Master Data Management (MDM) ensures the consistent and accurate organization of your organization's critical data across various systems and departments. Effective MDM reduces data silos, improves decision-making, and enhances overall operational efficiency. Explore this article to learn how implementing MDM can transform your business data strategy.
Table of Comparison
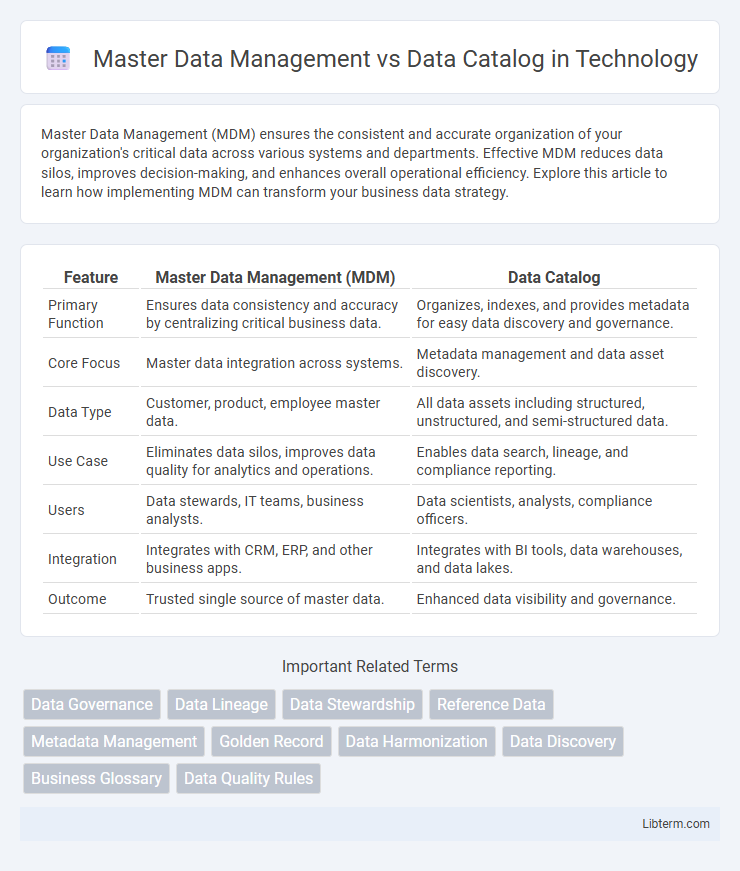
| Feature | Master Data Management (MDM) | Data Catalog |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Ensures data consistency and accuracy by centralizing critical business data. | Organizes, indexes, and provides metadata for easy data discovery and governance. |
| Core Focus | Master data integration across systems. | Metadata management and data asset discovery. |
| Data Type | Customer, product, employee master data. | All data assets including structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data. |
| Use Case | Eliminates data silos, improves data quality for analytics and operations. | Enables data search, lineage, and compliance reporting. |
| Users | Data stewards, IT teams, business analysts. | Data scientists, analysts, compliance officers. |
| Integration | Integrates with CRM, ERP, and other business apps. | Integrates with BI tools, data warehouses, and data lakes. |
| Outcome | Trusted single source of master data. | Enhanced data visibility and governance. |
Understanding Master Data Management (MDM)
Master Data Management (MDM) centralizes and integrates critical business data across an organization to ensure consistency, accuracy, and accountability. It focuses on creating a single, authoritative source of master data, including customers, products, and suppliers, enabling improved decision-making and operational efficiency. Unlike a Data Catalog, which primarily indexes and classifies data assets for discovery and governance, MDM actively governs and maintains data quality and relationships across multiple systems.
Defining a Data Catalog
A data catalog is an organized inventory that provides metadata, data lineage, and classification to enable users to easily find, understand, and trust data assets across an organization. It indexes data sources and platforms, offering searchable descriptions, data quality metrics, and access controls that facilitate data governance and compliance. Unlike Master Data Management (MDM), which focuses on maintaining a single, authoritative source of critical business data, a data catalog emphasizes discoverability and contextual understanding of all enterprise data.
