RunIt is a lightweight and efficient continuous integration tool designed to streamline your software development process by automating builds and deployments. Its simple configuration and fast execution help developers maintain high productivity and reduce downtime. Discover how RunIt can optimize your workflow by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
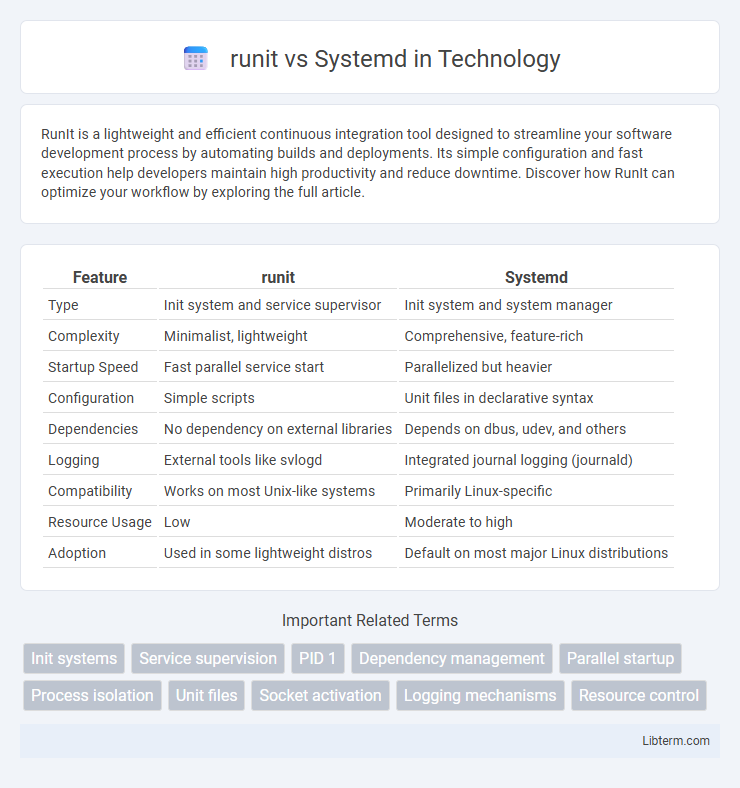
| Feature | runit | Systemd |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Init system and service supervisor | Init system and system manager |
| Complexity | Minimalist, lightweight | Comprehensive, feature-rich |
| Startup Speed | Fast parallel service start | Parallelized but heavier |
| Configuration | Simple scripts | Unit files in declarative syntax |
| Dependencies | No dependency on external libraries | Depends on dbus, udev, and others |
| Logging | External tools like svlogd | Integrated journal logging (journald) |
| Compatibility | Works on most Unix-like systems | Primarily Linux-specific |
| Resource Usage | Low | Moderate to high |
| Adoption | Used in some lightweight distros | Default on most major Linux distributions |
Introduction to Runit and Systemd
Runit is a lightweight, Unix-based init system designed for simplicity, speed, and reliability in process supervision and service management. Systemd, a more complex init system, offers extensive features for startup processes, service management, logging, and system state control across many Linux distributions. Both systems aim to initialize user space and manage services, but Runit emphasizes minimal resource usage and straightforward design, while Systemd integrates a wide range of system components into a unified management framework.
Core Architecture Overview
runit features a minimalistic, three-stage init system emphasizing simplicity and speed, using a straightforward supervision tree to manage services independently from the kernel. Systemd integrates a complex, monolithic architecture with parallelized service startup, leveraging cgroups and socket activation for fine-grained resource control and event-driven service management. Both aim to replace traditional SysVinit but differ fundamentally in design philosophy, with runit prioritizing modularity and Systemd focusing on comprehensive integration.
Boot and Initialization Speed
Runit offers a minimalist and efficient approach to boot and initialization, significantly reducing startup time compared to Systemd by executing services in parallel without complex dependency handling. Systemd, while feature-rich and comprehensive, often incurs longer boot times due to extensive dependency resolution and unit management during initialization. Benchmark tests reveal runit can achieve boot speeds up to 30% faster than Systemd, making it ideal for systems prioritizing rapid startup performance.
Process Supervision Capabilities
runit provides lightweight, fast process supervision with a simple three-stage init scheme designed for quick service start and restart, ensuring reliable monitoring and minimal overhead. Systemd offers comprehensive process management with advanced features like cgroups integration, socket activation, and resource control, enabling detailed supervision and logging of services. While runit excels in simplicity and speed, Systemd delivers robust process dependency handling and intricate service state tracking for complex system environments.
Service Management and Configuration
Runit excels in simplicity and speed, offering a minimalistic service management approach with straightforward configuration files that emphasize reliability and fast startup times. Systemd provides a comprehensive suite of service management features including dependency handling, parallel startup, and extensive logging, using unit files with rich declarative syntax for complex configurations. While Systemd supports advanced features like socket activation and cgroups integration, runit maintains a lean design prioritizing ease of use and robustness in service supervision.
Resource Usage and Performance
Runit offers a lightweight init system with minimal resource consumption, making it ideal for systems with limited CPU and memory capacity. Systemd, while more resource-intensive due to its extensive feature set and parallel service management, provides faster boot times and advanced process tracking. Benchmarks consistently show runit uses less RAM and CPU overhead, whereas systemd delivers improved performance in complex service orchestration and dependency handling.
Dependency Handling
runit handles service dependencies with simplicity, focusing on independent, parallel service management without complex dependency graphs, which reduces boot time and potential configuration errors. Systemd uses an intricate dependency model through units and targets, enabling precise service ordering and activation based on dependencies, resulting in fine-grained control over service startup sequences. While Systemd's approach provides robust dependency resolution and event-driven management, runit's minimalistic design offers faster startup and easier troubleshooting by avoiding elaborate dependency chains.
Security Features
Runit offers a minimalist design that limits attack surfaces by running services with minimal privileges, enhancing security through process isolation and straightforward supervision. Systemd incorporates advanced security features such as sandboxing, resource control with cgroups, and extensive logging to detect and mitigate threats effectively. While Systemd provides comprehensive security policies and integration with modern kernel security modules, Runit's simplicity reduces complexity-based vulnerabilities, making it a preferred choice for lightweight, secure environments.
Community Support and Documentation
Systemd benefits from a larger community support base with extensive documentation, actively maintained by major Linux distributions such as Fedora and Ubuntu, providing comprehensive guides, forums, and troubleshooting resources. Runit, while simpler and faster, has a smaller but dedicated community, offering clear and concise documentation that appeals to users prioritizing minimalism and ease of use. Systemd's widespread adoption ensures more frequent updates and broader third-party tool integration compared to runit's niche support environment.
Use Cases and Adoption Scenarios
runit excels in lightweight, minimalistic environments such as embedded systems, containerized applications, and init replacements for small Linux distributions due to its straightforward design and fast service startup times. Systemd dominates large-scale, complex server environments and desktop Linux distributions by offering extensive features like parallel service startup, socket activation, and integrated logging. Organizations prioritize runit when simplicity, low resource consumption, and ease of configuration are critical, while Systemd is favored for comprehensive system management and compatibility with modern Linux distributions.
runit Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com