OpenID Connect is a simple identity layer built on top of the OAuth 2.0 protocol, enabling secure user authentication and single sign-on across multiple applications. It allows your applications to verify user identities while accessing basic profile information with minimal effort. Explore the rest of this article to understand how OpenID Connect can enhance your authentication processes.
Table of Comparison
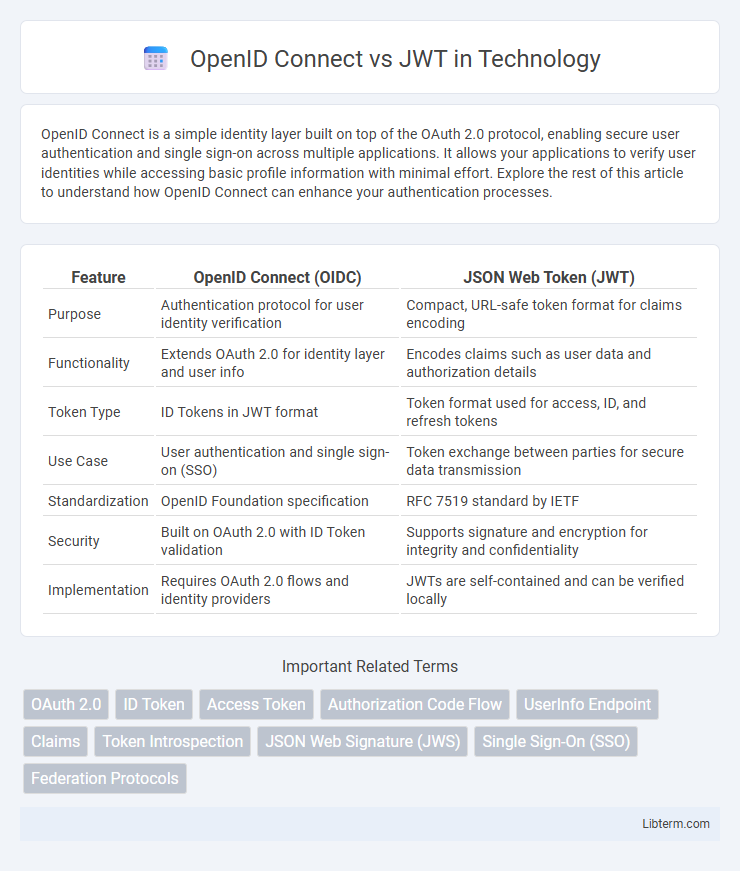
| Feature | OpenID Connect (OIDC) | JSON Web Token (JWT) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Authentication protocol for user identity verification | Compact, URL-safe token format for claims encoding |
| Functionality | Extends OAuth 2.0 for identity layer and user info | Encodes claims such as user data and authorization details |
| Token Type | ID Tokens in JWT format | Token format used for access, ID, and refresh tokens |
| Use Case | User authentication and single sign-on (SSO) | Token exchange between parties for secure data transmission |
| Standardization | OpenID Foundation specification | RFC 7519 standard by IETF |
| Security | Built on OAuth 2.0 with ID Token validation | Supports signature and encryption for integrity and confidentiality |
| Implementation | Requires OAuth 2.0 flows and identity providers | JWTs are self-contained and can be verified locally |
Introduction to OpenID Connect and JWT
OpenID Connect (OIDC) is an identity layer built on top of the OAuth 2.0 protocol, enabling clients to verify the identity of end-users based on authentication performed by an authorization server. JSON Web Token (JWT) is a compact, URL-safe token format used to securely transmit claims between parties, often utilized within OIDC for conveying identity and access information. While OIDC defines the authentication process and token exchange, JWT serves as the standardized token for encoding and validating user identity and session data.
What is OpenID Connect?
OpenID Connect is an authentication protocol built on top of the OAuth 2.0 framework that enables secure user identity verification and single sign-on (SSO) across applications. It uses JSON Web Tokens (JWT) to transmit identity information called ID tokens, which contain claims about the authenticated user. OpenID Connect standardizes the process of authenticating users while leveraging OAuth 2.0's authorization capabilities for seamless and secure access management.
