Anonymized data removes personally identifiable information to protect individuals' privacy while maintaining the utility of the dataset for analysis. This technique is crucial in sectors like healthcare and marketing, where sensitive information must be handled responsibly. Discover how anonymized data can enhance your privacy strategy and data management by reading further.
Table of Comparison
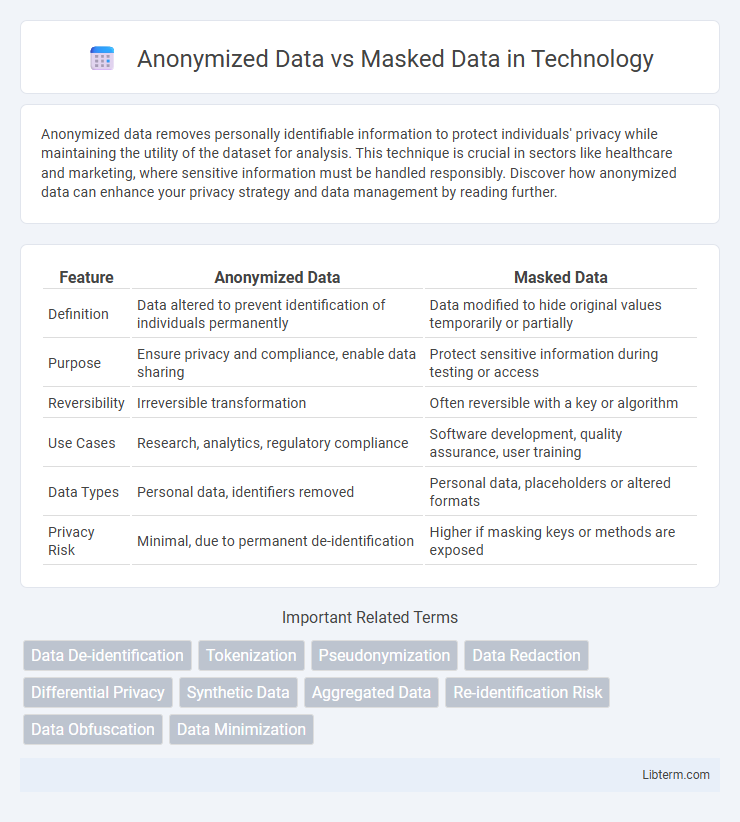
| Feature | Anonymized Data | Masked Data |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Data altered to prevent identification of individuals permanently | Data modified to hide original values temporarily or partially |
| Purpose | Ensure privacy and compliance, enable data sharing | Protect sensitive information during testing or access |
| Reversibility | Irreversible transformation | Often reversible with a key or algorithm |
| Use Cases | Research, analytics, regulatory compliance | Software development, quality assurance, user training |
| Data Types | Personal data, identifiers removed | Personal data, placeholders or altered formats |
| Privacy Risk | Minimal, due to permanent de-identification | Higher if masking keys or methods are exposed |
Understanding Anonymized Data
Anonymized data ensures the irreversible removal of personally identifiable information (PII), making it impossible to trace data back to an individual, thereby providing robust privacy protection compliant with regulations like GDPR. Unlike masked data, which obscures information temporarily or partially for testing or sharing, anonymized data undergoes rigorous processes such as aggregation, generalization, or perturbation to permanently eliminate re-identification risks. Effective anonymization techniques enable secure data sharing for analytics and research while maintaining compliance with data privacy laws and minimizing the risk of data breaches.
What Is Masked Data?
Masked data refers to information that has been altered to protect sensitive details by replacing original values with fictitious but realistic substitutes, preserving the data's format and usability. This technique ensures confidentiality while allowing data to remain functional for testing, analysis, or development purposes. Masking is commonly applied in environments where data privacy is critical but the context of the data must be retained for operational processes.
Key Differences Between Anonymization and Masking
Anonymized data irreversibly removes personally identifiable information (PII), ensuring that individuals cannot be re-identified even with additional data sets, whereas masked data replaces or obscures sensitive information in a reversible manner, allowing authorized users to restore the original content if necessary. Anonymization is mainly used for privacy compliance and statistical analysis by creating datasets that protect identity permanently, while data masking primarily supports secure testing and development environments by hiding sensitive details temporarily. The key distinction lies in the irreversibility and purpose: anonymization focuses on privacy preservation with permanent de-identification, while masking emphasizes data usability with reversible obfuscation.
Use Cases for Anonymized Data
Anonymized data is extensively used in healthcare research, enabling organizations to analyze patient trends without risking individual privacy. Financial institutions utilize anonymized datasets to detect fraud patterns without exposing sensitive customer information. Government agencies rely on anonymized data for public policy analysis, ensuring demographic insights can be gathered without compromising citizen identities.
Common Applications of Data Masking
Data masking is predominantly used in development and testing environments to protect sensitive information while maintaining data usability, enabling secure software testing without exposing real data. Common applications include safeguarding personal information in customer databases, such as credit card numbers, social security numbers, and email addresses, by replacing them with realistic but fictitious values. Masked data also plays a critical role in compliance with data privacy regulations like GDPR and HIPAA, ensuring organizations can share datasets internally and externally without risking data breaches.
Advantages of Data Anonymization
Data anonymization ensures permanent protection of personally identifiable information (PII) by irreversibly altering datasets, making re-identification impossible and thus enhancing compliance with GDPR and HIPAA regulations. Unlike masked data, which can be reversed under certain conditions, anonymized data supports secure data sharing and advanced analytics without risking individual privacy. This permanent de-identification enables organizations to leverage valuable insights while minimizing legal risks and maintaining customer trust.
Benefits of Using Data Masking
Data masking protects sensitive information by transforming original data into fictional but realistic values, enabling secure usage and testing without exposing confidential details. It helps organizations comply with data privacy regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA by preventing unauthorized access to personal information. Masked data maintains data format and usability, ensuring business continuity while reducing the risk of data breaches and enhancing overall data security.
Privacy Risks: Anonymized vs Masked Data
Anonymized data eliminates personally identifiable information (PII), significantly reducing privacy risks by preventing re-identification, whereas masked data obscures sensitive details but retains the original structure, posing higher risks if the masking method is reversible. In environments where data re-identification is a critical concern, anonymization offers stronger protection, although it may reduce data utility for detailed analysis. Masked data balances usability with privacy but requires robust techniques to prevent potential privacy breaches due to incomplete or weak masking algorithms.
Regulatory Compliance: Key Considerations
Anonymized data permanently removes personally identifiable information (PII), ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA by eliminating re-identification risks. Masked data partially hides sensitive information but retains key identifiers, requiring strict access controls and governance to meet regulatory standards. Organizations must assess data use cases to determine whether full anonymization or masking aligns best with compliance obligations and privacy impact assessments.
Choosing the Right Approach for Data Protection
Anonymized data irreversibly removes personally identifiable information, making re-identification impossible and ideal for compliance with strict privacy regulations like GDPR. Masked data substitutes sensitive information with fictitious values but retains the data structure for testing or analysis, useful when data utility is critical. Selecting between anonymization and masking depends on the balance between privacy risk and operational requirements, with anonymization preferred for long-term data privacy and masking favored for controlled data environments.
Anonymized Data Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com