Cloud computing revolutionizes data storage and processing by offering scalable, on-demand resources accessible via the internet. This technology enhances operational efficiency, reduces IT costs, and supports seamless collaboration across different locations. Discover how cloud computing can transform your business by exploring the following comprehensive insights.
Table of Comparison
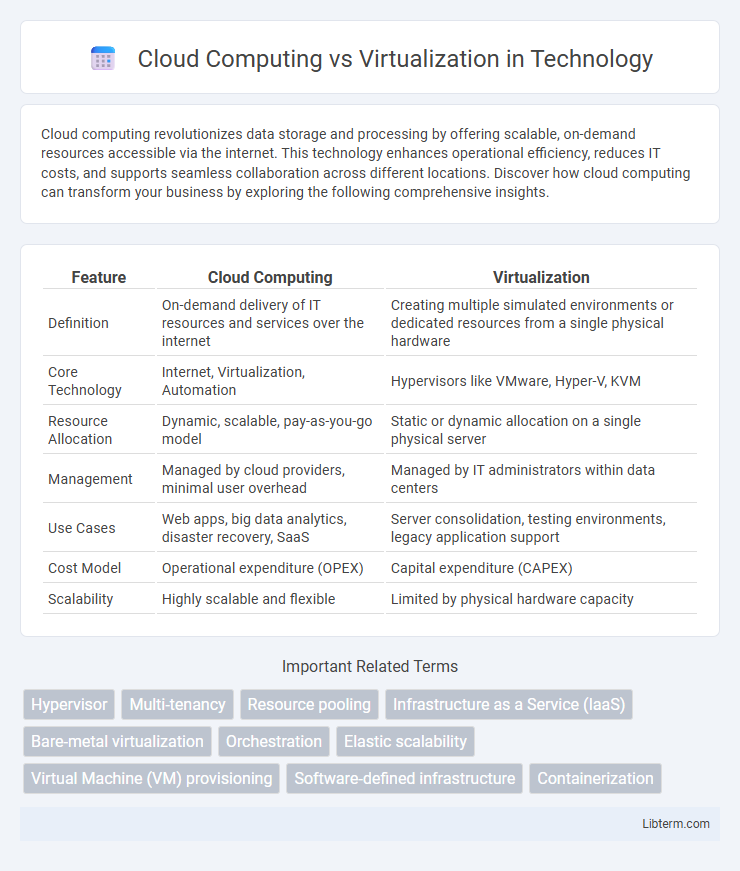
| Feature | Cloud Computing | Virtualization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | On-demand delivery of IT resources and services over the internet | Creating multiple simulated environments or dedicated resources from a single physical hardware |
| Core Technology | Internet, Virtualization, Automation | Hypervisors like VMware, Hyper-V, KVM |
| Resource Allocation | Dynamic, scalable, pay-as-you-go model | Static or dynamic allocation on a single physical server |
| Management | Managed by cloud providers, minimal user overhead | Managed by IT administrators within data centers |
| Use Cases | Web apps, big data analytics, disaster recovery, SaaS | Server consolidation, testing environments, legacy application support |
| Cost Model | Operational expenditure (OPEX) | Capital expenditure (CAPEX) |
| Scalability | Highly scalable and flexible | Limited by physical hardware capacity |
Introduction to Cloud Computing and Virtualization
Cloud computing delivers scalable computing resources over the internet, enabling on-demand access to servers, storage, and applications without physical hardware management. Virtualization is the foundational technology that creates virtual versions of physical hardware, allowing multiple operating systems to run concurrently on a single server. Together, virtualization enhances cloud computing efficiency by optimizing resource allocation and enabling dynamic workload management.
Key Differences Between Cloud Computing and Virtualization
Cloud computing delivers scalable and on-demand IT resources and services over the internet, enabling businesses to access computing power, storage, and applications without managing physical hardware. Virtualization is a technology that creates multiple simulated environments or virtual machines on a single physical server, improving resource utilization and isolation. The key difference lies in cloud computing's broader scope for service delivery and management, while virtualization is a foundational technology that underpins cloud infrastructure by abstracting hardware resources.
How Virtualization Works
Virtualization functions by creating a virtual version of physical hardware through a hypervisor, which allows multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical server simultaneously. Each VM operates as an independent system with its own operating system and applications, enabling efficient resource allocation and isolation. This technology underpins cloud computing by providing scalable, flexible infrastructure that supports on-demand resource provisioning and dynamic workload management.
How Cloud Computing Works
Cloud computing operates by delivering scalable and on-demand computing resources over the internet through data centers equipped with virtualization technology. Virtualization abstracts physical hardware into multiple virtual machines, enabling efficient resource allocation and multi-tenant environments. This infrastructure allows cloud service providers to offer services such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) with elasticity and pay-as-you-go pricing models.
Benefits of Virtualization
Virtualization enhances resource utilization by enabling multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical server, reducing hardware costs and energy consumption. It simplifies IT management through isolated environments, improving security and minimizing downtime during maintenance or failures. Virtualization also allows for rapid deployment and scalability of applications, increasing operational efficiency in data centers.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers scalable resources on-demand, reducing the need for significant upfront hardware investments compared to traditional virtualization. It provides enhanced accessibility by enabling users to access services from any location with an internet connection, improving operational flexibility. Moreover, cloud platforms often include integrated security measures, automated updates, and managed services that simplify maintenance and boost overall efficiency.
Use Cases for Virtualization and Cloud Computing
Virtualization enables multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical server, optimizing resource use for development, testing, and legacy application support. Cloud computing offers scalable on-demand resources, ideal for web hosting, big data analytics, and disaster recovery solutions. Enterprises use virtualization to maximize hardware efficiency, while cloud computing supports dynamic workloads and global accessibility.
Security Considerations: Cloud vs Virtualization
Cloud computing security involves managing risks associated with multi-tenancy, data breaches, and compliance across diverse platforms, requiring robust encryption, identity management, and continuous monitoring. Virtualization security focuses on isolating virtual machines, securing hypervisors, and preventing lateral attacks within shared physical hardware environments. Both technologies demand strict access controls, regular vulnerability assessments, and patch management to mitigate threats effectively.
Cost Comparison: Cloud Computing vs Virtualization
Cloud computing offers a pay-as-you-go pricing model, reducing upfront infrastructure costs and allowing businesses to scale resources dynamically based on demand, which leads to cost savings in maintenance and hardware upgrades. Virtualization requires significant initial investment in physical servers and management software, with ongoing expenses for power, cooling, and IT staff, making it less flexible in operational costs. Cloud computing often proves more cost-effective for fluctuating workloads due to its elasticity and reduced capital expenditure compared to the fixed costs associated with virtualization infrastructure.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
Cloud computing offers scalable, on-demand access to computing resources over the internet, ideal for businesses seeking flexibility and cost-efficiency without heavy infrastructure investment. Virtualization enables multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical server, optimizing hardware utilization and providing isolated environments, which suits organizations with specific hardware control requirements. Evaluating workload demands, budget constraints, and scalability needs helps determine whether cloud computing or virtualization best aligns with your business objectives and IT strategy.
Cloud Computing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com