An Internet Gateway serves as a crucial bridge between your private network and the public internet, managing traffic to ensure secure and efficient connectivity. It enables seamless data exchange by routing requests and responses, often incorporating security features like firewalls and traffic filtering to protect your network. Explore this article to understand how an Internet Gateway optimizes your network performance and security.
Table of Comparison
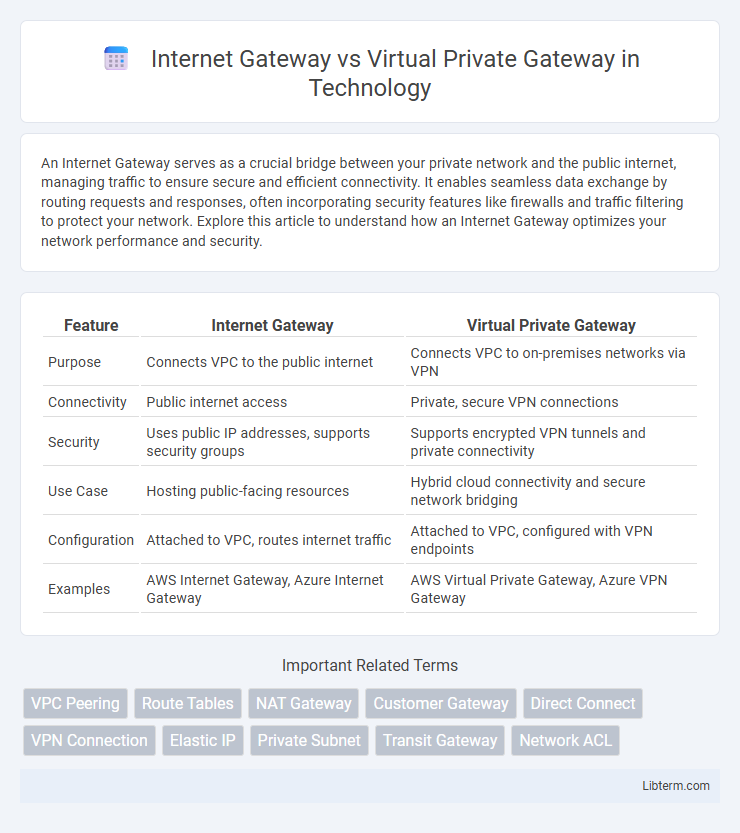
| Feature | Internet Gateway | Virtual Private Gateway |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Connects VPC to the public internet | Connects VPC to on-premises networks via VPN |
| Connectivity | Public internet access | Private, secure VPN connections |
| Security | Uses public IP addresses, supports security groups | Supports encrypted VPN tunnels and private connectivity |
| Use Case | Hosting public-facing resources | Hybrid cloud connectivity and secure network bridging |
| Configuration | Attached to VPC, routes internet traffic | Attached to VPC, configured with VPN endpoints |
| Examples | AWS Internet Gateway, Azure Internet Gateway | AWS Virtual Private Gateway, Azure VPN Gateway |
Understanding Internet Gateway: A Brief Overview
An Internet Gateway enables communication between an Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) and the internet, facilitating outbound and inbound traffic for resources within the VPC. It functions as a horizontally scaled, redundant, and highly available VPC component that provides a target in the VPC route tables for internet-routable traffic. Unlike a Virtual Private Gateway, which connects a VPC to a VPN or AWS Direct Connect, the Internet Gateway mainly supports internet traffic management and web accessibility.
What Is a Virtual Private Gateway?
A Virtual Private Gateway (VPG) is a critical component in AWS that enables secure, encrypted connections between a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) and on-premises networks via VPN or AWS Direct Connect. Unlike an Internet Gateway that facilitates unrestricted internet access for VPC resources, a Virtual Private Gateway serves as the VPN concentrator on the AWS side, managing private traffic and ensuring secure communication. This gateway provides controlled, scalable connectivity ideal for hybrid cloud architectures requiring private network integration.
