CloudFormation enables you to define and provision AWS infrastructure using code, streamlining deployment through automation and version control. It supports complex architectures with reusable templates, making infrastructure management scalable and consistent. Explore the full article to discover how CloudFormation can transform your cloud operations.
Table of Comparison
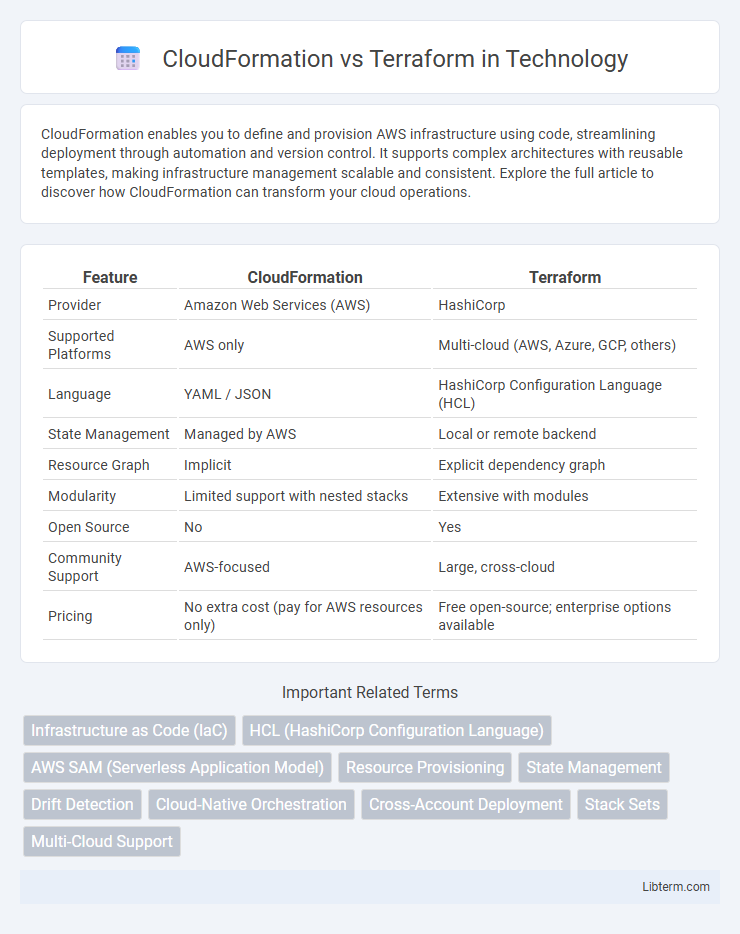
| Feature | CloudFormation | Terraform |
|---|---|---|
| Provider | Amazon Web Services (AWS) | HashiCorp |
| Supported Platforms | AWS only | Multi-cloud (AWS, Azure, GCP, others) |
| Language | YAML / JSON | HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL) |
| State Management | Managed by AWS | Local or remote backend |
| Resource Graph | Implicit | Explicit dependency graph |
| Modularity | Limited support with nested stacks | Extensive with modules |
| Open Source | No | Yes |
| Community Support | AWS-focused | Large, cross-cloud |
| Pricing | No extra cost (pay for AWS resources only) | Free open-source; enterprise options available |
Introduction to Infrastructure as Code
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) revolutionizes cloud resource management by automating provisioning and configuration through declarative templates. AWS CloudFormation enables users to define and deploy AWS infrastructure using JSON or YAML templates, ensuring consistent and repeatable resource setups. Terraform, an open-source IaC tool by HashiCorp, supports multi-cloud environments with its HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL), allowing unified management of diverse infrastructure components.
Overview of AWS CloudFormation
AWS CloudFormation is a robust infrastructure-as-code (IaC) service that automates the deployment and management of AWS resources via reusable templates written in JSON or YAML. It supports the provisioning of a broad range of AWS services, enabling consistent and repeatable infrastructure configurations for complex cloud environments. CloudFormation integrates natively with AWS, offering a seamless experience for resource monitoring, dependency management, and rollback capabilities during stack updates.
Overview of HashiCorp Terraform
HashiCorp Terraform is an open-source infrastructure as code (IaC) tool that enables users to define and provision data center infrastructure using a declarative configuration language called HCL (HashiCorp Configuration Language). It supports multi-cloud environments, allowing seamless management of resources across providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, offering enhanced flexibility and scalability. Terraform's state management and modular architecture facilitate version control and collaboration, making it a preferred choice for complex, large-scale infrastructure deployments.
Supported Cloud Providers and Ecosystem
CloudFormation supports only AWS, offering deep integration with AWS services and a mature ecosystem tailored for AWS cloud infrastructure management. Terraform provides multi-cloud support, including AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and many others, backed by a vibrant open-source community that contributes extensive providers and modules. The broader ecosystem of Terraform facilitates hybrid cloud and multi-cloud deployments, making it versatile for complex infrastructure needs across various platforms.
Language Syntax and Template Structure
CloudFormation uses JSON or YAML for its template syntax, defined by AWS-specific intrinsic functions and resource types tightly integrated with AWS services. Terraform employs HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL), designed for clarity and modularity, supporting multiple cloud providers and third-party infrastructure via provider plugins. Template structure in CloudFormation is declarative with nested stacks, while Terraform uses a modular approach with reusable modules and state management for resource dependency tracking.
State Management and Storage
CloudFormation natively integrates state management by storing stack states within AWS, ensuring tight synchronization with AWS resources and simplifying rollback processes. Terraform employs a separate state file to track infrastructure, supporting remote backends like AWS S3, Azure Blob Storage, or HashiCorp Consul for enhanced collaboration and state locking. This separation in Terraform provides flexibility in multi-cloud environments but requires explicit configuration to maintain state consistency and prevent conflicts.
Modularity and Reusability
CloudFormation offers modularity through nested stacks, enabling reusable templates within AWS environments but is limited to AWS services. Terraform provides enhanced modularity and reusability by leveraging modules that support multi-cloud infrastructure management with greater flexibility and community-driven resources. This makes Terraform more adaptable for complex, cross-platform deployments requiring consistent infrastructure as code practices.
Community Support and Resources
Terraform benefits from a vast, active community that regularly contributes to its extensive library of modules and plugins, enhancing flexibility across multiple cloud providers. CloudFormation, maintained by AWS, offers deep integration with AWS services and a comprehensive set of official templates but has a smaller, AWS-centric community. Terraform's open-source nature ensures continuous community-driven innovation, while CloudFormation relies more on official AWS documentation and support forums.
Pricing and Cost Considerations
CloudFormation is a free service provided by AWS, with users incurring costs only for the AWS resources deployed, making it cost-effective for AWS-centric infrastructures. Terraform, by HashiCorp, operates as an open-source tool with a free tier, but advanced features and enterprise support require a paid subscription, potentially increasing costs for complex or multi-cloud environments. Organizations must evaluate total cost of ownership including subscription fees, resource usage, and management overhead when choosing between CloudFormation and Terraform.
Final Comparison: Which Tool to Choose?
CloudFormation provides deep integration with AWS services, making it ideal for users focused exclusively on AWS environments, while Terraform offers multi-cloud support and greater flexibility across different providers. Terraform's extensive module ecosystem and state management capabilities cater to complex infrastructures requiring cross-platform consistency. Choosing between the two depends on your cloud strategy: CloudFormation suits AWS-centric operations, whereas Terraform is preferred for hybrid or multi-cloud deployments.
CloudFormation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com