Device Provisioning Service enables seamless and secure enrollment of IoT devices at scale, streamlining the process of device identity creation and management in the cloud. It supports automated provisioning workflows that reduce manual effort and improve deployment efficiency, ensuring devices are properly authenticated before gaining access to the network. Discover how this service can simplify your IoT deployments and enhance device lifecycle management by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
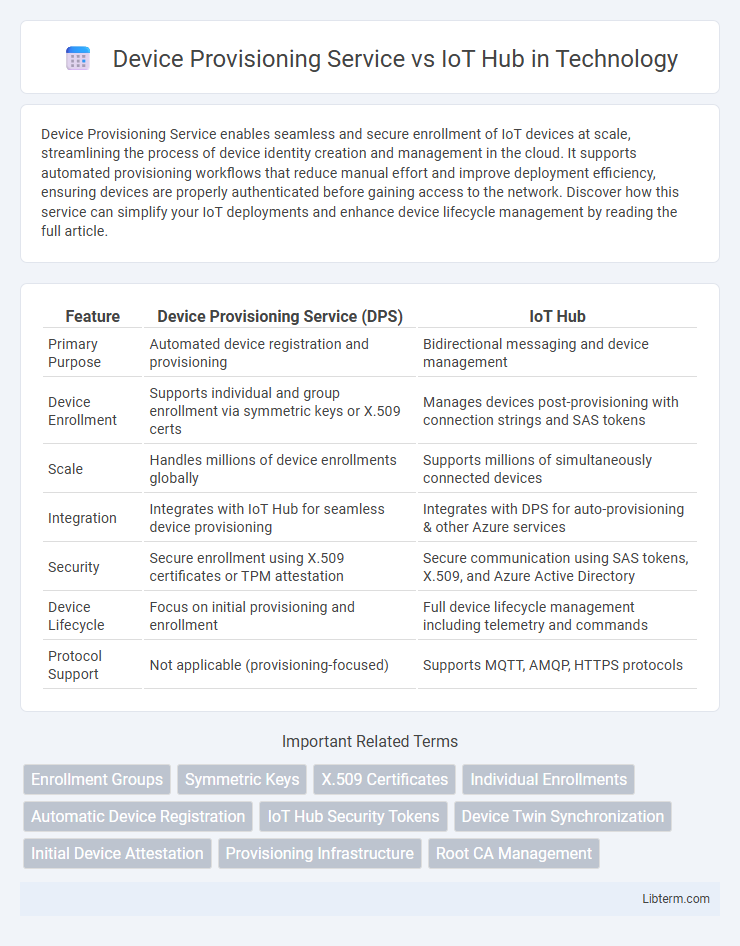
| Feature | Device Provisioning Service (DPS) | IoT Hub |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Automated device registration and provisioning | Bidirectional messaging and device management |
| Device Enrollment | Supports individual and group enrollment via symmetric keys or X.509 certs | Manages devices post-provisioning with connection strings and SAS tokens |
| Scale | Handles millions of device enrollments globally | Supports millions of simultaneously connected devices |
| Integration | Integrates with IoT Hub for seamless device provisioning | Integrates with DPS for auto-provisioning & other Azure services |
| Security | Secure enrollment using X.509 certificates or TPM attestation | Secure communication using SAS tokens, X.509, and Azure Active Directory |
| Device Lifecycle | Focus on initial provisioning and enrollment | Full device lifecycle management including telemetry and commands |
| Protocol Support | Not applicable (provisioning-focused) | Supports MQTT, AMQP, HTTPS protocols |
Introduction to Device Provisioning Service and IoT Hub
Device Provisioning Service (DPS) simplifies the large-scale provisioning of IoT devices by automating device enrollment and secure key management, enabling zero-touch device setup. IoT Hub acts as a central message hub, facilitating reliable bi-directional communication between IoT applications and devices at scale while enforcing security and device management protocols. Together, DPS streamlines initial device onboarding, while IoT Hub manages ongoing device interaction and telemetry data flow.
