Rule-based systems use predefined logical rules to analyze data and make decisions, providing clear and transparent reasoning processes. These systems excel in environments where decision criteria are well-understood and consistent, ensuring reliable outcomes. Discover how implementing a rule-based system can enhance Your decision-making capabilities by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
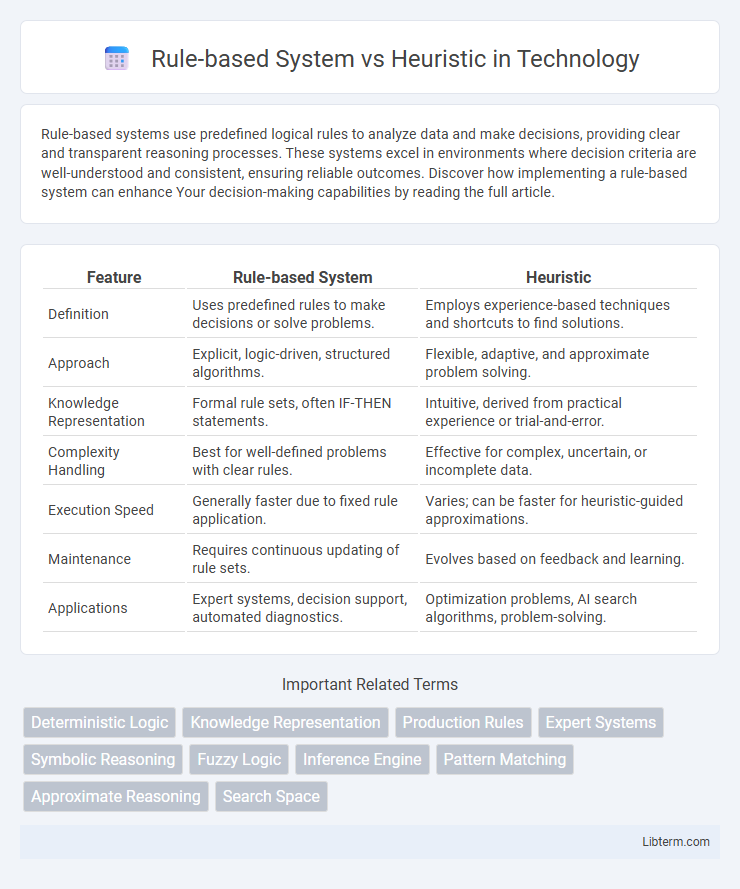
| Feature | Rule-based System | Heuristic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses predefined rules to make decisions or solve problems. | Employs experience-based techniques and shortcuts to find solutions. |
| Approach | Explicit, logic-driven, structured algorithms. | Flexible, adaptive, and approximate problem solving. |
| Knowledge Representation | Formal rule sets, often IF-THEN statements. | Intuitive, derived from practical experience or trial-and-error. |
| Complexity Handling | Best for well-defined problems with clear rules. | Effective for complex, uncertain, or incomplete data. |
| Execution Speed | Generally faster due to fixed rule application. | Varies; can be faster for heuristic-guided approximations. |
| Maintenance | Requires continuous updating of rule sets. | Evolves based on feedback and learning. |
| Applications | Expert systems, decision support, automated diagnostics. | Optimization problems, AI search algorithms, problem-solving. |
Introduction to Rule-based Systems and Heuristics
Rule-based systems rely on predefined rules and logic to derive conclusions or make decisions, using if-then statements to encode expert knowledge explicitly. Heuristics employ experience-based techniques or shortcut strategies to solve problems quickly when exhaustive rule application is impractical. Both methods support decision-making and problem-solving, but rule-based systems emphasize formalized knowledge representation, while heuristics focus on efficiency and approximate solutions.
Defining Rule-based Systems
Rule-based systems consist of a set of explicitly defined rules and logic that automate decision-making processes by applying these predetermined instructions to input data. These systems operate through if-then statements, enabling consistent reasoning and predictable outcomes, especially in well-structured environments. Compared to heuristic methods, which rely on experience-based techniques and approximations, rule-based systems emphasize formalized knowledge representation and transparent inference mechanisms.
Understanding Heuristic Methods
Heuristic methods leverage experience-based techniques to solve problems more efficiently than strict rule-based systems by using practical shortcuts and educated guesses. Unlike rule-based systems that rely on predefined, rigid rules, heuristics adapt dynamically to new information, enabling faster decision-making in complex or uncertain environments. This flexibility allows heuristic methods to handle incomplete data and optimize outcomes when exhaustive rule evaluation is impractical.
Key Differences Between Rule-based Systems and Heuristics
Rule-based systems rely on explicitly defined rules and logic to make decisions, providing transparency and predictability in outcomes, while heuristics use experience-based techniques or shortcuts to solve problems more quickly but with less certainty. Rule-based systems excel in structured environments with clear parameters, whereas heuristics are better suited to handling complex or uncertain scenarios where rules are incomplete or unavailable. The main difference lies in rule-based systems' deterministic approach versus heuristics' probabilistic and adaptive nature.
Advantages of Rule-based Systems
Rule-based systems offer clear advantages such as transparency and ease of maintenance due to their explicit if-then rules. They provide consistent and predictable results by following predefined logic, which enhances reliability in decision-making processes. The ability to easily update and expand rules allows for scalable and adaptable expert systems across various domains.
Benefits of Heuristic Approaches
Heuristic approaches offer significant benefits in problem-solving by providing faster decision-making processes compared to rigid rule-based systems, especially in complex or uncertain environments. These methods leverage experience-based techniques to generate approximate solutions, enhancing adaptability and efficiency without requiring exhaustive rules or complete information. Heuristics improve scalability and flexibility in dynamic systems, enabling more practical and context-sensitive outcomes.
Limitations and Challenges of Rule-based Methods
Rule-based systems face limitations in handling incomplete or ambiguous data due to their reliance on predefined rules, which restricts flexibility and adaptability in dynamic environments. They often require extensive manual rule creation and maintenance, making scaling and updating resource-intensive and error-prone. The rigid structure leads to poor performance in complex decision-making tasks where nuanced understanding or learning from new data is crucial.
Drawbacks of Heuristic Techniques
Heuristic techniques often suffer from a lack of guaranteed optimal solutions and can be prone to errors due to their reliance on shortcuts or rules of thumb. These techniques may produce inconsistent results when applied to complex or unfamiliar problems, limiting their reliability in mission-critical applications. Their performance heavily depends on the quality of the heuristic function, which can be difficult to design and validate across diverse scenarios.
Real-world Applications: Rule-based vs Heuristic
Rule-based systems excel in environments with clear, well-defined rules, such as expert systems for medical diagnosis or fraud detection, ensuring consistent and explainable outcomes. Heuristic approaches thrive in complex, dynamic scenarios like game playing or route optimization, where approximate solutions are needed quickly despite uncertainty. Real-world applications often combine both, leveraging rule-based precision and heuristic flexibility for improved decision-making and problem-solving efficiency.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Problem
Rule-based systems excel in applications requiring clear, deterministic decision-making with well-defined rules and predictable outcomes. Heuristic approaches offer flexibility and speed in complex or poorly defined problems by approximating solutions and handling uncertainty effectively. Selecting the right approach depends on factors such as problem complexity, availability of domain knowledge, and the need for adaptability versus precision.
Rule-based System Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com