Composition is the art of arranging ideas, words, and sentences to create clear, compelling pieces of writing that effectively communicate a message. Mastering composition involves understanding structure, grammar, and style to engage your audience and convey your thoughts precisely. Explore the rest of this article to enhance your writing skills and craft powerful compositions.
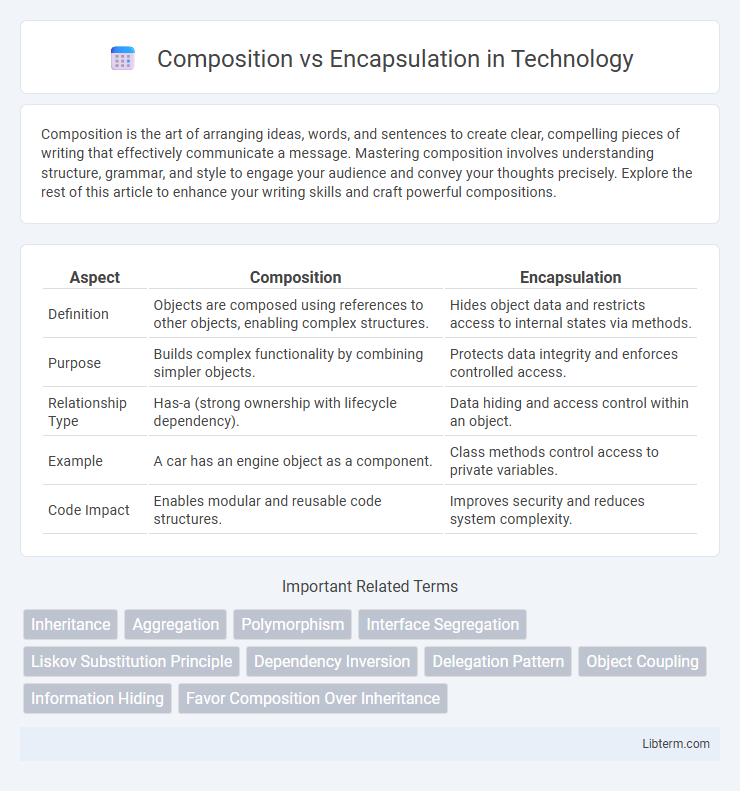
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Composition | Encapsulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Objects are composed using references to other objects, enabling complex structures. | Hides object data and restricts access to internal states via methods. |
| Purpose | Builds complex functionality by combining simpler objects. | Protects data integrity and enforces controlled access. |
| Relationship Type | Has-a (strong ownership with lifecycle dependency). | Data hiding and access control within an object. |
| Example | A car has an engine object as a component. | Class methods control access to private variables. |
| Code Impact | Enables modular and reusable code structures. | Improves security and reduces system complexity. |
Understanding Composition in Object-Oriented Design
Composition in object-oriented design refers to building complex objects by combining simpler, reusable components, promoting code modularity and flexibility. Unlike inheritance, composition delegates responsibilities to contained objects, enabling dynamic behavior changes at runtime. This design principle enhances maintainability and supports the "has-a" relationship, providing a clear structure for scalable software development.
The Core Principles of Encapsulation
Encapsulation is a fundamental object-oriented programming principle that restricts direct access to an object's data by bundling the data with methods that operate on it, ensuring controlled interaction through public interfaces. It promotes data hiding by making fields private and exposing only necessary functionalities via getters and setters, enhancing security and reducing system complexity. This core principle facilitates maintainability and modularity by preventing unintended interference and ensuring that object integrity remains intact during runtime.
Composition vs Encapsulation: Key Differences
Composition involves creating complex objects by combining simpler objects, emphasizing a "has-a" relationship, while encapsulation focuses on restricting access to an object's internal state through access modifiers, ensuring data hiding. Key differences include composition enabling object reuse and flexibility in building complex systems, whereas encapsulation enhances security and maintainability by controlling how data is accessed and modified. Composition often impacts system architecture by defining ownership and lifespan of components, whereas encapsulation is primarily a principle of information hiding within class design.
Benefits of Using Composition in Software Development
Composition promotes flexibility and reusability by allowing objects to be assembled from reusable components rather than relying on rigid inheritance hierarchies. This approach enhances maintainability and scalability by enabling developers to modify or replace individual parts without affecting the entire system. Composition also facilitates better encapsulation by keeping concerns separated, leading to clearer, more modular codebases in software development.
How Encapsulation Promotes Data Security
Encapsulation promotes data security by restricting direct access to an object's internal state through private variables and exposing only controlled interfaces or methods for interaction. This mechanism ensures that sensitive data cannot be altered or accessed unintentionally or maliciously, reducing the risk of data corruption. In contrast, composition focuses on building complex objects from simpler ones, emphasizing object relationships rather than safeguarding data integrity directly.
Real-World Examples: Composition and Encapsulation
Composition in software design represents a "has-a" relationship, such as a car having an engine and wheels as distinct objects within it, allowing modular assembly and reuse. Encapsulation involves restricting access to an object's internal state, exemplified by a class hiding its data fields and exposing only necessary methods for interaction, ensuring data integrity and security. Real-world applications include complex systems where composition builds flexible objects from components, while encapsulation safeguards internal processes from external interference.
When to Choose Composition Over Encapsulation
Choose composition over encapsulation when you need to build complex objects by combining simpler, reusable components, enabling flexibility and easier maintenance. Composition allows dynamic behavior changes at runtime by assembling different objects, whereas encapsulation primarily hides internal state within a single object. In scenarios requiring object collaboration and evolving functionality, composition offers superior design adaptability compared to encapsulation's data protection focus.
Common Pitfalls in Composition and Encapsulation
Common pitfalls in composition include tight coupling where objects overly depend on one another, making changes difficult and reducing reusability. In encapsulation, a frequent issue is inadequate access control, which can expose internal object states and lead to unintended side effects or misuse. Overusing encapsulation may also result in excessive getter and setter methods, undermining object-oriented principles by exposing too much internal detail.
Best Practices for Balancing Composition and Encapsulation
Balancing composition and encapsulation involves designing objects that use composition to delegate responsibilities while maintaining strict control over their internal state through encapsulation. Best practices include exposing only necessary interfaces, favoring composition to reuse functionality without inheritance, and ensuring that composed objects' internals remain hidden to prevent tight coupling. Adhering to principles like Single Responsibility and Law of Demeter enhances code maintainability and flexibility by promoting clear modular boundaries and controlled object interactions.
Future Trends in Object-Oriented Programming Design
Future trends in object-oriented programming design emphasize hybrid approaches combining composition and encapsulation to enhance modularity and maintainability. Advanced frameworks are leveraging composition patterns to achieve greater flexibility, enabling dynamic behavior changes at runtime while maintaining strict encapsulation of internal state. Increased adoption of microservices and component-based architectures drives demand for design principles that balance object independence with secure data hiding.
Composition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com