Automation enhances efficiency by streamlining repetitive tasks and reducing human error, allowing businesses to focus on strategic growth. Implementing automation tools can lead to significant cost savings and improved productivity across various industries. Discover how automation can transform your operations by exploring the rest of the article.
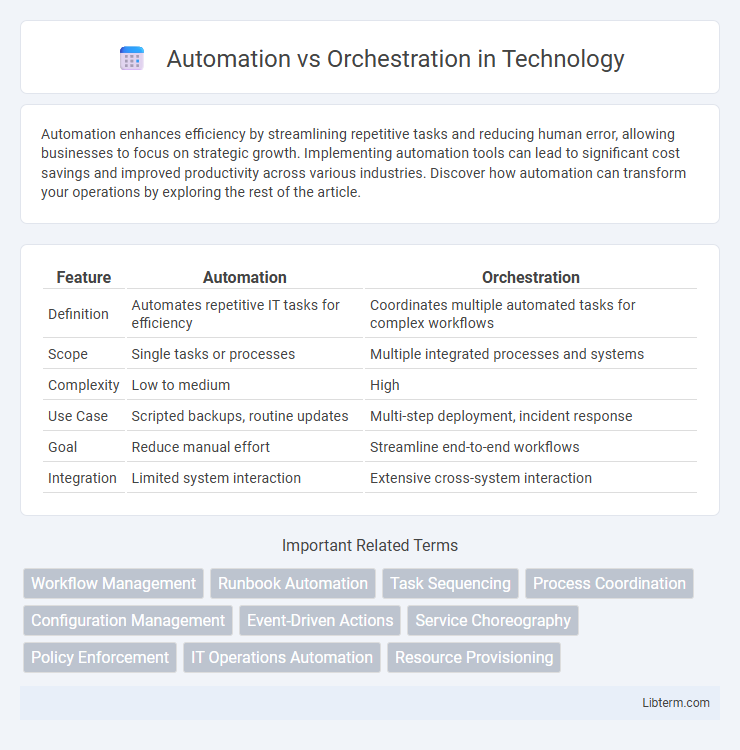
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Automation | Orchestration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automates repetitive IT tasks for efficiency | Coordinates multiple automated tasks for complex workflows |
| Scope | Single tasks or processes | Multiple integrated processes and systems |
| Complexity | Low to medium | High |
| Use Case | Scripted backups, routine updates | Multi-step deployment, incident response |
| Goal | Reduce manual effort | Streamline end-to-end workflows |
| Integration | Limited system interaction | Extensive cross-system interaction |
Understanding Automation: Definition and Scope
Automation refers to the use of technology to perform repetitive tasks with minimal human intervention, aiming to enhance efficiency and reduce errors. It encompasses processes such as scripting, software robots, and AI-driven tools that execute predefined actions based on specific triggers. The scope of automation spans individual tasks, workflows, and entire systems, enabling organizations to streamline operations and improve productivity.
What is Orchestration? Key Concepts
Orchestration refers to the automated arrangement, coordination, and management of complex workflows and IT processes across multiple systems and environments. Key concepts include workflow automation, service integration, and resource allocation, enabling seamless execution of interdependent tasks. Orchestration ensures end-to-end process efficiency by combining individual automated actions into a cohesive, managed operation.
Core Differences: Automation vs Orchestration
Automation focuses on executing individual tasks or processes with minimal human intervention, aiming to increase efficiency and reduce errors in repetitive activities. Orchestration integrates multiple automated tasks across various systems and teams, managing complex workflows to achieve a coordinated business outcome. The core difference lies in scope: automation targets single tasks, while orchestration oversees end-to-end process management and interdependency handling.
Use Cases for Automation in IT
Automation in IT streamlines repetitive tasks such as system backups, patch management, and user provisioning, enhancing efficiency and reducing human errors. It enables consistent execution of workflows like software deployments and security compliance checks, saving time and operational costs. Automation tools accelerate incident response by automatically triggering alerts and remediation actions, improving overall IT service reliability.
Orchestration in Modern Workflows
Orchestration in modern workflows integrates multiple automated tasks across diverse systems to achieve complex business processes efficiently. It enables seamless coordination between cloud services, applications, and infrastructure, improving scalability and reducing human error. By centralizing control and optimizing resource allocation, orchestration enhances workflow agility and accelerates digital transformation.
Benefits of Implementing Automation
Implementing automation significantly reduces manual errors and accelerates repetitive IT tasks, increasing overall operational efficiency. It drives cost savings by minimizing labor-intensive processes and freeing up human resources for strategic initiatives. Automation enhances consistency and scalability within complex environments, ensuring faster response times and improved service delivery.
Advantages of Orchestration in Complex Environments
Orchestration streamlines the management of complex IT environments by automating the coordination of multiple tasks and systems, enhancing efficiency and reducing human error. It enables seamless integration across diverse platforms and processes, ensuring consistent workflows and faster deployment. This centralized control improves scalability and flexibility, making it ideal for dynamic, multi-cloud, and hybrid infrastructure setups.
Automation and Orchestration Tools Comparison
Automation tools like Ansible and Puppet execute predefined tasks to reduce manual intervention, focusing on individual process efficiency. Orchestration tools such as Kubernetes and Apache Airflow coordinate multiple automated tasks, managing complex workflows and dependencies across distributed systems. Comparing these tools, automation emphasizes task-level execution speed, while orchestration ensures seamless integration and end-to-end process management for scalable IT operations.
When to Use Automation vs Orchestration
Automation is ideal for executing repetitive, predefined tasks such as server provisioning, software deployment, or data backups, streamlining processes to increase efficiency and reduce human error. Orchestration should be used when coordinating multiple automated tasks across diverse systems and workflows is necessary, ensuring seamless integration and complex process management in IT environments. Selecting automation for simple, isolated operations and orchestration for comprehensive, interconnected workflows optimizes resource utilization and operational performance.
Future Trends in Automation and Orchestration
Future trends in automation and orchestration emphasize increased integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance decision-making and system responsiveness. Cloud-native orchestration tools will dominate, enabling seamless management of complex, multi-cloud environments with improved scalability and resilience. The rise of hyperautomation merges robotic process automation (RPA) with orchestration, driving end-to-end business process optimization and real-time workflow adaptation.
Automation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com