Object storage offers scalable, cost-effective solutions for managing vast amounts of unstructured data by storing it as discrete units called objects with metadata. This approach ensures enhanced data durability, easy accessibility, and seamless integration with cloud environments, making it ideal for backup, archiving, and big data analytics. Explore the rest of this article to discover how object storage can optimize your data management strategy.
Table of Comparison
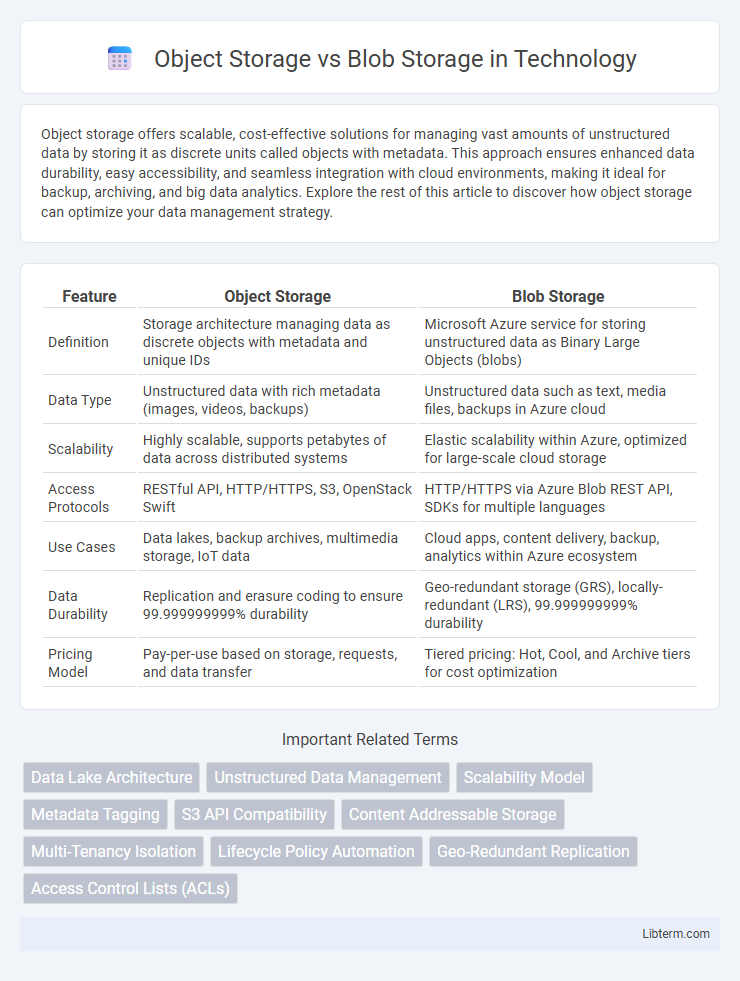
| Feature | Object Storage | Blob Storage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Storage architecture managing data as discrete objects with metadata and unique IDs | Microsoft Azure service for storing unstructured data as Binary Large Objects (blobs) |
| Data Type | Unstructured data with rich metadata (images, videos, backups) | Unstructured data such as text, media files, backups in Azure cloud |
| Scalability | Highly scalable, supports petabytes of data across distributed systems | Elastic scalability within Azure, optimized for large-scale cloud storage |
| Access Protocols | RESTful API, HTTP/HTTPS, S3, OpenStack Swift | HTTP/HTTPS via Azure Blob REST API, SDKs for multiple languages |
| Use Cases | Data lakes, backup archives, multimedia storage, IoT data | Cloud apps, content delivery, backup, analytics within Azure ecosystem |
| Data Durability | Replication and erasure coding to ensure 99.999999999% durability | Geo-redundant storage (GRS), locally-redundant (LRS), 99.999999999% durability |
| Pricing Model | Pay-per-use based on storage, requests, and data transfer | Tiered pricing: Hot, Cool, and Archive tiers for cost optimization |
Understanding Object Storage
Object Storage is a data storage architecture designed to handle vast amounts of unstructured data by managing data as objects, each with its own metadata and unique identifier, enabling scalable and efficient retrieval. Unlike traditional file systems, Object Storage provides enhanced durability, versioning, and metadata management, making it ideal for cloud-native applications, big data analytics, and multimedia storage. Its flat namespace and RESTful API access optimize performance and integration while supporting high availability and disaster recovery.
