This approach reduces deployment risks and accelerates innovation, making your development process more efficient. Explore this article to discover how adopting DevOps can transform your software lifecycle.
Table of Comparison
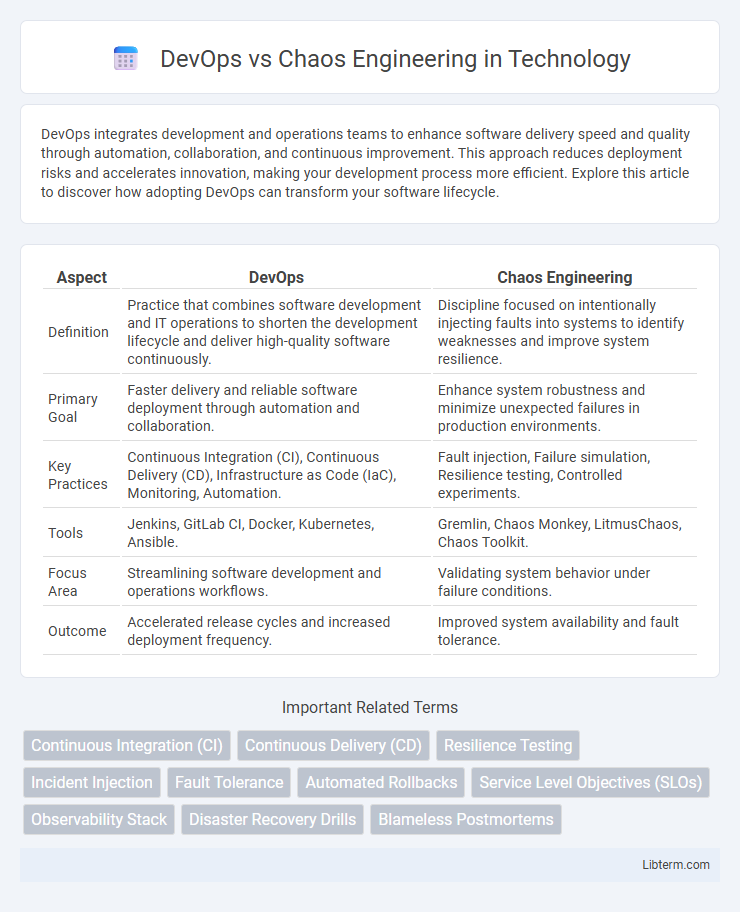
| Aspect | DevOps | Chaos Engineering |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Practice that combines software development and IT operations to shorten the development lifecycle and deliver high-quality software continuously. | Discipline focused on intentionally injecting faults into systems to identify weaknesses and improve system resilience. |
| Primary Goal | Faster delivery and reliable software deployment through automation and collaboration. | Enhance system robustness and minimize unexpected failures in production environments. |
| Key Practices | Continuous Integration (CI), Continuous Delivery (CD), Infrastructure as Code (IaC), Monitoring, Automation. | Fault injection, Failure simulation, Resilience testing, Controlled experiments. |
| Tools | Jenkins, GitLab CI, Docker, Kubernetes, Ansible. | Gremlin, Chaos Monkey, LitmusChaos, Chaos Toolkit. |
| Focus Area | Streamlining software development and operations workflows. | Validating system behavior under failure conditions. |
| Outcome | Accelerated release cycles and increased deployment frequency. | Improved system availability and fault tolerance. |
Introduction to DevOps and Chaos Engineering
DevOps is a collaborative approach that integrates software development and IT operations to accelerate delivery, improve quality, and enhance customer satisfaction through continuous integration, continuous delivery (CI/CD), and infrastructure automation. Chaos Engineering involves deliberately introducing failures into systems to identify weaknesses and improve system resilience by proactively testing real-world scenarios in distributed environments. Both methodologies aim to enhance system reliability but differ in their focus, with DevOps emphasizing streamlined workflows and Chaos Engineering concentrating on robustness through controlled experimentation.
