Integration streamlines diverse systems and processes to work seamlessly together, enhancing efficiency and reducing errors. By connecting software, data, and workflows, businesses can achieve real-time collaboration and improved decision-making. Explore the rest of this article to discover how integration can transform your operations.
Table of Comparison
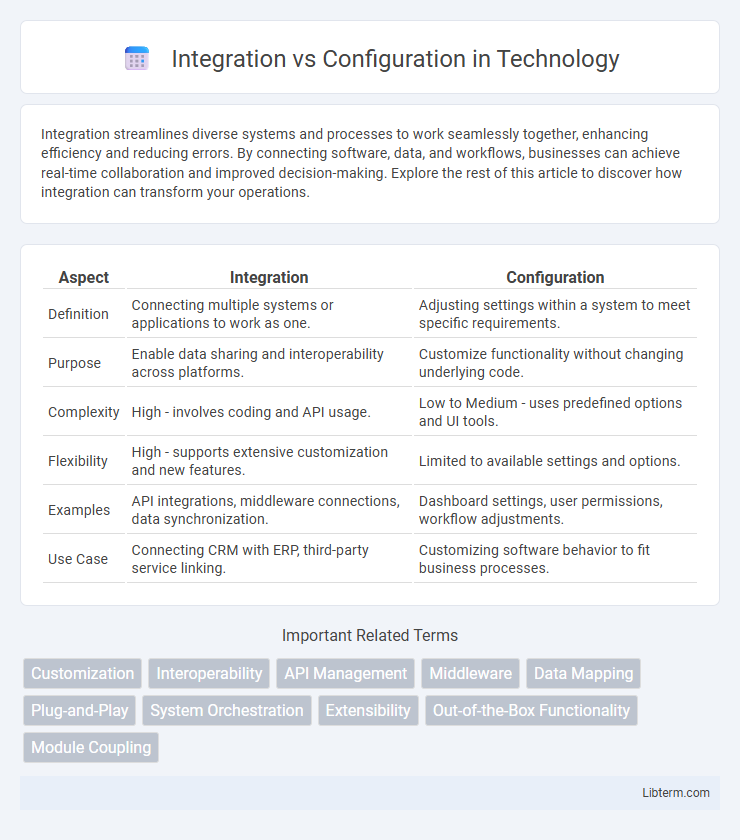
| Aspect | Integration | Configuration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Connecting multiple systems or applications to work as one. | Adjusting settings within a system to meet specific requirements. |
| Purpose | Enable data sharing and interoperability across platforms. | Customize functionality without changing underlying code. |
| Complexity | High - involves coding and API usage. | Low to Medium - uses predefined options and UI tools. |
| Flexibility | High - supports extensive customization and new features. | Limited to available settings and options. |
| Examples | API integrations, middleware connections, data synchronization. | Dashboard settings, user permissions, workflow adjustments. |
| Use Case | Connecting CRM with ERP, third-party service linking. | Customizing software behavior to fit business processes. |
Understanding Integration and Configuration
Integration involves combining different systems or software to work together seamlessly, enabling data sharing and unified workflows. Configuration refers to setting up software features and parameters to meet specific business needs without altering the underlying code. Understanding the distinction helps organizations choose whether to customize existing tools or connect multiple platforms for comprehensive solutions.
Key Differences Between Integration and Configuration
Integration involves connecting different software systems or components to work together seamlessly, enabling data exchange and unified workflows across platforms. Configuration refers to adjusting settings within a single system or application to customize its functionality according to user requirements without altering the underlying code. Key differences include integration's focus on interoperability between distinct systems and configuration's emphasis on optimizing a single system's performance and usability.
When to Choose Integration Over Configuration
Choose integration over configuration when complex data synchronization between multiple systems is required, ensuring real-time consistency and automation beyond static settings. Integration is essential when business processes demand seamless interoperability, such as connecting ERP systems with CRM platforms or enabling API-driven workflows. Opting for integration supports scalability and customization that configuration alone cannot achieve for dynamic, multi-system environments.
Benefits of Configuration in Modern Systems
Configuration in modern systems offers enhanced flexibility by allowing users to tailor software settings without altering core code, reducing deployment time and costs. It enables rapid adaptation to changing business requirements through parameter adjustments, improving system scalability and user experience. Maintaining configurations rather than custom integrations minimizes errors and eases system upgrades, fostering greater stability and maintainability.
Common Challenges in Integration Projects
Integration projects often face challenges such as data inconsistency, system incompatibility, and complex middleware management, which can delay deployment and increase costs. Ensuring seamless communication between disparate platforms requires robust API design, comprehensive error handling, and real-time data synchronization to maintain operational integrity. Addressing security vulnerabilities and maintaining consistent performance under varying loads are critical for successful and scalable integration outcomes.
Real-World Use Cases: Integration vs Configuration
Integration involves connecting different systems or software to enable seamless data flow and unified workflows, such as integrating CRM with ERP to synchronize customer and order information in real time. Configuration customizes software settings within its existing framework to match specific business requirements without altering the underlying code, exemplified by customizing Salesforce dashboards or adjusting workflow rules. Real-world use cases demonstrate integration when enterprises need complex interoperability across platforms, while configuration addresses tailored user experience and operational preferences within a single system.
Impact on System Scalability and Flexibility
Integration enhances system scalability by enabling seamless data exchange and interoperability across multiple platforms, allowing businesses to add or modify components without disrupting operations. Configuration supports flexibility by offering customizable settings within existing systems, enabling quick adjustments to meet changing requirements without extensive redevelopment. Combining integration and configuration optimizes both scalability and adaptability, ensuring systems can grow and evolve efficiently in dynamic environments.
Security Considerations for Both Approaches
Integration involves linking disparate systems to enable seamless data exchange, requiring robust authentication protocols, encrypted communication channels, and comprehensive access controls to mitigate risks of data breaches and unauthorized access. Configuration tailors system settings within a single platform, emphasizing granular permission management and secure default parameters to prevent misconfigurations that could expose vulnerabilities. Both approaches demand continuous monitoring, regular security audits, and adherence to compliance standards such as GDPR or HIPAA to ensure data integrity and protection throughout the system lifecycle.
Best Practices for Seamless Integration and Configuration
Adopting best practices for seamless integration and configuration involves using standardized APIs and modular design to ensure compatibility and scalability across systems. Leveraging automation tools for configuration management reduces errors and accelerates deployment time while maintaining consistency. Prioritizing clear documentation and version control supports efficient troubleshooting and smooth updates, fostering long-term system reliability.
Future Trends in Integration and Configuration
Future trends in integration emphasize the rise of AI-driven automation and low-code platforms, enabling seamless connectivity between diverse applications and systems. Configuration tools are evolving to become more user-centric, incorporating intuitive interfaces and adaptive settings that reduce the need for deep technical expertise. Both integration and configuration are moving towards cloud-native solutions, supporting scalability, real-time data synchronization, and enhanced security measures.
Integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com