Feature toggles enable developers to activate or deactivate software features without deploying new code, enhancing agility and reducing risk during releases. They support continuous delivery by allowing incremental feature rollout, A/B testing, and easy rollback in case of issues. Discover how feature toggles can improve Your development workflow and streamline releases by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
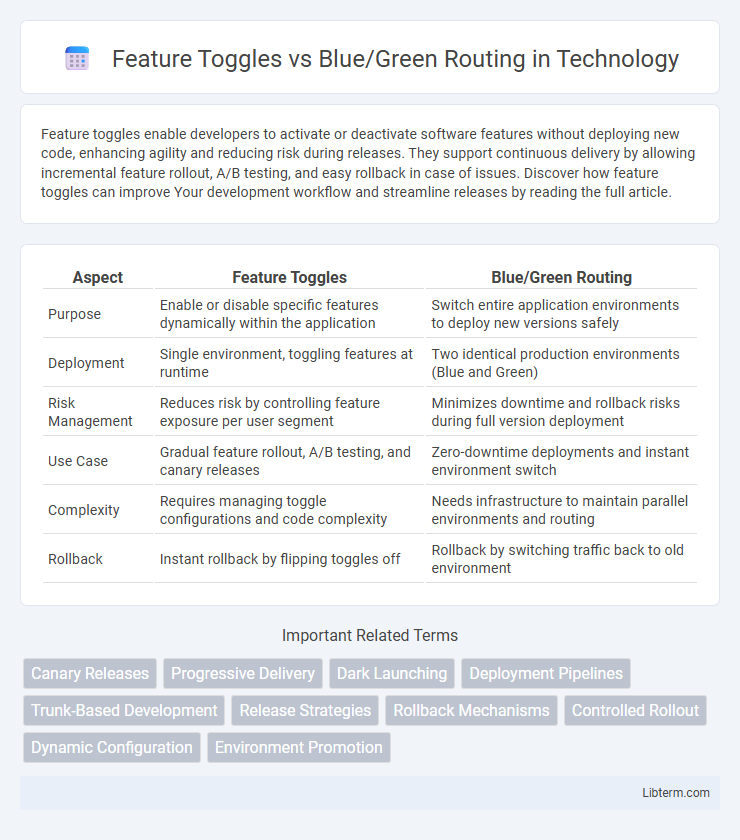
| Aspect | Feature Toggles | Blue/Green Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Enable or disable specific features dynamically within the application | Switch entire application environments to deploy new versions safely |
| Deployment | Single environment, toggling features at runtime | Two identical production environments (Blue and Green) |
| Risk Management | Reduces risk by controlling feature exposure per user segment | Minimizes downtime and rollback risks during full version deployment |
| Use Case | Gradual feature rollout, A/B testing, and canary releases | Zero-downtime deployments and instant environment switch |
| Complexity | Requires managing toggle configurations and code complexity | Needs infrastructure to maintain parallel environments and routing |
| Rollback | Instant rollback by flipping toggles off | Rollback by switching traffic back to old environment |
Introduction to Deployment Strategies
Feature toggles enable developers to activate or deactivate specific functionalities within a live application without redeploying code, facilitating continuous integration and delivery. Blue/green routing involves maintaining two identical production environments, allowing seamless traffic switching from the current (blue) to the new (green) version to minimize downtime and reduce deployment risks. Both strategies enhance deployment flexibility by managing feature exposure and environment transitions to improve application stability and user experience.
Understanding Feature Toggles
Feature toggles enable developers to activate or deactivate specific application features at runtime without deploying new code, facilitating continuous delivery and safer experimentation. They allow granular control over feature visibility, supporting A/B testing, canary releases, and gradual rollouts to targeted user groups. This approach reduces deployment risk by isolating code changes and enables rapid rollback through configuration changes instead of full redeployment.
Exploring Blue/Green Routing
Blue/Green Routing is a deployment strategy that uses two identical production environments to minimize downtime and reduce risk during software releases. Traffic is routed entirely to the "blue" environment while updates are deployed to the "green" environment; once the new version is tested, traffic switches seamlessly to green, enabling quick rollback to blue if issues arise. This approach ensures continuous availability and smooth transitions, making it ideal for high-availability applications requiring zero downtime deployments.
Key Differences Between Feature Toggles and Blue/Green Routing
Feature toggles enable dynamic activation or deactivation of software features within the same deployment, allowing granular control and rapid experimentation without redeploying. Blue/green routing involves maintaining two identical production environments (blue and green) and switching the entire user traffic between them for safe, full-version rollouts or rollbacks. The key differences lie in the deployment scope, where feature toggles target specific functionalities and blue/green routing switches entire application versions, impacting release flexibility and risk management strategies.
Use Cases for Feature Toggles
Feature toggles enable incremental feature rollout, dark launches, and A/B testing by allowing selective activation of features without deploying new code. They are ideal for continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines and can reduce risk by controlling exposure to new functionality at a granular level. Use cases include enabling beta features for specific user segments, performing gradual rollouts, and quickly disabling problematic features without downtime.
Use Cases for Blue/Green Routing
Blue/Green Routing is ideal for minimizing downtime and risk during deployment by running two identical production environments, allowing seamless traffic switching between the blue (current) and green (new) versions. This approach supports use cases such as safe rollout of major updates, quick rollback in case of failures, and zero-downtime deployments for high-availability applications. It is particularly effective for enterprise-grade systems where continuous uptime and gradual testing under real user loads are critical.
Benefits of Feature Toggles
Feature toggles enable developers to activate or deactivate specific functionalities without deploying new code, significantly reducing deployment risks and facilitating continuous integration. They allow for granular control over feature availability, supporting A/B testing and incremental rollouts to optimize user experience and gather real-time feedback. By decoupling feature release from code deployment, feature toggles enhance agility, improve collaboration between development and operations teams, and streamline rollback processes in case of issues.
Advantages of Blue/Green Routing
Blue/Green Routing enables seamless deployment by maintaining two identical production environments, allowing instant switch-over with minimal downtime and reduced deployment risk. This approach enhances system reliability and rollback capability, ensuring continuous availability and user experience consistency during updates. It simplifies testing in a real-world environment without affecting live traffic, providing a safer and more controlled release strategy compared to feature toggles.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Project
Feature toggles enable granular control over feature releases by allowing selective activation within the same environment, making them ideal for continuous integration and rapid experimentation. Blue/Green routing involves deploying two identical production environments to switch traffic seamlessly, minimizing downtime and risk during major releases. Choose feature toggles for incremental feature rollout and quick rollback, while blue/green routing suits projects demanding zero-downtime deployments and straightforward environment reversions.
Best Practices for Seamless Deployment
Feature toggles enable incremental feature rollout by selectively activating code paths, minimizing deployment risks through controlled exposure and fast rollback options. Blue/green routing maintains two identical production environments, directing traffic between them to ensure zero-downtime releases and instant rollback capability. Combining feature toggles with blue/green deployment ensures seamless updates by isolating feature releases within stable environment switches, optimizing both risk management and user experience continuity.
Feature Toggles Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com