What is Blob Storage?
Blob Storage is a type of object storage designed specifically for storing large amounts of unstructured data such as text, images, videos, and backups within cloud environments like Microsoft Azure. It enables scalable, cost-effective storage with features such as tiered access levels, high availability, and integration with content delivery networks. Blob Storage supports data types categorized as block blobs, append blobs, and page blobs, optimized for different use cases including streaming and random read/write operations.
Key Differences Between Object and Blob Storage
Object storage organizes data as discrete units called objects, each containing metadata, unique identifiers, and data, making it ideal for unstructured data and scalable applications. Blob storage specifically refers to a type of object storage optimized by platforms like Microsoft Azure for storing large amounts of unstructured binary data such as images, videos, and backups. The key differences include object storage's broader application scope and support for extensive metadata customization, while blob storage often emphasizes seamless integration with cloud services and tiered access for cost-effective data management.
Advantages of Object Storage
Object Storage offers scalable, cost-effective data management suitable for large volumes of unstructured data, providing metadata-rich objects that enhance data organization and retrieval. It supports distributed architectures, ensuring high durability and availability through replication and erasure coding, which optimizes data protection. Object Storage also facilitates seamless integration with cloud-native applications by offering RESTful APIs, enabling flexible and efficient data access across diverse environments.
Benefits of Blob Storage
Blob Storage offers scalable and cost-effective storage for unstructured data such as images, videos, and backups, enabling efficient handling of large amounts of data with high durability and availability. It supports advanced features like tiered storage options (hot, cool, and archive tiers) that optimize costs based on access frequency and data retention requirements. Blob Storage integrates seamlessly with Azure services, providing enhanced security, data management, and global accessibility for cloud-native applications and distributed architectures.
Use Cases for Object Storage
Object storage excels in managing vast amounts of unstructured data such as multimedia files, backups, and big data analytics, making it ideal for enterprises requiring scalable, durable, and cost-effective storage solutions. Use cases include cloud-native applications, media repositories, IoT data lakes, and archival storage that benefit from metadata-rich, distributed storage architectures. Its ability to handle billions of objects with high availability and seamless integration with data management platforms distinguishes it from blob storage, which is often optimized for simpler file storage scenarios.
Common Scenarios for Blob Storage
Blob Storage is ideal for storing unstructured data such as images, videos, backup files, and log files, making it perfect for web and mobile applications, content delivery, and disaster recovery scenarios. It supports massive scalability and allows for efficient handling of large amounts of data with high availability and durability, which is critical for big data analytics and media streaming. Enterprises commonly use Blob Storage to serve documents and media files directly to users, leveraging its tiered storage options to optimize costs based on access patterns.
Performance Comparison: Object vs Blob Storage
Object storage offers scalable, metadata-rich management ideal for unstructured data, while blob storage emphasizes optimized performance for large binary files often used in cloud applications. Performance comparison reveals blob storage typically provides faster data retrieval and lower latency for large sequential read/write operations, whereas object storage excels in handling massive volumes of smaller files with enhanced metadata querying capabilities. Choice depends on workload requirements: object storage suits complex data indexing and metadata needs, blob storage favors throughput-intensive scenarios such as streaming and backup solutions.
Security Considerations in Object and Blob Storage
Object storage and blob storage both employ robust security measures such as encryption at rest and in transit, access control policies, and multi-factor authentication to protect data from unauthorized access. Object storage often integrates with identity management systems like AWS IAM or Azure Active Directory for granular permissions, while blob storage emphasizes container-level access controls and Shared Access Signatures (SAS) for temporary, limited access. Both storage types support compliance certifications and logging mechanisms to ensure data integrity and auditability in secure cloud environments.
Choosing the Right Storage Solution
Object storage offers scalable management of unstructured data ideal for large-scale applications, while blob storage provides optimized storage for binary large objects commonly used in web and media services. Evaluating factors such as data access patterns, scalability requirements, integration capabilities, and cost efficiency is essential when choosing the right storage solution. Selecting the appropriate option enhances performance, supports data growth, and aligns with specific workload demands.
Object Storage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com