In-band management allows you to control network devices through the same channel used for regular data traffic, streamlining administration without the need for separate management interfaces. This approach simplifies infrastructure but requires robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access. Explore the rest of the article to understand how in-band management enhances network efficiency and security.
Table of Comparison
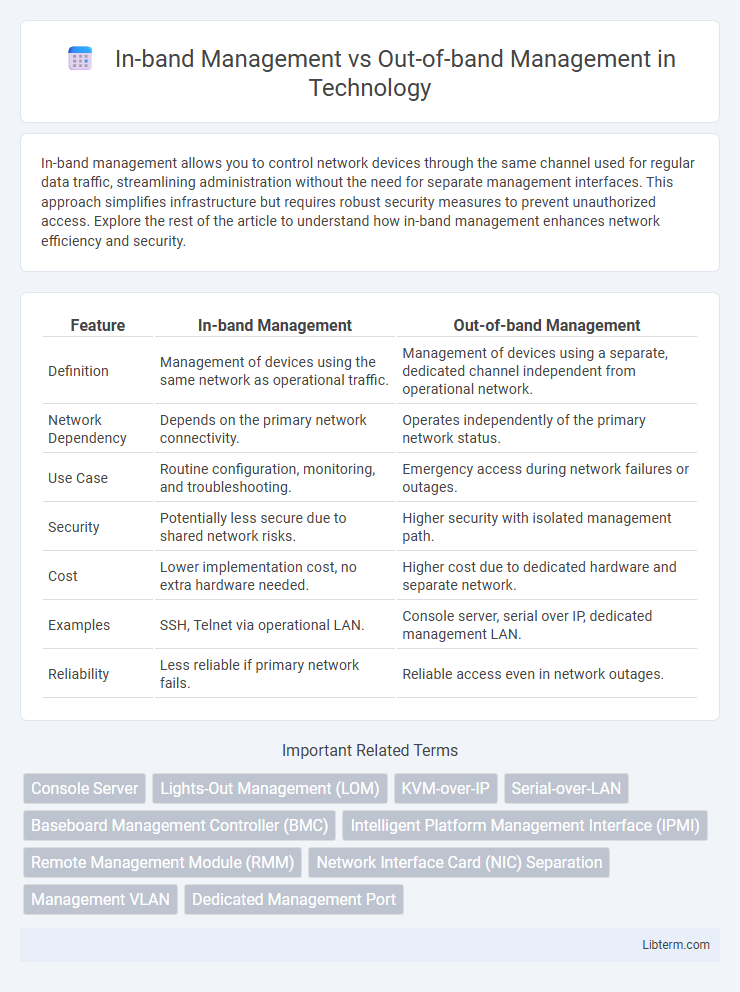
| Feature | In-band Management | Out-of-band Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Management of devices using the same network as operational traffic. | Management of devices using a separate, dedicated channel independent from operational network. |
| Network Dependency | Depends on the primary network connectivity. | Operates independently of the primary network status. |
| Use Case | Routine configuration, monitoring, and troubleshooting. | Emergency access during network failures or outages. |
| Security | Potentially less secure due to shared network risks. | Higher security with isolated management path. |
| Cost | Lower implementation cost, no extra hardware needed. | Higher cost due to dedicated hardware and separate network. |
| Examples | SSH, Telnet via operational LAN. | Console server, serial over IP, dedicated management LAN. |
| Reliability | Less reliable if primary network fails. | Reliable access even in network outages. |
Introduction to Network Management Methods
In-band management refers to network management methods that use the same communication channels and data paths as regular network traffic, enabling administrators to configure and monitor devices through the primary network connections. Out-of-band management utilizes dedicated management interfaces or separate networks specifically designed for administrative access, ensuring uninterrupted control even during network failures or outages. Effective network management strategies often combine both in-band and out-of-band methods to enhance reliability, security, and accessibility of network infrastructure.
Defining In-band Management
In-band management refers to the process of managing network devices through the same communication channels used for regular data traffic, typically via the primary network link. This method allows administrators to configure and monitor devices using protocols such as SSH, Telnet, or SNMP over the standard network infrastructure. In-band management is cost-effective and straightforward but can be vulnerable to network outages or performance issues since it relies on the operational state of the main network.
Understanding Out-of-band Management
Out-of-band management provides a dedicated, separate channel for network device access, enabling administrators to monitor and configure equipment even during primary network failures. This method uses independent management interfaces such as serial consoles, cellular modems, or dedicated Ethernet ports to ensure continuous availability and robust control. Out-of-band management enhances network reliability, reduces downtime, and supports secure remote troubleshooting without impacting regular data traffic.
Key Differences Between In-band and Out-of-band Management
In-band management uses the same network paths as regular data traffic to manage devices, making it cost-effective but vulnerable to network failures that impair management access. Out-of-band management operates on a separate and dedicated network interface, ensuring uninterrupted device control even when the primary network is down, enhancing reliability and security. Key differences include bandwidth usage, failure resilience, and security risks, with out-of-band offering superior isolation and direct hardware access compared to the shared resources in in-band management.
Advantages of In-band Management
In-band management allows network administrators to monitor and control devices using the same network channels as regular data traffic, reducing the need for additional hardware and lowering costs. This approach streamlines configuration and troubleshooting processes by enabling remote access through existing network infrastructure. In-band management supports real-time monitoring and quick response to network issues, enhancing operational efficiency and minimizing downtime.
Benefits of Out-of-band Management
Out-of-band management provides continuous remote access to network devices regardless of system status, enabling administrators to troubleshoot and resolve issues even during primary network failures. This method enhances security by isolating management traffic from standard data flows, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches. Reliable hardware interfaces dedicated to out-of-band management improve operational efficiency by allowing proactive maintenance and faster recovery without impacting regular network performance.
Security Implications: In-band vs Out-of-band
In-band management transmits management data over the same network used for regular traffic, increasing vulnerability to cyberattacks such as interception or denial-of-service that can compromise device control. Out-of-band management uses a separate, dedicated management channel isolated from the primary network, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access and ensuring continuous device availability during network outages. Security protocols for out-of-band management often include encrypted sessions and multi-factor authentication to enhance protection against intrusion and tampering.
Use Cases for Each Management Approach
In-band management uses the same network as regular data traffic, making it ideal for managing devices in stable network environments where cost efficiency and simplicity are prioritized. Out-of-band management employs a dedicated channel, enabling remote access to network equipment even during network failures or outages, which is critical for emergency troubleshooting and maintaining high-availability systems. Use cases for in-band management include routine configuration and monitoring within enterprise LANs, while out-of-band management is essential for data centers, remote branch offices, and disaster recovery scenarios.
Choosing the Right Management Solution
In-band management utilizes the same network used by regular data traffic, providing cost efficiency but risking performance issues during network outages. Out-of-band management operates via a dedicated channel, ensuring reliable access to devices even when the primary network fails, making it ideal for critical infrastructure. Selecting the right management solution depends on factors such as network complexity, required uptime, and budget constraints, with hybrid approaches often balancing cost and control effectively.
Future Trends in Network Management
Future trends in network management emphasize increasing reliance on out-of-band management for enhanced security and uninterrupted remote access during network failures. In-band management continues evolving with AI-driven automation and analytics to optimize real-time network performance and fault detection. Hybrid approaches integrating both in-band and out-of-band techniques enable scalable, resilient, and adaptive network infrastructures critical for next-generation IoT and 5G environments.
In-band Management Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com