Core Principles: DevOps vs Chaos Engineering
DevOps centers on continuous integration, continuous delivery (CI/CD), and collaboration between development and operations teams to accelerate software deployment and improve reliability. Chaos Engineering emphasizes proactive fault injection and controlled experimentation to identify system weaknesses and enhance resilience under unpredictable conditions. Both methodologies prioritize automation and monitoring, but DevOps aims for streamlined workflows while Chaos Engineering focuses on validating system robustness through intentional disruptions.
Goals and Objectives: Alignments and Differences
DevOps aims to streamline software development and IT operations through continuous integration, continuous delivery (CI/CD), and collaboration, focusing on speed, efficiency, and reliability. Chaos Engineering targets system resilience by proactively injecting failures to identify weaknesses, ensuring robust fault-tolerance and improved uptime in production environments. Both disciplines align on improving system reliability and performance but differ as DevOps emphasizes process automation and deployment velocity, while Chaos Engineering centers on uncovering vulnerabilities through controlled experimentation.
Key Practices and Methodologies
DevOps emphasizes continuous integration, continuous delivery (CI/CD), infrastructure as code (IaC), and automated testing to streamline software development and deployment processes. Chaos Engineering focuses on deliberately injecting failures into systems using controlled experiments to identify vulnerabilities and improve system resilience. Both methodologies utilize automation and monitoring tools, but DevOps prioritizes rapid development cycles while Chaos Engineering centers on robustness and fault tolerance through proactive failure scenarios.
Tools Comparison: DevOps and Chaos Engineering
DevOps utilizes tools such as Jenkins, Docker, Kubernetes, and Ansible to streamline continuous integration, delivery, and infrastructure automation. Chaos Engineering relies on specialized tools like Gremlin, Chaos Monkey, and LitmusChaos to inject faults and test system resilience under real-world failure conditions. Both toolsets prioritize automation and monitoring but serve distinct purposes: DevOps enhances deployment speed and reliability, while Chaos Engineering validates system robustness through controlled disruptions.
Impact on Software Reliability and Resilience
DevOps enhances software reliability by automating deployments, continuous integration, and continuous delivery, ensuring rapid feedback and consistent environments. Chaos Engineering improves resilience by intentionally introducing failures to identify system weaknesses, enabling teams to build robust architectures that withstand real-world disruptions. Together, DevOps streamlines development processes while Chaos Engineering validates system stability under stress, collectively elevating software reliability and resilience.
Collaboration and Culture Shift
DevOps emphasizes collaboration by integrating development and operations teams, fostering a culture of shared responsibility and continuous improvement to accelerate software delivery. Chaos Engineering promotes a proactive culture shift by encouraging experimentation and resilience testing, allowing teams to identify system weaknesses before failures occur. Both approaches drive cultural transformation towards transparency, accountability, and embracing failure as a learning opportunity within high-performing organizations.
Real-world Use Cases and Success Stories
DevOps enhances software delivery by automating workflows and fostering collaboration between development and operations teams, exemplified by Netflix's continuous integration pipeline that reduces deployment time by 50%. Chaos Engineering, pioneered by companies like Amazon, proactively injects failures into production environments to test system resilience, enabling them to minimize downtime during outages. Real-world successes demonstrate that combining DevOps' automation with Chaos Engineering's failure testing significantly improves system reliability and speeds up recovery from incidents.
Challenges and Considerations
DevOps faces challenges in integrating continuous deployment with robust monitoring to maintain seamless workflows while managing cultural shifts towards collaboration. Chaos Engineering demands careful consideration of system resilience by intentionally introducing failures in controlled environments to identify weaknesses without impacting production stability. Balancing the proactive testing of Chaos Engineering with the rapid iteration cycles of DevOps requires strategic alignment to prevent unforeseen downtime and ensure operational reliability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Organization
DevOps emphasizes continuous integration and delivery to enhance collaboration between development and operations teams, driving faster software deployment and improved reliability. Chaos Engineering focuses on proactively testing system resilience by injecting faults to identify weaknesses before they lead to outages. Choosing between DevOps and Chaos Engineering depends on your organization's priorities: adopt DevOps for optimized workflow automation and rapid releases, and integrate Chaos Engineering to strengthen system robustness and prepare for unexpected failures.
DevOps Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com