What is JWT (JSON Web Token)?
JWT (JSON Web Token) is a compact, URL-safe token format used to securely transmit information between parties as a JSON object, primarily for authentication and authorization purposes. It consists of three parts: a header, payload, and signature, enabling verification of the token's authenticity and integrity without requiring server-side session storage. JWT is widely adopted in identity management systems, often serving as the underlying token format in OpenID Connect protocols for establishing trusted user identities.
Key Differences Between OpenID Connect and JWT
OpenID Connect is an authentication protocol built on top of the OAuth 2.0 framework that uses JWT (JSON Web Tokens) as a standardized token format for securely transmitting user identity information. While JWT is a token format representing claims encoded as a JSON object, OpenID Connect defines specific endpoints, flows, and scopes for identity verification and user authentication. Key differences include OpenID Connect's scope for identity layer and user profile data exchange, while JWT serves as a versatile token structure used in various authorization and authentication contexts beyond just OpenID Connect.
Use Cases: When to Use OpenID Connect vs JWT
OpenID Connect is ideal for authentication use cases where verifying user identity and obtaining profile information from an identity provider is required, such as single sign-on (SSO) in web and mobile apps. JWTs are primarily used for securely transmitting claims between parties, often applied in authorization scenarios to grant access to resources via access tokens. Choose OpenID Connect when conducting authentication flows with standardized user identity data, and opt for JWTs when implementing stateless authorization and securely exchanging information between services.
Security Considerations in OpenID Connect and JWT
OpenID Connect enhances security by building on OAuth 2.0 with ID tokens that are digitally signed and optionally encrypted, ensuring authenticity and confidentiality of user identity information. JWTs, often used as ID tokens or access tokens, rely on secure key management and appropriate signature algorithms like RS256 to prevent token forgery and replay attacks. Implementing proper token validation, audience restriction, and expiration handling are critical security practices in both OpenID Connect and JWT to mitigate risks such as token theft and impersonation.
Implementation Overview: OpenID Connect vs JWT
OpenID Connect is an authentication layer built on top of OAuth 2.0 that uses JWT (JSON Web Tokens) to securely transmit user identity information. JWT functions as a compact, URL-safe token format used in various protocols, including OpenID Connect, to encode claims about authentication and authorization. Implementing OpenID Connect involves configuring identity providers and handling ID tokens, while JWT implementation centers on creating, signing, and validating tokens for secure data exchange.
Performance Comparison: OpenID Connect vs JWT
OpenID Connect leverages JWT as its token format, ensuring efficient token transmission with compact and self-contained claims, which enhances performance in authentication workflows. JWT, being stateless and easily verifiable using cryptographic signatures, enables faster validation without frequent server lookups, reducing latency in distributed systems. However, OpenID Connect involves additional protocol flows and metadata exchange, which may introduce slight overhead compared to standalone JWT usage focused purely on token validation.
Pros and Cons of OpenID Connect and JWT
OpenID Connect offers robust identity verification and seamless integration with OAuth 2.0, enhancing user authentication through standardized ID tokens, but can introduce complexity and overhead in implementation. JWT (JSON Web Token) provides compact, URL-safe tokens ideal for stateless authentication and efficient data exchange, yet lacks built-in identity management features and requires careful handling to maintain security. Both technologies serve complementary roles, with OpenID Connect focusing on authentication and JWT on token-based authorization.
Choosing the Right Protocol: OpenID Connect or JWT
OpenID Connect extends OAuth 2.0 by adding an identity layer, making it ideal for user authentication and single sign-on scenarios, while JWT (JSON Web Token) serves as a compact token format used within various protocols for securely transmitting claims. Selecting OpenID Connect is optimal when user identity verification, session management, and standardized authentication flows are required. Use JWT independently when lightweight, stateless token exchange is needed, especially for authorization and information sharing without the overhead of a full authentication protocol.
OpenID Connect Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com