Key Differences Between MDM and Data Catalog
Master Data Management (MDM) centralizes and governs critical business data to ensure accuracy, consistency, and control across an organization, while a Data Catalog primarily serves as an inventory tool that indexes and organizes metadata to improve data discoverability. MDM focuses on creating a single, authoritative source of truth for master data entities such as customers, products, and suppliers, emphasizing data quality, stewardship, and synchronization. In contrast, Data Catalogs facilitate data search, classification, and lineage tracking but do not enforce data governance or integration like MDM systems.
Core Functions of Master Data Management
Master Data Management (MDM) centralizes and harmonizes critical business data across an organization, ensuring consistent and accurate master records like customer, product, and supplier information. Core functions of MDM include data integration, data quality management, and governance, which establish a single source of truth and improve data reliability for decision-making and operational processes. Unlike Data Catalogs that primarily focus on data discovery and metadata management, MDM enforces data stewardship and synchronization across multiple systems, driving enterprise-wide data consistency.
Essential Features of a Data Catalog
A Data Catalog provides essential features such as metadata management, data discovery, and data lineage tracking, enabling organizations to efficiently find, understand, and govern their data assets. Unlike Master Data Management (MDM), which focuses on creating a single, authoritative source for critical business entities, a Data Catalog emphasizes comprehensive data inventory with user-friendly search capabilities and automated data classification. Integration with various data sources, collaboration tools, and access control are also vital features that enhance data catalog effectiveness in driving data governance and self-service analytics.
Use Cases for MDM Solutions
Master Data Management (MDM) solutions are primarily designed to create a unified, accurate, and consistent master dataset across an organization, enhancing data quality and governance for critical entities like customers, products, and suppliers. Typical use cases include customer 360-degree views, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency improvement by eliminating data silos. In contrast, a Data Catalog focuses on data discovery and metadata management, helping users find and understand data assets but lacks the consolidation and governance capabilities central to MDM.
Business Applications of Data Catalogs
Data catalogs enhance Master Data Management (MDM) by providing comprehensive metadata management, enabling businesses to quickly discover, understand, and govern enterprise data assets effectively. Business applications of data catalogs include improving data literacy across organizations, accelerating data onboarding for analytics and reporting, and supporting regulatory compliance through data lineage and audit trails. These capabilities allow firms to maximize data value, reduce operational risks, and foster a data-driven culture.
How MDM and Data Catalogs Complement Each Other
Master Data Management (MDM) ensures consistency and accuracy of critical business data by creating a single source of truth, while Data Catalogs enhance data discoverability and governance by providing metadata, lineage, and context. Together, MDM and Data Catalogs complement each other by combining authoritative master data with comprehensive metadata frameworks, enabling better data quality, compliance, and efficient data usage across the organization. Integrating MDM with Data Catalogs drives data transparency and supports data-driven decision-making through unified data governance strategies.
Challenges in Implementing MDM vs Data Catalog
Implementing Master Data Management (MDM) faces challenges such as integrating disparate data sources, establishing data governance frameworks, and ensuring data quality consistency across the enterprise. Data Catalog implementation struggles mainly with metadata accuracy, user adoption, and maintaining up-to-date information in dynamic data environments. Both MDM and Data Catalog require significant organizational alignment and technical investment to overcome scalability and complexity issues.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Organization
Master Data Management (MDM) centralizes and ensures the accuracy of key business data across systems, essential for organizations requiring consistent, authoritative data sources. Data Catalogs enhance data discovery and metadata management, ideal for teams focused on data governance and self-service analytics. Selecting the right solution depends on your organization's priority between data consistency (MDM) and data accessibility with context (Data Catalog).
Master Data Management Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com