Log analysis enables you to uncover critical insights by systematically examining event logs generated by software applications and systems. This process helps identify security breaches, operational issues, and performance bottlenecks, improving overall system reliability and efficiency. Discover how mastering log analysis can transform your troubleshooting and monitoring strategies by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
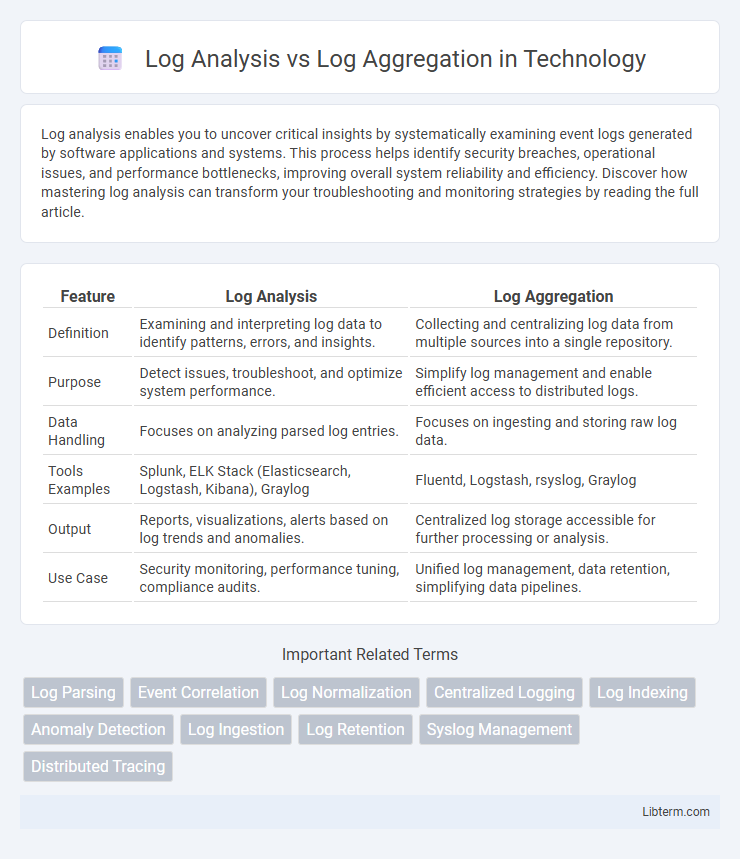
| Feature | Log Analysis | Log Aggregation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Examining and interpreting log data to identify patterns, errors, and insights. | Collecting and centralizing log data from multiple sources into a single repository. |
| Purpose | Detect issues, troubleshoot, and optimize system performance. | Simplify log management and enable efficient access to distributed logs. |
| Data Handling | Focuses on analyzing parsed log entries. | Focuses on ingesting and storing raw log data. |
| Tools Examples | Splunk, ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana), Graylog | Fluentd, Logstash, rsyslog, Graylog |
| Output | Reports, visualizations, alerts based on log trends and anomalies. | Centralized log storage accessible for further processing or analysis. |
| Use Case | Security monitoring, performance tuning, compliance audits. | Unified log management, data retention, simplifying data pipelines. |
Introduction to Log Analysis and Log Aggregation
Log analysis involves examining and interpreting log data to identify patterns, anomalies, and insights essential for troubleshooting and security purposes. Log aggregation refers to the centralized collection of log files from various sources into a single platform, enabling easier management and quicker access to comprehensive data sets. Together, log analysis and log aggregation optimize IT operations by enhancing data visibility and accelerating incident response times.
Defining Log Analysis
Log analysis involves examining and interpreting log data to identify patterns, detect anomalies, and derive actionable insights for system performance and security monitoring. It uses tools and techniques such as parsing, correlation, and visualization to transform raw logs into meaningful information. Unlike log aggregation, which centralizes log data from multiple sources, log analysis focuses on understanding and troubleshooting the data to improve operations.
Understanding Log Aggregation
Log aggregation involves collecting and centralizing log data from multiple sources into a unified platform, enabling efficient storage, search, and analysis. This process simplifies monitoring, troubleshooting, and security by providing a consolidated view of system events across distributed environments. Effective log aggregation tools support scalability, real-time processing, and integration with alerting systems to enhance operational visibility.
Key Differences Between Log Analysis and Log Aggregation
Log analysis involves examining log data to identify patterns, anomalies, and insights for troubleshooting and performance monitoring, while log aggregation focuses on collecting and centralizing logs from multiple sources into a single repository. The key differences lie in their purposes: log aggregation serves as the foundation for organizing log data, whereas log analysis interprets that data to support decision-making and incident response. Effective IT management relies on combining robust log aggregation tools like Elasticsearch or Splunk with advanced log analysis techniques such as pattern recognition and machine learning algorithms.
Use Cases of Log Analysis
Log analysis is essential for real-time monitoring, security threat detection, and troubleshooting by examining application and system logs to extract actionable insights. It enables proactive incident response, compliance auditing, and performance optimization through detailed pattern recognition and anomaly detection. Use cases include identifying root causes of errors, monitoring user activity for suspicious behavior, and enhancing operational efficiency across IT environments.
Scenarios Suited for Log Aggregation
Log aggregation is ideal for environments with multiple distributed systems or microservices requiring centralized log collection and real-time analysis to quickly identify system-wide issues. Scenarios involving compliance audits, troubleshooting complex multi-node infrastructure, and performance monitoring benefit greatly from consolidated logs in a unified platform. This approach enhances log query efficiency, supports scalability, and enables correlation of events across diverse sources for comprehensive insights.
Benefits of Log Analysis vs Log Aggregation
Log analysis enables real-time insights and proactive issue detection by examining log data for patterns, anomalies, and errors, which improves system monitoring and troubleshooting efficiency. Log aggregation centralizes logs from multiple sources but lacks the in-depth analytical capabilities necessary for predictive maintenance and detailed root cause analysis. Organizations gain greater operational visibility and faster incident response through log analysis compared to basic log aggregation, enhancing overall IT infrastructure performance.
Limitations and Challenges
Log analysis faces challenges such as processing vast volumes of unstructured data, leading to slow query response times and difficulty in detecting anomalies without advanced machine learning models. Log aggregation struggles with scalability issues, as centralizing logs from diverse sources can create bottlenecks and data redundancy, complicating storage management and cost efficiency. Both approaches encounter limitations in real-time monitoring and require robust infrastructure to maintain data integrity and security across distributed environments.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Needs
Log analysis involves examining and interpreting log data to identify patterns, errors, and trends, providing actionable insights for troubleshooting and performance optimization. Log aggregation collects and centralizes logs from multiple sources into a unified platform, enabling easier access, correlation, and storage. Choosing the right approach depends on your organization's complexity, volume of data, and need for real-time insights versus long-term storage and compliance requirements.
Conclusion: Log Analysis or Log Aggregation?
Log analysis provides deep insights by examining and interpreting log data patterns, enabling proactive issue detection and performance optimization. Log aggregation centralizes log data from multiple sources, enhancing accessibility and simplifying management without inherently analyzing the content. For comprehensive IT monitoring, combining log aggregation with advanced log analysis delivers the most effective solution.
Log Analysis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com