Key Differences Between Internet Gateway and Virtual Private Gateway
An Internet Gateway enables direct communication between an Amazon VPC and the public internet, facilitating inbound and outbound traffic for resources like web servers. In contrast, a Virtual Private Gateway provides a secure VPN connection between an AWS VPC and on-premises networks, supporting private, encrypted data transfer. Internet Gateway is used for public access, while Virtual Private Gateway supports hybrid cloud connectivity and private network integration.
Architecture and Connectivity Explained
An Internet Gateway enables communication between an Amazon VPC and the public internet, serving as a horizontally scaled, redundant, and highly available gateway that allows outbound and inbound traffic using public IP addresses. In contrast, a Virtual Private Gateway facilitates secure connectivity between a VPC and on-premises networks via a VPN connection or AWS Direct Connect, acting as the VPN concentrator on the Amazon side of the VPN tunnel. The Internet Gateway supports internet-bound traffic using public IP routing, while the Virtual Private Gateway handles private, encrypted traffic to extend corporate networks securely to the cloud.
Use Cases for Internet Gateway
Internet Gateways enable communication between a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) and the public internet, facilitating use cases such as hosting public-facing web applications, enabling external API access, and supporting direct internet traffic for instances within a VPC. Virtual Private Gateways, by contrast, are designed for secure VPN connections between on-premises networks and AWS VPCs, primarily supporting private communication. Internet Gateway use cases emphasize public access, scalability in serving global user bases, and integration with services requiring public IP addressing or internet connectivity.
Use Cases for Virtual Private Gateway
Virtual Private Gateway (VPG) primarily enables secure communication between an AWS Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) and external networks, typically supporting VPN connections for hybrid cloud architectures where on-premises data centers connect to AWS environments. Unlike Internet Gateway, which allows direct internet access to resources within a VPC, Virtual Private Gateway is tailored for private, encrypted traffic routing, essential for compliance-sensitive applications and private corporate networks. Use cases include extending enterprise networks to the cloud securely, enabling Site-to-Site VPN connections, and supporting AWS Direct Connect for high-bandwidth, low-latency links to AWS.
Security Implications: IGW vs VGW
An Internet Gateway (IGW) allows communication between an Amazon VPC and the public internet, exposing resources to potential external threats if proper security groups and network ACLs are not configured. In contrast, a Virtual Private Gateway (VGW) enables secure VPN connections between an on-premises network and the VPC, providing encrypted data transfer and stronger perimeter security by restricting traffic to private tunnels. Choosing VGW over IGW reduces the attack surface by limiting exposure to public internet traffic, reinforcing compliance with strict security policies for sensitive workloads.
Performance and Scalability Comparison
Internet Gateway enables seamless connectivity between AWS VPCs and the public internet, offering robust scalability by handling large amounts of traffic with low latency due to its distributed architecture. Virtual Private Gateway facilitates secure VPN connections between AWS VPCs and on-premises networks, focusing on encrypted data transmission but may introduce higher latency and throughput limitations compared to Internet Gateways. Scalability for Virtual Private Gateway is constrained by VPN connection limits and bandwidth caps, making Internet Gateways more suitable for high-performance, scalable internet-facing applications.
Cost Considerations: IGW vs VGW
Internet Gateways (IGW) are free of charge in AWS, making them a cost-effective solution for enabling internet access to instances within a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). In contrast, Virtual Private Gateways (VGW) incur costs based on the hours the gateway is provisioned and the amount of data transferred through VPN connections, which can increase expenses in hybrid cloud scenarios. Choosing between IGW and VGW depends heavily on whether public internet access or secure private connectivity justifies the cost differences for the specific AWS networking use case.
Choosing the Right Gateway for Your Network Infrastructure
Internet Gateway connects a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) to the public internet, enabling resources within the VPC to communicate externally and allowing inbound traffic. Virtual Private Gateway establishes an encrypted VPN connection between a VPC and on-premises network or remote sites, ensuring secure and private communications over the internet. Choosing the right gateway depends on your network needs: use Internet Gateway for public access and Virtual Private Gateway for secure, private connections.
Internet Gateway Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com