Core Functions of Device Provisioning Service
Device Provisioning Service (DPS) automates the secure and scalable provisioning of IoT devices to IoT Hub, enabling zero-touch device enrollment and configuration at scale. DPS assigns device identities, handles initial authentication, and dynamically allocates devices to the appropriate IoT Hub based on predefined rules. Core functions include managing device enrollment types, supporting certificate-based authentication, and ensuring reliable device lifecycle management in multi-tenant IoT environments.
Key Features of IoT Hub
IoT Hub offers secure device-to-cloud and cloud-to-device messaging, supporting bi-directional communication, device management, and scalable device provisioning. It provides advanced features like message routing, twin device synchronization, and enterprise-grade security protocols including per-device authentication. IoT Hub integrates seamlessly with Azure services, enabling real-time analytics, device monitoring, and automated responses for large-scale Internet of Things deployments.
Device Registration: DPS vs IoT Hub
Device Provisioning Service (DPS) automates IoT device registration by securely provisioning devices to the appropriate IoT Hub without manual intervention, supporting zero-touch enrollment at scale. IoT Hub handles direct device registration but requires manual enrollment or preconfiguration of devices, limiting scalability and flexibility in large deployments. DPS enhances device lifecycle management by integrating with IoT Hub for streamlined, secure, and scalable device onboarding processes.
Security Mechanisms Comparison
Device Provisioning Service (DPS) enhances IoT Hub security by automating secure device enrollment using attestation methods such as X.509 certificates, TPM, and symmetric keys, ensuring only authenticated devices connect. IoT Hub provides robust security through per-device identity registry, end-to-end encryption, and access control policies that limit permissions via shared access keys or Azure Active Directory integration. Combining DPS with IoT Hub creates a layered security model that mitigates risks by separating the provisioning process from ongoing device communication and management.
Scalability Considerations
Device Provisioning Service (DPS) offers critical scalability advantages by enabling zero-touch, just-in-time provisioning for millions of IoT devices across multiple IoT hubs. IoT Hub efficiently manages bi-directional communication and device telemetry but relies on DPS for large-scale automated enrollment and device provisioning workflows. Together, DPS and IoT Hub provide a scalable, secure infrastructure that supports massive device fleets with dynamic provisioning and seamless lifecycle management.
Workflow Integration and Automation
Device Provisioning Service (DPS) automates the registration and initial configuration of IoT devices by securely assigning them to the appropriate IoT Hub, streamlining bulk device onboarding workflows. IoT Hub manages two-way communication, device twin synchronization, and command execution, enabling real-time device management and telemetry data processing within automated systems. Integrating DPS with IoT Hub creates a seamless workflow automation framework, enhancing scalability, security, and operational efficiency in large-scale IoT deployments.
Cost and Pricing Differences
Azure Device Provisioning Service (DPS) offers a cost-effective solution for automatic device enrollment, charging based on the number of registration operations, typically priced per million operations. In contrast, Azure IoT Hub pricing depends on the number of messages, tiers, and features, with higher tiers providing advanced capabilities but at increased monthly rates per unit. Organizations managing large-scale device onboarding may reduce costs with DPS by minimizing manual provisioning, whereas IoT Hub costs scale with telemetry volume and device connectivity demands.
Use Case Scenarios
Device Provisioning Service (DPS) excels in large-scale, zero-touch device enrollment where automated and secure device registration is required before connecting to the IoT Hub. IoT Hub acts as the central message hub for bi-directional communication, telemetry data ingestion, and device management post-provisioning. Use cases involving fleet deployment, device identity lifecycle management, and secure onboarding rely heavily on DPS, while IoT Hub is crucial for real-time monitoring, command and control, and data routing in operational IoT solutions.
Choosing the Right Solution: DPS or IoT Hub
Choosing between Device Provisioning Service (DPS) and IoT Hub depends on the specific IoT deployment requirements; DPS streamlines the initial device registration and provisioning process by automating secure device onboarding at scale. IoT Hub offers comprehensive device management, bi-directional communication, and telemetry data ingestion, making it essential for ongoing device control and monitoring after provisioning. For scalable, secure onboarding, DPS is ideal, whereas IoT Hub is better suited for full lifecycle management and continuous interaction with connected devices.
Device Provisioning Service Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com