An Integrated Development Environment (IDE) streamlines coding by combining editing, compiling, and debugging tools into a single platform, enhancing programming efficiency. Debuggers enable you to identify and fix errors by allowing step-by-step code execution and inspection of variables during runtime. Explore this article to understand how mastering IDEs and debuggers can significantly improve your development workflow.
Table of Comparison
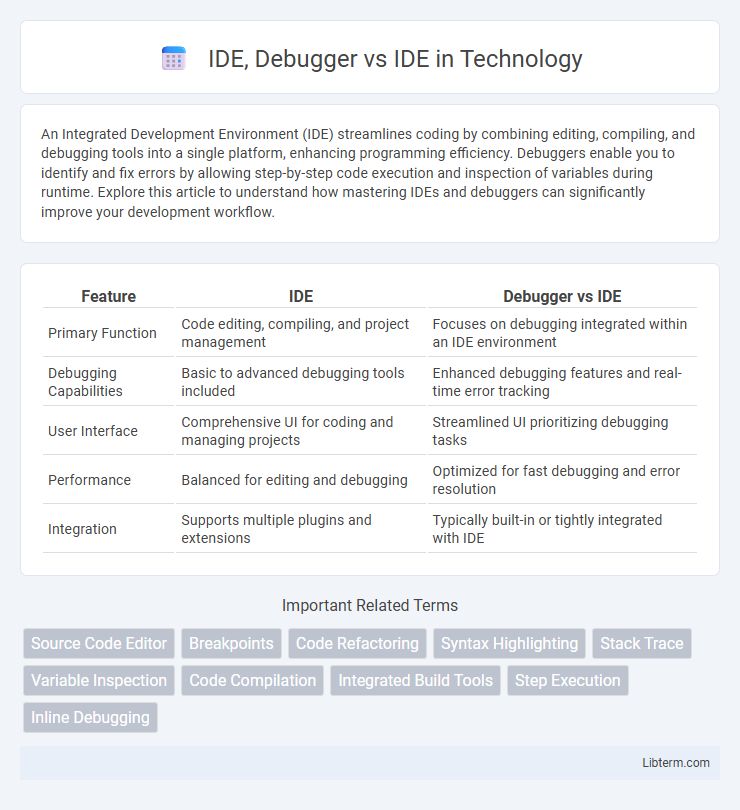
| Feature | IDE | Debugger vs IDE |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Code editing, compiling, and project management | Focuses on debugging integrated within an IDE environment |
| Debugging Capabilities | Basic to advanced debugging tools included | Enhanced debugging features and real-time error tracking |
| User Interface | Comprehensive UI for coding and managing projects | Streamlined UI prioritizing debugging tasks |
| Performance | Balanced for editing and debugging | Optimized for fast debugging and error resolution |
| Integration | Supports multiple plugins and extensions | Typically built-in or tightly integrated with IDE |
Introduction to IDEs
Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) combine code editors, debuggers, and build automation tools into a single application, streamlining software development. Debuggers within IDEs allow developers to identify and fix errors by inspecting code execution and variable states in real-time. The comprehensive integration of editing, compiling, and debugging features enhances productivity and accelerates the development process.
What is a Debugger?
A debugger is a specialized software tool integrated within an IDE (Integrated Development Environment) that helps developers identify, diagnose, and fix errors or bugs in their code by allowing step-by-step execution, breakpoints, and variable inspection. Unlike the broader IDE, which combines code editing, compiling, and project management features, a debugger focuses exclusively on runtime analysis and troubleshooting. Popular IDEs like Visual Studio, Eclipse, and IntelliJ IDEA include built-in debuggers that enhance programming efficiency and code quality.
Core Features of an IDE
An Integrated Development Environment (IDE) combines core features like code editing, syntax highlighting, project management, and version control integration to streamline software development. A debugger, often embedded within an IDE, provides essential tools for setting breakpoints, inspecting variables, and stepping through code to identify and fix errors efficiently. The synergy of these components in an IDE enhances developer productivity by centralizing coding and testing workflows in a single interface.
Debugger vs IDE: Key Differences
A debugger is a specialized tool within an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) designed to test and debug code by allowing developers to set breakpoints, inspect variables, and step through execution line-by-line. An IDE combines multiple development tools, including a code editor, compiler, debugger, and build automation, providing an all-in-one platform for software development. The key difference lies in the scope: the debugger focuses solely on identifying and fixing code errors, while the IDE supports the entire development lifecycle from writing and testing to debugging and deploying code.
Benefits of Using an IDE
Using an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) enhances productivity by combining code editing, debugging, and build automation tools in a single application. IDEs like Visual Studio and IntelliJ IDEA provide advanced features such as syntax highlighting, code completion, and real-time error detection that debugging tools alone lack. This integration streamlines development workflows, reduces context switching, and accelerates error identification, resulting in faster and more efficient software development.
Debugging Tools Inside IDEs
Debugging tools inside IDEs provide integrated breakpoints, step-through execution, and variable inspection, streamlining the error identification process. These tools enhance productivity by enabling real-time code analysis and seamless interaction with the runtime environment. Compared to standalone debuggers, IDE-integrated debugging features offer comprehensive project context, improving accuracy and efficiency in troubleshooting complex applications.
Standalone Debugger Advantages
Standalone debuggers provide specialized tools for in-depth code analysis, allowing developers to inspect memory, variables, and thread behavior with high precision, often outperforming the integrated counterparts in modular IDEs. They enable more customizable workflows and support a broader range of programming languages and platforms, making them ideal for complex debugging scenarios and legacy codebases. Enhanced performance and focused resource usage reduce overhead, resulting in faster load times and smoother debugging sessions outside the typical IDE environment.
When to Choose a Debugger Over an IDE
Choose a debugger over an IDE when the primary need is to inspect and control code execution in real-time, especially for identifying runtime errors, logical bugs, and variable state changes. Debuggers provide precise breakpoints, step-through execution, and watch expressions that facilitate in-depth analysis without the overhead of a full IDE environment. Opting for a debugger is ideal in performance-critical scenarios or when working with minimal resources, where lightweight tools enhance efficiency and streamline troubleshooting.
IDE Selection Tips for Developers
Choosing the right IDE significantly impacts developer productivity by offering integrated debugging tools that streamline error detection and resolution. Prioritize IDEs with robust debugger support, real-time code analysis, and seamless integration with version control systems to enhance workflow efficiency. Consider platform compatibility, plugin availability, and community support to ensure long-term adaptability and innovation in development projects.
Future Trends in IDEs and Debuggers
Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) and debuggers are evolving with advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning, enabling more intelligent code completion, real-time error detection, and automated bug fixing. Future IDEs are expected to integrate cloud-based collaboration features and support for multiple programming languages through modular architectures, enhancing developer productivity and code quality. Debuggers will increasingly leverage AI to predict potential runtime issues and provide proactive suggestions, making software debugging more efficient and less error-prone.
IDE, Debugger Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com