An exclusive lock prevents multiple users from accessing the same data simultaneously, ensuring data integrity during critical operations. This lock type is vital in scenarios where you need to avoid conflicts and maintain consistency in databases or file systems. Explore the rest of this article to understand how exclusive locks can safeguard your data effectively.
Table of Comparison
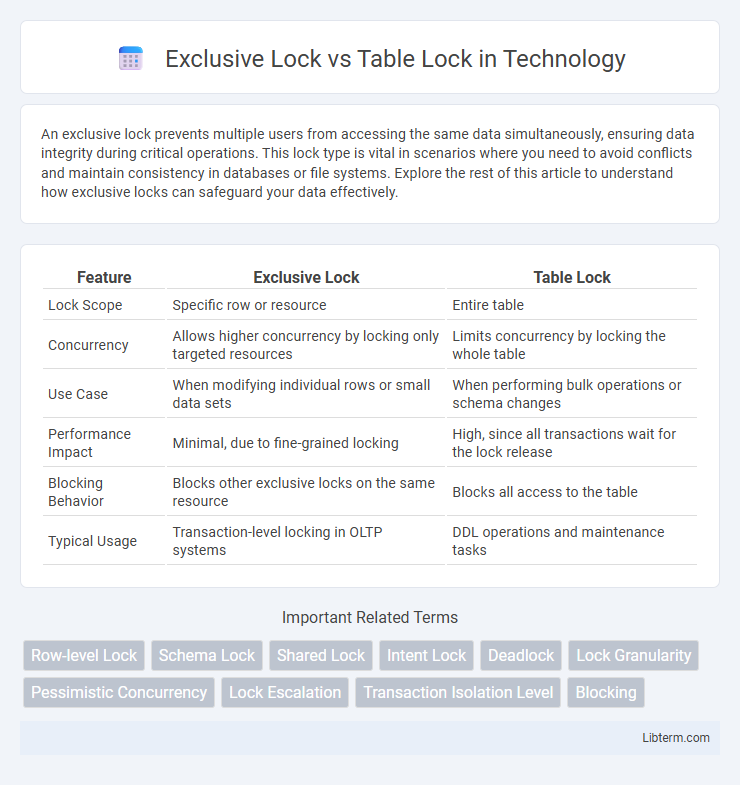
| Feature | Exclusive Lock | Table Lock |
|---|---|---|
| Lock Scope | Specific row or resource | Entire table |
| Concurrency | Allows higher concurrency by locking only targeted resources | Limits concurrency by locking the whole table |
| Use Case | When modifying individual rows or small data sets | When performing bulk operations or schema changes |
| Performance Impact | Minimal, due to fine-grained locking | High, since all transactions wait for the lock release |
| Blocking Behavior | Blocks other exclusive locks on the same resource | Blocks all access to the table |
| Typical Usage | Transaction-level locking in OLTP systems | DDL operations and maintenance tasks |
Introduction to Database Locking Mechanisms
Exclusive locks prevent other transactions from reading or writing to a locked resource, ensuring data integrity during critical operations. Table locks restrict access to an entire table, limiting concurrent modifications and simplifying conflict resolution but potentially reducing system concurrency. Understanding these locking mechanisms is crucial for optimizing database performance and preventing deadlocks.
What is an Exclusive Lock?
An Exclusive Lock in database management prevents other transactions from reading or writing the locked resource, ensuring data integrity during updates. It specifically restricts access to a particular row or page, allowing only the transaction holding the lock to perform modifications. This differs from a Table Lock, which blocks access to the entire table, potentially reducing concurrency and performance.
Understanding Table Lock
A table lock restricts access to an entire database table, preventing other transactions from reading or writing to it simultaneously, which ensures data integrity during critical operations. Exclusive locks are a specific type of table lock that block all other access types until the lock is released, providing a higher level of protection but potentially causing increased contention and blocking. Understanding table locks helps optimize concurrency control and improve performance in database management systems by balancing data consistency with multi-user access.
Key Differences Between Exclusive Lock and Table Lock
Exclusive locks prevent other transactions from reading or writing the locked resource, ensuring data integrity during updates by allowing only one session to access the locked row or page. Table locks restrict access to an entire table, blocking other operations on any part of that table regardless of the row or page involved. The key difference lies in granularity: exclusive locks target specific rows or pages for minimal contention, while table locks apply to the whole table, potentially causing greater concurrency bottlenecks.
Advantages of Using Exclusive Locks
Exclusive locks enhance data integrity by preventing concurrent access and modifications to a resource, ensuring transactions are executed without conflicts. They provide superior control over data consistency, especially in high-concurrency environments where isolated operations are critical. This lock type reduces risk of deadlocks and race conditions compared to broader table locks, optimizing transactional performance.
Benefits of Table Locks in Database Management
Table locks enhance performance by preventing multiple transactions from modifying the same table simultaneously, ensuring data integrity and consistency. They reduce overhead compared to row-level locks by managing fewer lock objects, leading to more efficient resource usage in high-concurrency environments. Table locks simplify conflict resolution in complex operations like bulk updates or schema changes, improving overall database management stability.
Use Cases for Exclusive Lock vs Table Lock
Exclusive locks are ideal for transactions requiring modification of specific rows without impacting access to the entire table, ensuring data integrity during row-level updates. Table locks are suited for maintenance tasks or bulk operations where preventing simultaneous access to the entire table is necessary to avoid conflicts and ensure consistency. Use exclusive locks for fine-grained control in concurrent environments, while table locks are effective for operations that demand full table isolation.
Impact on Performance and Concurrency
Exclusive locks restrict access to a specific data resource, blocking other transactions from reading or writing until the lock is released, which can significantly reduce concurrency but ensures data integrity during critical operations. Table locks apply to an entire table, preventing simultaneous modifications and often causing greater contention and higher wait times compared to exclusive locks that target finer-grained resources like rows or pages. Using exclusive locks optimized at a row level enhances performance by allowing more concurrent access, whereas table locks, although simpler, can lead to bottlenecks and decreased throughput in multi-user environments.
Best Practices for Choosing Lock Types
Choosing between exclusive locks and table locks depends on transaction scope and concurrency requirements. Exclusive locks provide row-level control, minimizing contention and improving performance in high-concurrency environments, while table locks ensure consistency by preventing access to the entire table but can cause bottlenecks. Best practices involve using exclusive locks for targeted updates to enhance throughput and resorting to table locks only when bulk operations or schema changes require complete table isolation.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Locking Strategy
Choosing the appropriate locking strategy depends on the balance between concurrency and data integrity requirements. Exclusive locks provide higher data protection by preventing concurrent access but can reduce system throughput due to blocking. Table locks simplify management and reduce overhead in low-concurrency environments but may limit scalability in high-transaction databases.
Exclusive Lock Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com